* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies
Weak gravitational lensing wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Health threat from cosmic rays wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
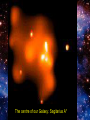
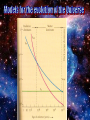
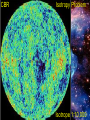
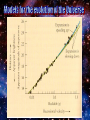
This animation begins with a collapsing interstellar cloud of gas and dust. Most of the material becomes part of the young Sun, but some debris forms a disk. Within this disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the outer solar system, where miniature disks form around the Jovian planets. Within the Orion Nebula—a giant cloud of gas and dust some 1500 light-years from Earth—new stars, and perhaps new planets, are being formed. The final closeup is a young star surrounded by a dark disk of material within which planets may be forming. (HST images). The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies This supercomputer simulation shows the collision and merger of two disk-shaped galaxies. Stars in the disk of each galaxy are colored blue, while stars in their central bulges are shown in yellow. Red indicates dark matter that surrounds each galaxy. The total elapsed time for this simulation is one billion years. This supercomputer simulation shows six galaxies merging to form a single giant galaxy. Toward the end of the simulation a large galaxy forms that "devours" other, smaller galaxies, a process called galactic cannibalism. (In ordinary galactic mergers, galaxies of about the same size are involved.) Galactic cannibalism may explain how giant elliptical galaxies form near the centers of rich clusters of galaxies, where galactic collisions are frequent. The centre of our Galaxy: Sagitarius A* Curved Spacetime Physics can reconstruct the history of the universe up to the Planck-time ~ 1.35 .10-34 sec Before that time QM and RT contradict 2D-Analogy: inflation of a baloon • All points move apart a la Hubble • There is no centre of the universe • Space itself expands Critical density : crit = 2.10-27 kg/m3 = /crit Up to 300,000 yrs Hot and opaque Matter and radiation coupled Universe cooled by expansion: matter and radiation become suddenly decoupled Universe becomes transparant This is the oldest radiation and the farthest we can possibly see This radiation is the Cosmic Background Radiation (CBR) Because of subsequent expansion the the universe this is now cooled to ~ 2.7 Kelvin Since january 2003 a entire map of the CBR is available CBR Isotropy Problem Isotrope 1:10,000 Newest measurements indicate that space is almost flat and isotrope Solution: inflation theory Short after Plancktime space grew during about 10-24 seconds a factor 1050 Newest measurements also indicate that redshift grows stronger than Hubble’s law The expansion is accelerating !!! Possible solution: reintroduction of Cosmological Constant ? What would Einstein say ??? Big Crunch : not likely Big Sleep : 1036 yrs from now only lowenergy radiation