* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chart - Appeal of Islam
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Unit 4: 300 CE – 1500 CE
Project 3: ISLAM
Part II: Core Knowledge: Define the following terms and apply them to your project.
Abraham:
Moses: a religious leader, lawgiver and prophet, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally
attributed.
Jesus: considered to be a Messenger of God and the Masih (Messiah) who was sent to guide the
Children of Israel
Kaaba: the most sacred site in Islam, holds sacred value to Muslims around the world.
Muhammad: was a leader from Mecca who unified Arabia into a single religious polity under Islam.
Root S-L-M: Knowledge in Islam
Quran/Koran: sacred book to Muslims, believed to be direct words from god.
Mecca: is the birthplace of Muhammad, founder of Islam, and Muslims believe it is one of the holiest
cities.
Hajj/Hadj: is the Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is one of the largest pilgrimages in the
world
Medina: is the second holiest city in Islam, known primarily for its importance in the early years of
Muhammad's preaching as well as the site the Mosque
Jerusalem: is built on the site of the second place of worship ('Masjid' in Arabic) built by man, after the
Masjid al-Haram in Makkah. Al-Aqsa is the third holiest site in Sunni Islam
Dome of the Rock Mosque: is a shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. The
structure has been refurbished many times since its initial completion in 691 CE at the order of Umayyad
Caliph Abd al-Malik.
Umma: refers to all of the Islamic world unified
5 Pillars of Islam:
the shahada (Islamic creed)
daily prayers
almsgiving
fasting during Ramadan
the pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj) at least once in a lifetime.
Caliph: the title for the ruler of the Islamic Ummah, an Islamic community ruled by the Shari'ah.
Abu Bakr: was a senior companion and the father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He ruled
over the Rashidun Caliphate from 632–634 CE when he became the first Muslim Caliph following
Muhammad's death
Uthman: was one of the companions of Islamic prophet, Muhammad. He played a major role in early
Islamic history as the third of the Sunni Rashidun or Rightly Guided Caliphs.
Umar/Omar: was one of the most powerful and influential Muslim rulers in history. He was a sahabi of
the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He succeeded Caliph Abu Bakr as the second Caliph of Rashidun
Caliphate on 23 August 634.
Ali: was the cousin and son-in-law of Islamic prophet Muhammad, ruling over the Islamic Caliphate from
656 to 661.
Battle of Karbala: The battle was between a small group of supporters and relatives of Muhammad's
grandson Husain ibn Ali, and a much larger military detachment from the forces of Yazid I, the Umayyad
caliph, whom Husain had refused to recognise as caliph.
Sunni:is the largest branch of Islam and are referred to in Arabic as ʾAhlu-s-Sunnati wa-l-Jamāʿah
(Arabic: )ةالمجلاة ال س نة أهل, "people of the tradition of Muhammad and the consensus of the Ummah
Shiite: member of the smaller of the two major branches of Islam, distinguished from the majority
Sunnis. Early development Early in the history of Islam.
Umyyad Empire: was the second of the four major Islamic caliphates established after the death of
Muhammad. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty.
Abbasid Empire: was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs,
who built their capital in Baghdad.
Mongol Sacking of Bahgdad: committing numerous atrocities and destroying the Abbasids' vast libraries,
including the House of Wisdom.
Jihad
Lesser: an individual's striving for spiritual self-perfection.
Greater: is a religious duty of Muslims.
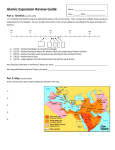
PART III: KEY MUSLIM EMPIRES
Directions: Starting on page 310 as you read the text through page 333, identify and analyze, how and
why individuals, events and/or ideas developed to impact the following Islamic empires.
Empire
Muhammad
and First
Successors
(632-661)
Abu Bakr
Umar
Uthman
Umayyad (661—750)
(756-1031) in Spain
Abbasid (750 –
1258)
Ottomans (late 1200s –
1922)
Muawiya I
Marwan II
al-Musta'sim
Mehmad II
Turkish Sultans
Abdul-Hamid II
Capital
Medina
Damascus
Samarra
Constantinople
Form of
Islam
Caliphs
Sunnis and Shiites
Shiites
Key Military
Events
Arabs conquer
Egypt. Persian
Empire falls to
Arabs.
Arabs reach
Morocco. Franks
defeat Muslim forces
at the Battle of
Tours. Muslims enter
Spain.
Discrimination
against non-Arabs
and Sunnis and
Shiites
Seljuk Turks begin
invasions of
Muslim regions.
Cultural
Achievemen
ts/Ideas/
Innovations
Death of
Muhammad
The empire expands
and Arabs liberate
harsh Persian rule
Golden Age of
Islam
Seljuk Turks take control
Summarize
Reasons for
Decline:
Expansions to
bigger cities.
Ruling large cities
from deserts to more
rural areas.
Turks invade the
religion.
Mongols attack the city
of Baghdad and disease
of the Mongols reach
people through rats and
die.
Key
Leader(s)
Mongols attack Baghdad
Due Thursday October 18
Content
Name:_____________Hour:_______________
Islam Perspective Project
Due Thursday October 18
Quality Sources: 30 points 1 quality source from each
The student will give validity to their product by using high quality resources, such as:
on-line databases
primary sources
original interviews
expert secondary sources including use of
textbook
Quality Thesis: 20
Answers the question with an individual position
and provides a factual rationale.
Did you answer the question
with a position
did you provide a why
did you provide a result (Describe the
effect)
Term Sheet 10
Comparison 20
Total
80
Name:______________
Hour:_______________