* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
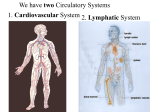
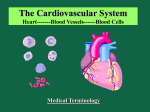
Lesson 11.1 Heart anatomy; function of the Cardiovascular system · The heart is located in the cavity, above the , in between the . · The heart is the size of a , and weighs ounces. · The four chambers of the are… 1. 2. 3. 4. · The heart valves are… 1. 2. · Blood flow through the heart …. 1. blood flows from the body to the inferior and superior vena cavae to right atrium 2. atrium contracts, forcing blood through the tricuspid valve to right ventricle 3. Right ventricle contracts, forcing blood through the , to the pulmonary artery 4. Blood exits to the . 5. blood from lungs travels through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium 6. Left atrium contracts, forcing blood through the to the left ventricle 7. contracts, forcing blood through the aortic valve 8. Blood passes to the . 9. Blood travels out to parts of the . · Walls of the heart …. 1. 2. 3. · Cardiac Cycle… o Diastole: . o Systole: . o Mean arterial pressure: . · Is the amount of blood pumped by heart in 1 minute measured in liters/minute · Stoke volume is . · Heart rate is the number of per . Lesson 11.2 Regulation of the heart · · · · · Internal control of the heart o o o o o External control of the heart o Cardiac center: ● ● o Endocrine system: ● Regulation of Heart rate: o What increases heart rate? ● ● ● o What decreases heart rate? ● ● ● Electrocardiogram o activity of the heart o Depolarize: . o Repolarize: . Cardiac Arrhythmias: o Normal contractility condition ● rhythm o Abnormal contractility condition ● . o Bradycardia ● heart beat o Tachycardia ● heart beat o (PACs) ● Atria contracts before SA node o Atrial fibrillation ● Atria contract faster than bpm o (PVCs) ● Ventricles contract too soon o (VT) ● Ventricles, rather than SA node, cause beat o (VF) · · · · ● Ventricles contract faster than 350 bpm o Heart block ● Impulse from SA node to AV node First– . Second– . Third– . AED stand for . Lesson 11.3 Blood Vessels and Circulation · types of vessels form a closed loop that carry blood from the heart to the body 1. 2. 3. · layers of a blood vessel 1. Tunica intima. 2. Tunica media. 3. Tunica externa. · Arteries vs. veins: o Arteries: o Veins: · Circulation o Cardiopulmonary circulation● between and . o Systematic circulation – ● between and . · Cardiac circulation artery- supply blood to the inferior and posterior walls of the heart artery- divides into two arteries and supply’s oxygen rich blood to anterior, lateral, and posterior walls of the heart · Hepatic portal circulation o Provides blood to the . · vital signs ● ● 11.4 D&D ● ● ● Valve Abnormalities ○ ○ ○ Infamamitory diseases ○ ○ ○ Disease of the arteries ○ ○ ○ ○