* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint to accompany
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
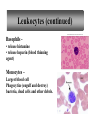
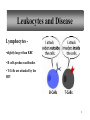
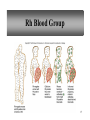
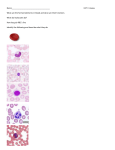
The Blood 1 Blood Volume • varies with • body size • changes in fluid concentration • changes in electrolyte concentration • amount of adipose tissue • about 8% of body weight • about 5 liters 2 Characteristics of Erythrocytes • Also known as Red Blood Cells (RBC) • biconcave discs (depression on both sides) • one-third hemoglobin (Hemoglobin carries oxygen that makes blood bright red) •Survive approximately 120 days 3 Leukocytes • Also known as White Blood Cells (WBC) • protect against disease Neutrophils – •first to arrive at infections. •Elevated in bacterial infections. Eosinophils – •Moderate allergic reactions •Defend against parasitic worm infestations 4 Leukocytes (continued) Basophils • release histamine • release heparin (blood thinning agent) Monocytes – Largest blood cell Phagocytize (engulf and destroy) bacteria, dead cells and other debris. 5 Leukocytes and Disease Lymphocytes •slightly larger than RBC • B cells produce antibodies • T-Cells are attacked by the HIV 6 Blood Composition Platelets – •also known as thrombocytes • cell fragments that are essential for blood clotting 7 Blood Plasma • straw colored • liquid portion of blood • 55% of blood • 92% water 8 Platelet Plug Formation (Clotting) 9 Blood Coagulation Coagulation • hemostatic mechanism • causes the formation of a blot clot via a series of reactions which activates the next in a cascade 10 Antigens and Antibodies Antigens – a chemical that stimulates cells to produce antibodies Antibodies – a protein that reacts against a specific antigen 11 Antigens and Antibodies 12 ABO Blood Group Based on the presence or absence of two major antigens on red blood cell membranes • antigen A • antigen B 13 ABO Blood Group 14 Blood Types for Transfusion 15 Rh Blood Group Rh positive – presence of antigen D or and other Rh antigens on the red blood cell membranes Rh negative – lack of these antigens 16 Rh Blood Group 17