* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence of evolution
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
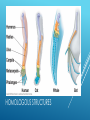
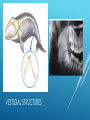
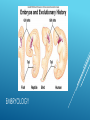
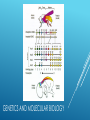
EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Evolution is the process of change over time. Biogeography is the study of where organisms live now and where their ancestors lived in the past. Patterns in the distribution of living and fossil species tell us how modern organisms evolved from their ancestors. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION To Darwin, the biogeography of the Galapagos species suggested that populations on the island had evolved from mainland species. Overtime, natural selection on the islands produced variations among population that resulted in different, but closely related, species. CLOSELY RELATED BUT DIFFERENT Darwin also noted that similar ground dwelling birds inhabit similar grasslands in Europe, Australia, and Africa. Differences in body structures provide evidence that they evolved from different ancestors. Similarities provide evidence that similar selection pressures had caused distantly related species to develop similar adaptations. DISTANTLY RELATED BUT SIMILAR Geologists have used radioactivity to establish the age of fossils and rocks. Using this technology, we know that the earth is ~ 4.5 billion years old. This supports Hutton and Lyell’s notion that the earth was very old. It also supports Darwin’s theory of evolution because if the earth were only a few thousand years old, natural selection wouldn’t have enough time to take place. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Darwin struggled with the “imperfection of the fossil record”. Many recently discovered fossils form series that trace the evolution of modern species from extinct ancestors. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION Researchers have found more than 20 related fossils that document the evolution of modern whales from ancestors that walked on land. Modern whales still retain reduced pelvic bones and, in some cases, upper and lower limb bones. Other recent fossil finds connect the dots between dinosaurs and birds. Homologous structures are structures that are shared by related species and that have been inherited from a common ancestor. Evolutionary theory explains the existence of homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Body parts that share a common function, but not structure, are called analogous structures. ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES Vestigial structures are inherited from ancestors but have lost much or all of their original function due to selection pressures acting on the descendent. VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES Similar patterns of embryological development provide further evidence that organisms have descended from a common ancestor. EMBRYOLOGY EMBRYOLOGY At the molecular level, the universal genetic code and homologous molecules provide evidence of common descent. All living cells use information coded in DNA and RNA to carry information from one generation to the next. This is identical in all living organisms. GENETICS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Cytochrome C, which functions in cellular respiration, is a homologous protein that is found in almost all living cells, including plants, animals, and bacteria. GENETICS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Hox genes help determine the “head to tail axis” in embryonic development. Some form of these genes are found in almost all multicellular animals. A small change in this gene can produce a dramatic change in the structures they control. GENETICS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY During his time on the Galapagos Islands, Darwin observed several different types of finches. Despite how different they looked from one another, Darwin hypothesized that they all came from a common ancestor. NATURAL SELECTION IN ACTION Darwin noted that several finch species had beaks of different sizes and shapes. He proposed that natural selection had shaped the beaks of different bird populations as they became adapted to eat different foods. He couldn’t test this hypothesis. NATURAL SELECTION IN ACTION 35 years later, Peter and Rosemary Grant came along with a way to test Darwin’s hypothesis. There were two assumptions: For beak size and shape to evolve, there must be enough heritable variation in those traits to provide raw material for natural selection Differences in beak size and shape must produce differences in fitness. NATURAL SELECTION IN ACTION The Grants studied a species of finch on an island big enough to support good sized populations, but small enough to allow the catching and tagging of every bird of the species. They recorded individual characteristics (beak length, beak depth, wing length, color, etc.) and which individuals lived and died. NATURAL SELECTION IN ACTION The Grants found that individual finches with different sized beaks have better or worse chances of surviving both season draughts and longer dry spells. NATURAL SELECTION IN ACTION This work shows that variation within a species increases the likelihood of the species’ adapting to and surviving environmental change. NATURAL SELECTION IN ACTION