* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Divergent Boundary
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
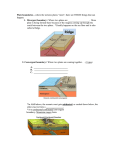
Understanding Plate Motions Directions: Read the following article. Make at least 2 annotations per plate boundary type. Answer the questions at the end of each boundary type. 1. Divergent Boundary Also known as spreading boundary, a divergent boundary occurs where two plates move apart, allowing magma, or molten rock, to rise from the Earth's interior to fill in the gap. The two plates move away from each other like two conveyor belts moving in opposite directions. The Earth's longest mountain chain isn't the Andes in South America, or the Himalayas in Asia, or even North America's Rockies. It's an underwater chain of mountains 47,000 miles long. The chain runs down the middle of the Atlantic Ocean (surfacing at Iceland), around Africa, through the Indian Ocean, between Australia and Antarctica, and north through the Pacific Ocean. As the two sides of the mountain move away from each other, magma wells up from the Earth's interior. It then solidifies into rock as it is cooled by the sea, creating new ocean floor. The speed at which new ocean floor is created varies from one location on the ocean ridge to another. Between North America and Europe, the rate is about 2.2 inches (3.6 cm) per year. At the East Pacific rise, which is pushing a plate into the west coast of South America, the rate is 12.6 inches (32.2 cm) per year. Rift Zone Reflection Note 1. In your own words describe transform boundaries. What are some geologic features that happen at divergent boundaries? Divergent boundaries are… Geologic features that occur at divergent boundaries are… 2. Convergent Boundary Also known as a subduction boundary at most places, a convergent boundary occurs where two plates come together. When at least one of the plates is an oceanic plate, then one plate slides under another as the two are pushed together. If there is land at the edge of one of these plates, the oceanic plate will subduct, or slide under that plate. New crust is continually being pushed away from divergent boundaries (where sea-floor spreading occurs), increasing Earth's surface. But the Earth isn't getting any bigger. What happens, then, to keep the Earth the same size? The answer is subduction. In locations around the world, ocean crust subducts, or slides under, other pieces of Earth's crust. The boundary where the two plates meet is called a convergent boundary. Deep trenches appear at these boundaries, caused by the oceanic plate bending downward into the Earth. At a depth between 190 and 430 miles (300 and 700 kilometers), the rock of the descending plate melts. Some of this molten ocean floor makes its way to Earth's surface, producing volcanoes. Most of it, though, becomes part of the Earth's mantle, perhaps to reappear much later at a distant divergent boundary. At other locations, two continental plates come together and form mountains. Reflection Note 2. In your own words describe convergent boundaries. What are some geologic features that happen at convergent boundaries? Convergent boundaries are… Geologic features that occur at convergent boundaries are… 3. Transform Boundary A transform boundary occurs where two plates slide against each other. But rather than sliding smoothly, the plates build up tension, then release the tension with a spurt of movement. This movement is felt as an earthquake. Transform boundaries neither create nor consume crust. Rather, two plates move against each other, building up tension, then releasing the tension in a sudden and often violent jerk. This sudden jerk creates an earthquake. The San Andreas Fault is undoubtedly the most famous transform boundary in the world. To the west of the fault is the Pacific plate, which is moving northwest. To the east is the North American Plate, which is moving southeast. Los Angeles, located on the Pacific plate, is now 340 miles south of San Francisco, located on the North American plate. In 16 million years, the plates will have moved so much that Los Angeles will be north of San Francisco! Reflection Note 3. In your own words describe transform boundaries. What are some geologic features that happen at transform boundaries? Transform boundaries are… Geologic features that occur at transform boundaries are…