* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INTRODUCTION TO SPORT SCIENCE
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
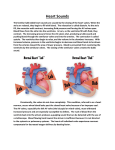
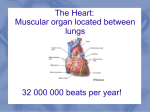
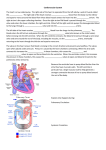
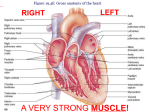
INTRODUCTION TO SPORT SCIENCE Class 2 : Heart Rate Contents 1) Theory (15min) 2) Practical (25 min) Heart: Location Centre of the thoraxic cavity Flanked by the lungs Heart Chambers Superior vena cava Aorta Pulmonary trunk Left atrium Right atrium Left ventricle Right ventricle Inferior vena cava Intraventricular septum Heart Atrium Superior vena cava Aorta Left lung Pulmonary trunk Ventricle Apex Diaphragm Ventricles “Power-pack” of the heart Thick muscle - provides the pumping force for the circulatory system Both ventricles contract together 100% of blood from R ventricle goes to the lungs where it is oxygenated Returned to L atria (receptacle) and flows to L ventricle Pumped from L ventricle to the rest of the body Heart Valves Blood flows through the heart in one direction One way traffic is enforced by 4 heart valves 1. Atrioventricular (AV) valves 2. Semilunar valves Opening and closing of valves is a passive process resulting from pressure differences across the valves Atrioventricular Valves Located between the atrium and ventricle in each half of the heart Prevent backflow into atria when the ventricles contract Right AV valve - tricuspid valve Left AV valve - bicuspid (mitral) valve Chordae tendineae anchor the cusps to the papillary muscles protruding from the ventricle walls Papillary muscles do not open or close the valves - act only to limit the valves movements and prevent them from being everted Opening the AV Valves Blood returning the the heart fills the atria This puts pressure against the AV valves The AV valves are forced open Closing the AV Valves Ventricles contract and force blood against the cusps of the AV valves, causing them to close Papillary muscles contract and chordae tendineae tighten preventing valve flaps from everting into atria Semilunar Valves Pulmonary valve - opening of the right ventricle into the pulmonary trunk Aortic valve - opening of the left ventricle into the aorta Prevent backflow into the ventricles Opening Semilunar Valves When the ventricles contract the pressure inside rises When the pressure inside the ventricles is greater than the pressure in the aorta and pulmonary artery the semilunar valves are forced open and the cusps are flattened against the arterial walls and blood flows past Closing Semilunar Valves When the ventricles relax the pressure inside falls Blood flow back from the arteries Fills the cusps of the valves forcing them the close Aortic Stenosis Disease can damage the aortic valve Unable to open fully during contraction of the left ventricle Causes an obstruction to blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta Results in a compensatory increase in the thickness of the left ventricle forcing the heart to work harder Systemic Circulation Oxygen rich blood is pumped from the L atrium L ventricle aorta to the organs and tissues of the body (except the lungs) and then to the R atrium Transfer of gases, nutrients and waste products occurs in the capillary beds Heart Rate Number of times that the heart beats each min (beats/min) Usually between 60 and 80 beats/min in a healthy individual Heart Rate Determination You can feel a pulse in an artery that lies close to the body surface by compressing the artery against firm tissue Use your two index finder to locate the pulse in your radial artery Heart Rate Determination Count the number of pulses in 10 seconds and multiply by 6 to calculate the heart rate per minute Repeat this 3 times Select a partner and calculate his/her heart rate per minute Heart Rate Determination: Questions Draw a histogram to illustrate the heart rate of each member of the class What is the average heart rate of the class ? What is the lowest heart rate in the class? What is the highest heart rate in the class? What is the median heart rate in the class? What is the mode heart rate in the class? What does the mode, median and mean tell you about the distribution of heart rates in the class What is your Estimated Maximal Heart Rate? Calculated by subtracting your age from 220 220-age Calculate your estimated maximal heart rate? Breathing Rate Number of times that an individual breaths per min (breaths/min) Usually between 12-16 breaths/min in a healthy individual Breathing Rate Determination Place your hand on your breastbone (sternum) and count the number of inhalations (chest expands) in10 seconds Multiply by 6 to calculate the breathing rate per minute Repeat this 3 times Breathing Rate Determination: Questions Draw a histogram to illustrate the breathing rate of each member of the class What is the average breathing rate of the class ? What is the lowest breathing rate in the class? What is the highest breathing rate in the class?