* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics – Study Guide
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
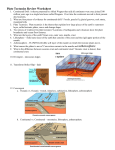
Plate Tectonics – Study Guide Name: _________________________ Date: ______________ Pd: __________ 1. A_____ W______ found evidence of continental drift. When he proposed this theory at first he could not identify the force that would move tectonic plates; other _____ did not accept his theory because he could not explain what could move such large plates. Later scientists linked the idea of c________ c________ in the Earth to the motion of the continents. 2. Convection currents inside the Earth happen when hot, plastic-like rock _____, move along the top of the asthenosphere, _____, and then drop back deeper into the asthenosphere. 3. A ______ plant fossil found in a currently polar region is evidence that the _____ region was once tropical. 4. Identical fossils of species found on different continents may indicate those __________ were once joined. 5. Match the theory with the correct description: THEORY Continental Drift DESCRIPTION Earth’s asthenosphere moves in a current as the mantle is heated (& rises) and cools (& falls). Plate Tectonics Continents have moved slowly to their current positions. Convection Currents Earth’s lithosphere is divided into many ‘plates.’ 6. Matching rock structures, like __________, on several continents supports the theory of continental drift. 7. _________, the super continent, was the once single land mass that split and drifted into several continents according to Alfred Wegner. 8. Which is more dense? Circle the one that has a greater density: a. Continental plate / Oceanic plate b. Cool magma (asthenosphere) / Hot magma (asthenosphere) c. Oceanic plate that is older / Oceanic plate that is newer 9. _________ zones can produce volcanoes. C_______ boundaries of oceanic and continental plates OR oceanic and _________ plates can produce these Subduction zones. 10. Rocks closest to the mid-ocean ridge are oldest/youngest while rocks farthest from the mid-ocean ridge are oldest/youngest. 11. Do the math! (1km = 100,000 cm) You may use a calculator, but SHOW YOUR WORK: a. The sea floor is spreading at a rate of 5 cm per year. The sea is 8,000 km wide. How many years ago did the sea begin to form? b. An ocean is 140,000,000 years old. The sea floor has spread at a rate of 5 cm per year. How wide is the sea now? 12. Sea-floor spreading (d_______ boundary beneath the sea) makes new o_____ lithosphere; lithosphere is destroyed at __________ zones. Your plate tectonics test is your exam. For ____ period your exam will be ____ . This Study Guide is due ____ . Use this and the questions from my Flexbook in the course to prepare for your exam!