* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AbsiteGIHormones - Open Source Surgery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
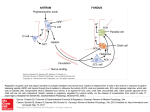
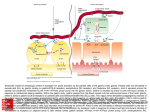
1/19/2013 Gastrin Absite: GI Hormones http://opensourcesurgery.com • Produced: in G cells in the antrum • Stimulated by: Amino acids, Vagal Input, Calcium, Alcohol, Antral Distention, normal or high pH, histamine • Inhibited by: Low pH in duodenum, Somatostatin, Secretin, CCK, VIP, Gastrointestinal inhibitory peptide • Acts on: Parietal and chief cells to increase – Acid/H+ release(Parietal), blocked by PPI at H/K ATPASE in parietal cell. – Intrinsic factor(Parietal) binds B12 absorbed at TI, – Pepsinogen secretion(Chief) Somatostatin Produced by: D‐cells in the antrum Stimulated by: Acid in the stomach Inhibitor: Many, known as the great inhibitor Acts to decrease the action of most of the other GI Hormones, decrease motility, decrease blood flow to GI Tract • Octreotide: Somatostatin Analogue, Decreases Pancreatic Fistula output. Also used in variceal bleeding. • • • • CCK • Produced by I Cells of the Duodenum • Stimulated by: Amino Acids and Fatty Acids • Acts on: Gallbladder causing contraction, relaxation of sphincter of Oddi, Increases pancreatic enzyme secretion, decreases gastric emptying. • CCK given when checking ejection fraction in HIDA scans. Gastric Inhibitory Peptide • Produced by K cells in duodenum • Stimulated by Amino acids, glucose, long chain fatty acids, decreased pH • Acts on parietal cells, and Beta Cells of the pancreas. Decreases HCl+ Pepsin, Increases insulin. Secretin • Produced by S cells of the Duodenum • Stimulated by: Low pH and Fatty Acids in Duodenum • Inhibited by: High pH, gastrin • Acts to: Increase pancreatic HCO3 Release, increased bile flow, inhibits gastrin release, inhibits HCL release. 1 1/19/2013 Motilin • Produced by M cells in Duodenum • Stimulated by: Duodenal acid, food, vagus input, gastrin‐releasing Peptide • Inhibited by: Somatostatin, Secretin, Pancreatic Polypeptide, duodenal fat • Causes increased small bowel motility • Erythromycin acts here Insulin • Insulin – Released by Beta cells of pancreas – Stimulated by glucose, glucagons, cck – Causes: Glucose uptake, protein synthesis – Reglan acts as antagonist on D2 Receptors Glucagon • Glucagon – – – – Alpha Cells of Pancreas Increased Glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis Breaks down fats and proteins Relaxes Sphincter of Oddi – used to power flush stones out of the common duct in lap chole. Vasoactive intestinal peptid • Produced in GI tract and Pancreas – – – – Secretion stimulated by fat, acetylcholine Causes increase in water secretion and motility Inhibits gastrin release Relaxation of GI smooth muscle – Over production in VIPoma leads to watery diarrhea. Pancreatic Polypeptide • Secreted by the islet cells of the pancrease • Stimulated by: Food, Vagal Stimulation • Acts to: Decrease pancreatic endocrine and exocrine function Bombesin(aka gastrin releasing peptide) • Released from post‐synaptic fibers of vagus nerve • Increases gastrin/gastric acid secretion, intestinal motility, pancreatic secretion 2 1/19/2013 Peptide YY • Released from Terminal Ileum • Inhibits gastric motility • Increases water and electrolyte absorption in the colon • Decreases Pancreatic secretion 3