* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
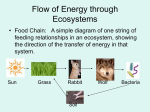
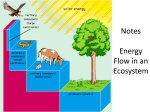
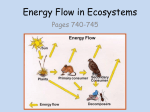
Feeding relationships • Basic terminology: • Food chain: a simplified way of showing a feeding relationship of an ecosystem. 1 consumer feeds on 1 consumer and so on. • Food web: a more accurate way of showing the feeding relationship may show 2 or more consumers feeding on several organisms at a time. Producers are organisms which make their own food from inorganic (non-Living) sources, generally they are plants and form the basis of all food chains. Consumers are the animals which consume plants(producers) and other organisms. Producers Plants Primary consumers Herbivores Decomposers Secondary consumers Carnivores Tertiary consumers Carnivores Decomposers are organisms which gain nutrients and energy from dead matter. All things die and so all food chains lead to decomposers. They make the nutrients and energy contained by the bodies of the dead organisms available to other organisms Producers First trophic level •Each organism represents a trophic or feeding level of a food chain. Plants Primary consumers Second trophic level Herbivores Decomposers Secondary consumers Third trophic level Fourth trophic level Carnivores Tertiary consumers Carnivores Available energy decreases down the food chain: Producers • Only 10% of the energy At each trohpic level is available to the members of the next level 100% Primary consumers 10% Secondary consumers 1% Tertiary consumers 0.1% Example of a food web Shows the feeding relationship between several animals at once. Note the many branches. At which trophic level(s) is the insectivorous bird? Predators and prey • Predators are animals that feed on other animals called prey. • Rosebush aphid ladybird spider bird The food chain above shows That the ladybird,spider and the bird are all predators. Question: Why isn’t the aphid considered a predator? Ecosystem • An ecosystem is a unique collection of animals and the surroundings which they interact with Ecosystem contains living and nonliving factors: • An ecosystem consists of abiotic factors such as the non-living environment, soil, air, water,etc which the animals would not be able to do without and biotic factors, or the organsisms which live there. • The abiotic factors are also called the habitat or the area which provides a suitable environment where an organism can live. Niche’ • Each organism plays a specific role as part of an ecosystem, E.g the robin below is an insect hunter. It’s niche’ can be thought of as it;s job description. Describing animals • All the animals of the same species occupying the same geographical area are termed a population. E.g a family of mice living in a barn, or a school of fish living near a bank. • Several populations of different species of animals interacting together are termed a community. • A log carries a few members of a species of snake from a mainland to nearby island. Why are these 2 groups not considered to be the same population? Extinction