* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Evolution and nat selection and
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
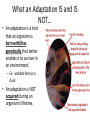
8/11 • Good Afternoon • Please turn in your Natural Selection Simulation… don’t forget to turn in the packet, 2 graphs, 2 paragraph summaries, and 3 discussion questions. • Please remove all hats and put electronics away. Good morning • Please pick up an iRespond remote. • Turn in your evidence for evolution webquest. • Get ready for your quiz! Evolution and Natural Selection How did life evolve on Earth? What is Evolution? -Evolution is the gradual change in a POPULATION over a long period of time. Evidence of Evolution 1) Fossils – Found in sedimentary rock layers (strata) – Fossils found deeper very different from fossils found closer to surface – Relative dating- idea that fossils found deeper are older – Radiometric dating- A fossil’s carbon14 can be measured to determine actual age – Fossils have revealed changes in organisms over time and provide clues to changes in climate. Evidence for Evolution 2) Biogeography - We can compare island species with their mainland ancestors - Ex: Darwin’s discovery of a species of finches in the Galapagos Islands Evidence of Evolution 3) Homology- Similarity in characteristics of different species resulting from common ancestor -homologous structures: same structure, different function Evidence for Evolution 4) Vestigial structures: structures that have a reduced or no function today, but had a function in a common ancestor Evidence for Evolution 5) Embryological- if the embryonic development was similar then this may indicate a close relationship and common ancestor Evidence of Evolution 6) Biochemical Evidence: if two species have similar DNA sequences then they may have common ancestor (most reliable source) What is Natural Selection? • A process in nature that only the organisms best adapted to their environment tend to survive and pass on the surviving traits to their offspring. • It is a key mechanism of evolution. Natural Selection 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Individuals within a population vary in their traits. More offspring are produced than can survive. Many will get eaten or will not be able to compete for resources. There is competition for limited resources that creates a struggle for existence. Individuals with advantageous traits will survive and reproduce. Those with bad traits will die, taking those bad traits with them. Concept was called survival of the fittest by Herbert Spencer after Spencer read Darwin’s book, On the Origin of Species. • Natural Selection of “the best” traits leads to EVOLUTION. What an Adaptation IS and IS NOT… • An adaptation is a trait that an organism is born with/has genetically that better enables it to survive in an environment. – Ex: webbed feet on a duck • An adaptation is NOT acquired during an organism’s lifetime. What are two types of evolution? Divergent Evolution: • When a species diverges into 2 or more descendant species which results in once related species becoming more and more dissimilar. What are two types of evolution? Convergent Evolution – Unrelated species evolve similar traits even though they live in different parts of the world. – Similarity in environment has led to evolution of similar traits. – EX: Madagascar aye-aye and New Guinea striped opossum both have elongated middle fingers. Live separately but have same structure What is Speciation? • Species: group of individuals that actually or potentially interbreed in nature. • Speciation: process of one species splitting into two species. Usually due to a geographic divide that separates the species. – Ex: Kaibab squirrel and Abert squirrel were once the same species but were divided by creation of Grand Canyon. • Phylogenetic Trees show evolutionary relationships among organisms. • They also show how they evolved from a common ancestor