* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Greatest Show on Earth Review
Survey
Document related concepts
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
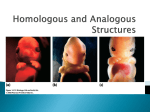
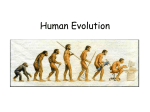
The Greatest Show on Earth By: Richard Dawkins Chapter 1: Only a Theory? (Oct. 14) Discusses a roman history teacher having to always explain that the Romans existed because of a well financed and strong political ties says that the Romans never existed and Spanish, Italians, French, etc. all languages and their dialects sprang spontaneously Holocaust deniers Educated priests and professors of theology hole heartedly accept evolution as fact the problem is their congregations do not, >40 percent of Americans deny humans evolved from other animals and the earth is less than 10,000 years old. Theory sense 1 vs. theory sense 2 – very different definitions Many philosophers think the only things that can be proved is math Evolution is a fact as Paris is in the northern hemisphere Goldbach’s Conjecture – hypotheses that any even integer can be expressed as a sum of prime numbers, not proven until 1995; proof in math = theorem Dawkins will use the word theorum meaning the same as the math term just changing the wording to prevent confusion. Approach the book as a detective coming onto a scene of a crime, the crime has already happened, make inferences using evidence, Eyewitness accounts can be false = Professor Daniel J. Simons at the University of Illinois with counting basketball passes, all the observers missed the gorilla in the middle of the 25 second film, eyewitness accounts can be unreliable Chapter 2: Dog, Cows and Cabbages (Oct. 14) Alfred Russel Wallace called his paper “on the tendency of varieties to depart indefinitely from the original type” How long do you keep calling a rabbit until you have to call it something else when its evolving one generation at a time over a long time Rabbits and leopards o “like all animals, it was a member of the same species as its daughters and its mother. We now continue our walk, except that we have turned the bend in the hairpin and are walking forwards in time, aiming towards the leopards (among the haipin’s many and diverse descendents, for we shall continually meet forks in the line, where we consistently choose the fork that will eventually lad to leopards). Each shrew-like animal along our forward walk is now followed by her daughter. Slowly, by imperceptible degrees, the shrew-like animals will change, through intermediates that might not resemble any modern animal much but strongly resemble each other, perhaps passing through vaguely stoatlike intermediates, until eventually without ever noticing an abrupt change of any kind, we arrive at a leopard.” o No matter how radical and extensive the difference between a rabbit and leopard, each step along the chain is as similar to its neighbors in the chain as mothers and daughters are expected to be Wild cabbage – undistinguished plant, weedy; in a few centuries of selective breeding we have sculpted domestic cabbage Sculpting of the wolf – Canis lupus, all domestic dogs descendents of gray wolf (not jackals as proposed by Lorenz) o Artificial breeding of dogs provides different varities, breeding boxers for a smaller and smaller snout o Control of gene pool o Coppinger speculates that the human desire to breed borzois for long snouts has reached a limit imposed by survival capacity of the puppies trying to suck o How easy its is for the non-random selection of genes “carving and whittling’ of gene pools to produce truly dramatic changes in anatomy and behavior and so fast” Mendel and All or Nothing Principle Over-muscled physiques of human-body builders, Belgian Blue cattle o Cow – genetic alteration called ‘double muscling’ Disable myostatin gene (limits muscle growth) Political opposition to eugenic breeding of humans sometimes spills over into almost certainly false assertion that its impossible, not impossible o If you had enough time and enough political power, you could probably build a superior sprinter, etc. Darwin had first hand experience of the power of artificial selection and gave it place in ch 1 of Origin of Species If human breeders can transform a wolf into a Pekinese in just a few centuries why shouldn’t the non random survival of wild animals and plants do the same thing over millions of years Chapter 3 – The Primrose Path to Macro-evolution (Oct. 15) Humans deliberately chose attractive roses, sunflowers, etc. for breeding, thereby preserving the genes that produce the attractive features. This is called artificial selection, its something humans have known about since long before Darwin and everybody understands that it is powerful enough to turn wolves into Chihuahuas and to stretch maize cobs from inches to feet Peahens choose attractive peacocks for breeding, again thereby preserving attractive genes. This is called sexual selection and Darwin discovered it, or at least clearly recognized it and named it Small prey fish choose attractive angler fish for survival, by feeding the most attractive ones with their own bodies, thereby inadvertently choosing them for breeding and passing on, and therefore preserving, the genes that produce the attractive features. This is called – yes, we’ve finally got there – natural selection Without any kind of choosing agent those individuals that are chosen by the fact that they happen to possess superior equipment to survive are the most likely to reproduce, and therefore to pass on the genes for possessing superior equipment. Therefore every gene pool, in each species tends to become filled with genes for making superior equipment for survival and reproduction Artificial selection constitutes a true experimental –as opposed to observational – test of the hypotheses that selection causes evolutionary change o Two lines of maize selected for high and low oil content (p.67) o Two lines of rats selected for high and low resistance to tooth decay (p.68) If its is so easy to improve the teeth of rats by artificial selection, did natural selection apparently make such a poor job of it in the first place? o Used domesticated rats Shielded from the cutting edge of natural selection Trade-offs Putting more calcium toward tooth production takes away from bone density and milk production o Not necessarily economically favorable for rats survival in wild What happens under domestication is that animals are artificially shielded from many of the risks that shorten the lives of wild animals. o Pedigree dairy cow may yield prodigious quantities of milk, but its pendulously cumbersome udder would seriously impede it in any attempt to outrun a lion Initial domestication of dog was self-domestication then artificial selection Tameness and silver fox with Dimitri Belyawe o Beginning no foxes were in the elite class (tamest of all, positively approached the handlers, wagging their tails, and whining), ten generation- 18%, twenty – 35%, thirty – 70 – 80% Flowers and co evolution (occurs between organisms that have something to gain from each other) with orchids and euglossine bee Nature as the selection agent and geological time Chapter 4 – Silence and Slow Time (Oct. 19) A variety of zero-able natural clocks is available, good b/c we can check accuracy of other clocks Tree Rings o Used to date a piece of wood, literally to the nearest year o Existence of rings signifies seasonal cycles of rich and poor growth Radioactive clocks o Known half-life’s o Margin of error (about 1 percent) o Each unstable isotope decays at its own characteristic rate which is precisely known o Half life of rubidium-87 is 49 billion years, carbon-15 is 2.4 seconds, wide range o Potassium/Argon clock Measure igneous rock because it is zeroed out b/c it crystallizes very fast, no argon crystals are in rock at time of crystallization, only potassium-40 o o Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks, so you have to measure igneous rocks in similar known layers (Permian, cretaceous, etc.) Another point All the elements that occur on earth 150 stable and 158 are not stable, making 308; 121 are either extinct or exist only because they are constantly renewed (carbon-14-dead organic matter), 37 have not gone extinct (every one of them has a half life greater than 700 million years); of the 121 that have gone extinct every single one has a half-life of less than 200 million years (remember taking half-life’s) Carbon One atom in a trillion is carbon-14 decays at a rate of 5,730 yrs. Clock is zeroed when a living creature (animal or plant) dies, detached from the food chain and detached from the inflow of fresh carbon-14 via plants from the atmosphere, as centuries go by the carbon-14 slowly decays to nitrogen-14, therefore the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 can be used to calculate the time elapsed since the death of the creature cut off from the food chain Mass spectrometry (only tiny organic molecule is needed) Shroud of Turin (cloth seems to mysteriously to have imprinted on it the image of a bearded crucified many, many hoped it was jesus) –property of Vatican since 1983 Divided and sent to 3 leading dating labs (Arizona, Oxford, and Zurich) o Independent research 1304, 1274, and 1200 A.D. – all within margin of error Controversy of possibly being in fire, not relevant to dating but history Chapter 5 – Before our very eyes (Oct. 20) Elephants and response to hunting for large ivory tusks o Ugandan elephants – statically relevant reduction in tusk size since 1925 Points evolutionary adaptation to have smaller tusks (increases survival) o Dr. Iain Douglas-Hamilton (elephant expert) takes it seriously and believes that it needs more looking into Lizards of Pod Mrcaru o Transplanted from ancestral island o 36 years Lizards on Pod Mrcaru have much larger head sizes (more bite force) than ancestral lizards from ancestral island; new lizards transition to herbivore, caecum transition also. Forty-Five Thousand Generations of Evolution in the Lab o o o Led by Richard Lenski at Michigan State University Escherichia coli, long term experiment In 1988, took one such population and infected 12 identical flasks, all of which contained the same nutrient broth including glucose as the vital food source, placed in shaking incubator, founded 12 lines of evolution that were destined to be kept separate for 2 decades and counting, each tribe was put into a new flask every day (exactly onehundredth of the volume of old flask into new flask with fresh supply of glucose-rich broth) o Population of bacteria would skyrocket; but always leveled off by the next day as supply of food gave out and starvation set in (glucose was limiting factor) – selection pressure to consume glucose more efficiently o About 7,000 flask generations and 45,000 bacterial generations (6-7 per day) o Used genetic mutation of Ara+ and Ara- for color labeling (no effect on selection – previously established) o All twelve lines improved over their ancestors: got better in different ways – that is, different tribes developed different sets of mutations Comparing the fitness of each sample against fossils are frozen sample of bacteria which when unfrozen carry on living and reproducing normally Showed step by step cumulative natural selection o Ara -3 around 33,000 generations threw up one dramatic exception Went berserk, liquid became cloudy by the sheer number of bacteria Evolve the ability to eat citrate (e.coli cannot normally us it), therefore the amount of food in each successive flask in the linage therefore shot up Found that a mutation happened around 20,000 generations that primed a later mutation (explanation for rarity compared with other flasks) Guppies o Guppies were assigned randomly to ten ponds, five with coarse gravel and five with fine gravel and allowed to breed for 6 months (number of spots went up dramatically). All ten colonies were allowed to breed freely for six months with no predators. Put 1 dangerous predator into each of two coarse gravel and two fine gravel, 6 weak predators into each of two gravel and fine gravel, last 2 carried on as before with no predators o In ponds with dangerous predator; number of spots decreased; with weak predator, spots increase (sexual selection overweighed predator selection); no predators, spots increased o Fine gravel favored large spots on males and coarse favored small spots, they are more conspicuous if they do not mimic the stones on their respective backgrounds and that is good for attracting females o Repeated in wild o Repeated by other researches – found even more support for sexual selection and predation Chapter 6 – Missing Link? What do you mean, ‘Missing’? (Oct. 27) Creationists are deeply enamoured of the fossil recored because they have been taught by each other that it is full of gaps. We do not need fossils to prove evolution is true; enough evidence in the comparative study of modern species and their geographical distribution. Biggest “gap” one that preceded Cambrian explosion o Creationists “forget” that it was a period of 20 million years Commonly bring up Piltdown Man hoax, ignore the mast amount of fossils that cover the intermediates linking modern human to the common ancestor that we share with chimpanzees Show me Your Crocoduck o Why donesn’t the fossil record contain a fronkey Of course monkeys are not decended from frogs Monkeys and frogs share a common ancestor which certainly looked nothing like a frog or monkey (salamander like fossils dating to about the right time have been discovered) I’ll believe in Evolution when a Monkey gives birth to a human baby o Once again, humans are not descended from monkeys (share a common ancestor) o No animal gives birth to an instant new species, or at least not that different o Evolution is a gradual process, huge leaps in a single generation are almost as unlikely as divine creation The Pernicious Leagacy of the Great Chain of Being o Ladder system of being: god, angles, humans, animals, plants; “higher animals and lower animals”, confusing Monkeys evolved from earthworms The common ancestor of monkeys and earthworms was more like an earthworm than like a monkey Monkeys are cleverer (or prettier, have larger genomes, more complicated body plans) than earthworms Monkeys are more like humans than earthworms are Monkeys are better at surviving than earthworms and other lower animals o Degrees of resemblance can be hard to measure o Birds are example of good class (all birds are decended from a single ancestor o Reptiles are not a good class in this sense Excludes birds Crocodiles and dinosaurs are closer cousins to birds than lizards and turtles Artificial class because birds are excluded Cladistically inclined zoologists used Archosaurs (crocodiles, dinosaurs, and birds), Lepidosaurs (snakes, lizards), and Testudines (turtles and tortoises) Up from the Sea o Leaving water for dry land (very different) o Water is alma mater of all life o Devonian and early Carboniferous Eusthenopteron, surface hunting fish, probably never came to land; Ichthyostega, mostly in water, made occasional forays on to the land (looked like giant salamander; Acanthostega, flat amphibian skull, eight digits, largely a water dweller; Panderichthys, slightly more like an amphibian but if you saw it you would probably still call it a fish Left with a gap between Panderichtys (amphibian like fish) and Acanthosetga (fish like amphibian) Tiktaalik, crocodiles head on a salamanders trunk attached to a fish’s rear end and tail o Perfect missing link, splits the difference between fish and amphibian Chapter 7 – Missing Persons? Missing no Longer Darwin had no fossils, but correctly predicted that humans closet living ancestor was the gorillas and chimpanzees and bonobos and the place to look was Africa Predecessors looked in Asia o Eugene Dubois 1891 Found Pithecanthropus erectus (java man) Homo erectus Thought he found the “missing link” o Oldest know fossil outside of Africa; Georgia; “Georgian man’ 1.8 million years old Rather more primitive than the rest of the early refugees from Africa, who are all classified as Homo erectus Possible theoretical candidates for missing links o Intermediate brain size and intermediate gait; perhaps a sort to stooping shamble rather than the proudly erect bearing favored by sergeant majors and deportment mistresses o Chimpanzee sized brain with human upright gait o Large, more human-like brain, walking on all fours like a chimp I’m still michievoulsly hoping o Common ancestor with chimps expected to have lived about 6 million years ago o Split the difference (human evolution tree) Lucy – Australopithecus afarensis (3 million yrs ago) Walked upright but probably also sought refuge in trees; good climber Small cranium similar to chimp size Taung Child/Mrs. Ples – Australopithecus africanus (2.5 million yrs ago) Eaten by eagle Bigger Homo habilis Forward pointing muzzle Been placed in Australopithecus and Homo genuius Brain volume: 400 cc Homo habilis (2 million years ago) Brain volume: 600 cc Homo Ergaster/Erectus (Java Man/ Peking Man) Brain volume: 1,000 cc Links between Ergaster/Erectus and Sapiens Heidelbergensis, rhodesiensis and neanderthalensis Homo Sapiens Modern Homo Sapiens vs. Brain volume: 1,300 to 1,400 cc o Previous 3 million years (from upright ancestor: before lucy) Orrorin (Millennium Man) Sahelanthropus (Toumai) – 6 mya Found of the Rift Valley Close in age to common ancestor of chimpanzees Ardipithecus (4-5 million years ago) o Drawing the line between Australopithecus and Homo Can be difficult / where do you draw the line o Ancestor of 3 million years ago walked upright but still had a brain the size of a chimpanzee First 3 million years: evolution of walking upright Last 3 million years: evolution of brain size increase Resemblance of chimpanzees at birth illustrate the interesting idea that in human evolution juvenile characteristics were retained into adulthood o Lang’s photos of infant and adult chimpanzees o Focus on head only, posture of infant not valid o Great deal of evolutionary change consists of changes in the rate at which different body parts grow relative to other parts (heterochronic) Chapter 8 –You Did It Yourself in Nine Months (Nov. 1) How embryology works Key point is that there is no choreographer and no leader; Order, organization, structure all emerge as by-products of rules which are obeyed locally and many times over, not globally Flocking behavior of starlings (picture page 16) Modeling Cells like Starlings o Oster’s model of blastula gastrulating Kept in mind that the beginning of embryo activity is simple and can be simulated on computer programming o Sperry transplant of skin from tapdoles back to belly and from belly to back Adult frog had light skin on back and dark skin patch on belly Axons connected as if attached to normal place; tickled the back side it would scratch its belly Postulated idea of chemo-affinity Nervous system wires itself up not by following an overall blueprint but by each individual axon seeking out end organs to which it has a particular chemical affinity Enzymes o The right enzyme achieves its rightness largely through its physical shape (and that’s important, because the physical shape is determined by genes, and it is genes whose variations are ultimately favored or disfavored by natural selection o The whole corse of embryonic development is controlled via an intricate sequence of events, by genes o Dealing with local self-assembly processes all the way Then Worms Shall Try o Whether gene is turned on or not at a given time is determined, by switch genes or controller genes, by the chemical environment of the cell. o A gene that tends, on average, to have a good effect on the survival prospects of the bodies in which it finds itself will tend to increase in frequency in the gene pool Chapter 9 – The Ark of the Continents How new species are born o Any two species are descended from an ancestral species which split into two o Example in book – hypothetical Protamnio darwinii (lizard like creature catching insects) Cannot diverge if the population keep interbreeding / something has to cut off interbreeding (valley, mountain range, river, etc.-created a separate island) Speciation – splitting of a species into two daughter species Protamnio darwinii split with Protamnio saurops, one gave rise to all modern mammals and the other reptiles One Might Really Fancy o How do two populations of a species find themselves on opposite sides of a geographical barrier? Earthquake opens up a impassable gorge Iguana iguana on island of Anguilla, actually seen arriving; floating on driftwood and uprooted trees from Guadeloupe o Galapagos Islands Marine vs. Land iguanas Marine only found in Galapagos very unique adaptations Darwins finches Evolved different beaks for different food on different islands Tortoises –evolved from mainland turtle Distinctive shell shapes on different islands Larger islands had higher domes (high grasses, browers), smaller islands have saddle –shaped shells with a high-lipped window at the front of head (browsing on cactuses) o Cichlids in Africa Even in same lake, species get isolated and evolve differently Did the Earth Move o Wegener and theory of continental drift, known today as continental drift On how Africa fit together so well with South America, N.A. and Europe Distribution of fossils o About 250 mya – all continents were together, formed Pangea Due to seafloor spreading, move apart; subduction o Evidence for Seafloor spreading Dating rock on both sides of mid Atlantic drift As you get farther away from ridge on either side (they mirror each other) older the rock is Reverse magnetic fields throughout earth’s history Chapter 10 – The Tree of Cousinship (Nov. 5) Bone to his Bone o Everything is a cousin of something else o For example: all mammals share the same bone structure; bats have a elongated phalanges; suppression and elongation of certain bones in the mammals defines it; human skull and horse skull No Borrowing o If feathers are a good idea within the bird ‘theme’, such that every single bird ,without exception has them whether it flies or not, why do no mammals have them? All birds have inherited their feathers from their shard ancestor, which had feather. No mammal is descended from that ancestor o The sexual shuffling of the genes in a gen pool could be regarded as a kind of borrowing or sharing of genetic ideas – remained within species Bacteria – borrowing ideas is indeed one of the main ways by which bacteria pick up useful tricks such as resistance to particular antibiotics What would D’Arcy Thompson have done with a computer? o Scottish zoologist Drew an animal on graph paper, and then he would distort the graph paper in a mathematically specifiable way and show that the form of the original animal had turned into another, related animal Five species of crab – mathematical distortions Important point – mutations selected would have worked in the developing embryo by changing the rate of growth of parts of the body relative to other parts Comparative evidence has always suggested, told even more compellingly than fossil evidence in favor of the fact of evolution Molecular Comparisons o Want to work out how closely related any pair of species is Look at the complete molecular texts of every gene of both species Not economically feasible so you compare strains of DNA and project those values across the entire sequence Compare the DNA melting points Two strongly bonded DNA strands have the highest melting point Say a human strand bonded to chimpanzee strand, slightly lower Human strand to frog strand, even lower o Complete tree of species David Hills, brother of Dan Hillis who pioneered one of first supercomputers The Hillis plot makes the tree diagram more compact by wrapping it around in a circle. P.329 Molecular Clock o Assumes that evolution is tree and positive mutation rate is constant on average o When you do stop saying a mutation is a mutation, when its in 50% of the gene pool, if positive it will eventually be in 100% of population Chapter 11 – History Written All Over Us (Nov. 10) Intro o Hair erection machinery in land mammals (hair raising in gorillas, goose bumps in humans, when scared or threatened.) o Dolphins Lungs not gills Blow hole is on top of head Give birth to live babies Placenta is mammalian/ young suckle for milk Brain is mammalian/increased surface area with folds and fissures (unique to mammals) Constant body temperature/warm-blooded Once Proud Wings o Ostriches and emus are fast runner that never fly, but they have stubs of wings as a legacy from remote flying ancestors o Numerous groups of insects,too, have lost their wings Diptera have only two wings, the second pair of wings has become reduced to a pair of halters Worker ants have lost their wings but not the capacity to grow wings. We know this because queen ants (and males) have wings and workers are females who could have been queens but who, for environmental, not genetic reasons failed to become queens Lost Eyes o Cave salamander lives in perpetual darkness so has no use for eyes Over time lose ability to see but have not completely lost eyes (much reduced,etc.) Unintelligent Design o Pattern of major design flaws, compensated for by subsequent tinkering is exactly what we should not expect if there really were a designer at work Giraffes and laryngeal nerve As the giraffes neck slowly lengthened over evolutionary time, the cost of the detour gradually increased. The marginal cost of each millimeter of increases was slight. As the giraffes neck began to approach its present impressive length, the total cost of the detour might have begun to approach the point where hypothetically a mutant individual would survive better if its decending laryngeal nerve fibers hived themselves off from the vagus bundle and hopped across the tiny gap to the larynx Humans and walking upright and sinuses Chapter 12-Arms Races and Evolutionary Theodicy The Solar Economy o Tree height o Trees at top of canopy receive more light, waste energy to become tall; benefit outweighs the cost of growing tall Running to Stay in the Same Place o The five fastest runners among mammal species are cheetah, pronghorn, wildebeest, lion, Thomson’s gazelle Predator vs. prey arms race o Gazelle slower but jinks and more endurance where cheetahs are very fast short sprinters but lose stamina fast Evolutionary Theodicy? o A beneficent designer might you’d idealistically think to minimize suffering. Doesn’t happen in nature o Predators and parasites induce much suffering o Icheneumon wasps paralyze their victim, then lay an egg in it with the promise of a larva gnawing it hollow from within Chapter 13 – There is Grandeur in this view of life Thus from the war of nature, from famine and death, the most exalted object which we are capable of conceiving, namely, the production of the higher animals, directly follows. There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being evolved. - Darwin