* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AngelasPPT
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
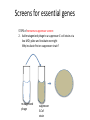
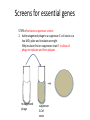
Identifying essential genes in phage Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? conditional lethal mutations Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? conditional lethal mutations What are the two types of conditional lethal screens that you can do in phage? Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? conditional lethal mutations. What are the two types of conditional lethal screens that you can do in phage? • Temperature sensitivity • Nonsense suppression Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? conditional lethal mutations. What are the two types of conditional lethal screens that you can do in phage? • Temperature sensitivity • Nonsense suppression Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? conditional lethal mutations. What are the two types of conditional lethal screens that you can do in phage? • Temperature sensitivity • Nonsense suppression What is the observable phenotype in screens for essential genes? Screens for essential genes To identify essential genes, you can screen for what types of mutations? conditional lethal mutations. What are the two types of conditional lethal screens that you can do in phage? • Temperature sensitivity • Nonsense suppression What is the observable phenotype in screens for essential genes? Dead (don’t form plaques) at non-permissive conditions Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 1. Mutagenize phage particles phage Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 2. Add mutagenized phage to E. coli at a low MOI phage E.coli Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 3. Plate and incubate overnight at permissive temperature Mutagenized phage Mutagenized phage E.coli Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 3. Plate and incubate overnight at permissive temperature Why first incubate at permissive temperature? Mutagenized phage Mutagenized phage E.coli Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 3. Plate and incubate overnight at permissive temperature Why first incubate at permissive temperature? To allow all phage to replicate Mutagenized phage Mutagenized phage E.coli Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 3. Plate and incubate overnight at permissive temperature Why first incubate at permissive temperature? To allow all phage to replicate Mutagenized phage Mutagenized phage E.coli Control: Wild type phage Wild type E.coli phage Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 3. Plate and incubate overnight at permissive temperature Why first incubate at permissive temperature? To allow all phage to replicate Mutagenized phage Mutagenized phage E.coli Control: Wild type phage Wild type E.coli phage What is the reason for wild type control? Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 3. Plate and incubate overnight at permissive temperature Why first incubate at permissive temperature? To allow all phage to replicate Mutagenized phage Mutagenized phage E.coli Control: Wild type phage Wild type E.coli phage What is the reason for wild type control? to ensure that the temperature change is not lethal to all phage Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 4. Transfer plaques to duplicate plates and incubate overnight: Mutagenized phage • At permissive temperature • At non-permissive temperature mutagenized Permissive temp Non-Permissive temp Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 4. Transfer plaques to duplicate plates and incubate overnight: Mutagenized phage • At permissive temperature • At non-permissive temperature Control: Wild type phage • At permissive temperature • At non-permissive temperature mutagenized Permissive temp Wild type Non-Permissive temp Permissive temp Non-Permissive temp Screens for essential genes STEPS of temperature sensitivity screen: 5. Mutagenized phage that form plaques at permissive temp but not at non-permissive temp are temperature-sensitive mutants Mutagenized phage • At permissive temperature • At non-permissive temperature Control: Wild type phage • At permissive temperature • At non-permissive temperature mutagenized Wild type Temperaturesensitive mutant Permissive temp Non-Permissive temp Permissive temp Non-Permissive temp Screens for essential genes STEPS of nonsense-suppressor screen: 1. Mutagenize a known concentration of phage particles phage Screens for essential genes STEPS of nonsense-suppressor screen: 2. Add mutagenized phage to a suppressor E. coli strain at a low MOI; plate and incubate overnight mutagenized phage suppressor E.Coli strain Screens for essential genes STEPS of nonsense-suppressor screen: 2. Add mutagenized phage to a suppressor E. coli strain at a low MOI; plate and incubate overnight Why incubate first on suppressor strain? mutagenized phage suppressor E.Coli strain Screens for essential genes STEPS of nonsense-suppressor screen: 2. Add mutagenized phage to a suppressor E. coli strain at a low MOI; plate and incubate overnight Why incubate first on suppressor strain? to allow all phage to replicate and form plaques mutagenized phage suppressor E.Coli strain Screens for essential genes STEPS of nonsense-suppressor screen: 3. Transfer plaques to duplicate plates and incubate overnight: • On a lawn of suppressor E.coli strain • On a lawn of wild type E.coli Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Screens for essential genes STEPS of nonsense-suppressor screen: 4. Those phage that are nonsense mutants produce a plaque on the suppressor E.coli strain but not on the wild type E.coli strain Nonsense mutant Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Complementation test Complementation tests allow you to determine whether your isolated mutations affect the same gene. Complementation test STEPS 1. Infect wild type strain with two of your isolated mutants at high MOI for 1 hour (to allow one round of infection) am2- am1- Wild type E.Coli strain Complementation test STEPS 1. Infect wild type strain with two of your isolated mutants at high MOI for 1 hour (to allow one round of infection) Why at high MOI? am2- am1- Wild type E.Coli strain Complementation test STEPS 1. Infect wild type strain with two of your isolated mutants at high MOI for 1 hour (to allow one round of infection) Why at high MOI? So each cell can be infected by both mutants am2- am1- Wild type E.Coli strain Complementation test STEPS 2. To determine whether the mutations complemented each other, you must determine the amount of phage that was successfully replicated in the co-infected wild type E. coli strain: • Perform a plaque assay of the phage supernatant, this time on a suppressor E.coli strain. am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli Complementation test STEPS 2. To determine whether the mutations complemented each other, you must determine the amount of phage that was successfully replicated in the co-infected wild type E. coli strain: • Perform a plaque assay of the phage supernatant, this time on a suppressor E.coli strain. • Positive control: wild type phage in suppressor E.coli strain am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli wt phage + suppressor E.coli Complementation test STEPS 2. To determine whether the mutations complemented each other, you must determine the amount of phage that was successfully replicated in the co-infected wild type E. coli strain: • Perform a plaque assay of the phage supernatant, this time on a suppressor E.coli strain. • Positive control: wild type phage in suppressor E.coli strain • Negative control: each single mutant phage in suppressor E.coli strain am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli wt phage + suppressor E.coli am1- + suppressor E.coli am2- + suppressor E.coli Complementation test STEPS 3. If plaques are formed in the plaque assay involving am1- + am2+ suppressor E.coli, the mutations complement each other and are likely mutations in two different genes. am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli wt phage + suppressor E.coli am1- + suppressor E.coli am2- + suppressor E.coli Complementation test STEPS 3. If plaques are not formed in the plaque assay involving am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli, the mutations do not complement each other and are likely mutations in the same gene. am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli wt phage + suppressor E.coli am1- + suppressor E.coli am2- + suppressor E.coli Complementation test STEPS 3. If plaques are not formed in the plaque assay involving am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli, the mutations do not complement each other and are likely mutations in the same gene. Why are plaques are not formed? am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli wt phage + suppressor E.coli am1- + suppressor E.coli am2- + suppressor E.coli Complementation test STEPS 3. If plaques are not formed in the plaque assay involving am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli, the mutations do not complement each other and are likely mutations in the same gene. Why are plaques are not formed? The phage produced are unable to infect further cells. am1- + am2- + suppressor E.coli wt phage + suppressor E.coli am1- + suppressor E.coli am2- + suppressor E.coli Mapping Once you determine that two mutations complement each other and thus are mutations in different genes, you can map the genes to determine the physical distance between them. Mapping STEPS 1. Infect suppressor strain with your two different mutants at high MOI am2- am1- Suppressor E.Coli strain Mapping STEPS 2. Allow infected cells to produce phage (1 hour) 1 hour Suppressor E.Coli strain Mapping STEPS: 3. Perform a plaque assay to determine total number of phage and number of recombinants: - Serial dilutions of phage - Plate on suppressor strain AND wild-type strain 100 phage Wild type E.coli phage buffer ~1000 phage Suppressor E.coli Mapping STEPS: 4. Count the # of plaques formed on the suppressor strain and on the wild type strain. Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping STEPS: 5. Calculate the frequency of recombination: Frequency of recombination = total recombinants/total phage Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping What is the genotype of the plaques formed on the wild type E.coli strain? Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping What is the genotype of the plaques formed on the wild type E.coli strain? am1+, am2+ Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping Recalling that we are dealing with essential genes, do the total recombinants = # of plaques formed on the wild type E.coli strain? Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping Recalling that we are dealing with essential genes, do the total recombinants = # of plaques formed on the wild type E.coli strain? No Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping Recalling that we are dealing with essential genes, do the total recombinants = # of plaques formed on the wild type E.coli strain? No What do the actual # of total recombinants equal? Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping Recalling that we are dealing with essential genes, do the total recombinants = # of plaques formed on the wild type E.coli strain? No What do the actual # of total recombinants equal? 2 X # of plaques formed on wild type E.coli Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping Why multiply by 2? Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping Why multiply by 2? To account for the recombinants that cannot grow on wild type E.coli: am1-, am2- Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli Mapping The farther the genes are from each other, the higher the frequency of recombination is between them. Suppressor E.coli Wild type E.coli