* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An ecosystem is a - colegio agustiniano ciudad salitre
Survey
Document related concepts
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of the San Francisco Estuary wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
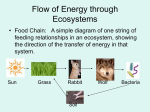
AGUSTINIANO CIUDAD SALITRE SCHOOL NATURAL SCIENCE AND ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION SIXTH GRADE MAKE UP WORKSHOP NAME: _________________________________________________ COURSE: _____ DATE: _____________________________ ECOSYSTEM Fill in the blanks using the word box: trophic levels food chain environment abiotic interactions components trophic interactions producers consumers decomposers community food webs biotic An ecosystem is a ____________________ of organisms interacting with each other and with their ____________________such that energy is exchanged and system-level processes, such as the cycling of elements, emerges. Ecosystems may be observed in many possible ways, so there is no one set of ____________________that make up ecosystems. However, all ecosystems must include both ____________________ and ____________________ components, their ____________________, and some source of energy. At a basic functional level, ecosystems generally contain primary ____________________ capable of harvesting energy from the sun by photosynthesis and of using this energy to convert carbon dioxide and other inorganic chemicals into the organic building blocks of life. ____________________ feed on this captured energy, and ____________________ not only feed on this energy, but also break organic matter back into its inorganic constituents, which can be used again by producers. These interactions among producers and the organisms that consume and decompose them are called ____________________ ____________________ and are composed of ____________________ ____________________ in an energy pyramid, with most energy and mass in the primary producers at the base, and higher levels of feeding on top of this, starting with primary consumers feeding on primary producers, secondary consumers feeding on these, and so on. Trophic interactions are also described in more detailed form as a ____________________ ____________________, which organizes specific organisms by their trophic distance from primary producers, and by ____________________ ____________________, which detail the feeding interactions among all organisms in an ecosystem. Together, these processes of energy transfer and matter cycling are essential in determining ecosystem structure and function and in defining the types of interactions between organisms and their environment. It must also be noted that most ecosystems contain a wide diversity of species, and that this diversity should be considered part of ecosystem structure. Make a chart to list all the abiotic things, primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and decomposers that are found in the simplified ecosystem above. ABIOTIC THINGS PRIMARY PRODUCERS PRIMARY CONSUMERS SECONDARY CONSUMERS DECOMPOSERS Remember that the biotic factors in an ecosystem could be organized in domains and kingdoms. Complete the concept map about them. Use the names, the cell types, cell numbers and which are their names based on how they can obtain the energy: FOOD CHAINS The feeding of one organism upon another in a sequence of food transfers is known as a food chain. Another definition is the chain of transfer of energy (which typically comes from the sun) from one organism to another. TROPHIC LEVELS Trophic levels are the feeding position in a food chain such as primary producers, herbivore, primary carnivore, etc. Green plants form the first trophic level, the producers. Herbivores form the second trophic level, while carnivores form the third and even the fourth trophic levels. Summarizing write the name of the trophic levels: 1. ____________________________________ ___________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 3. ___________________________________ FOOD WEBS In an ecosystem there are many different food chains and many of these are cross-linked to form a food web. Ultimately all plants and animals in an ecosystem are part of this complex food web. SOME TYPES OF ECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS Competition Competition describes multiple organisms fighting for the same resources. Interspecies competition is competition between different species; intraspecies competition is competition between organisms of the same species. The competition may or may not involve active interference. Parasitism Parasitism is when one species (PARASITE) benefits from a second species (HOST) that is disadvantaged, but generally not killed. Mutualism Mutualism is an interaction characterized by mutual benefit, so both species benefit from the relationship. Mutualism can also be thought of as "mutual exploitation." Commensalism Commensalism describes a relationship in which one species benefits but the other is unaffected. Predation Predation describes one species, the predator, feeding on and typically killing another organism, the prey species. Predators use various methods to capture prey, just as their prey use various methods to avoid capture. Name the images and explain the reason of each relationship: _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________