* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Notes - Madeira City Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
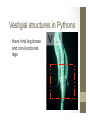
What is Evolution? • Evolution: • Process by which populations change over time What are these changes? • Evolutionary changes in the sex cells result in the organism changing in structure, function, and behavior over time • A change in the DNA Genetic Variation eventually leads to changes in a species • In sexually reproducing species: Variation is found in the genes of sex cells and passed on to its offspring • Mutations of genes • Random chance events • New combinations of genes during fertilization Evidence of a Common Ancestor in Evolution Fossil Record • Background • Earth is approximately 4.5 billion years old • Organisms started as single-celled and eventually evolved to multi-celled organisms How do we determine the age of fossils? 1.Relative dating (Law of Superposition) • Oldest fossils are found on the lowest layer • Newest fossils found on the top layer How do we determine the age of fossils? 2. Radioactive Carbon Dating • Certain elements have unstable isotopes • Nuclei of these elements breakdown or radioactively decay • Rate of radioactive decay is fixed and is unchangeable • Half-life is the time required for ½ of the atoms of an isotope to decay • Ex. Carbon 14-half life=5,730 years Other evidence found in living species of a common ancestor • Comparative embryology-closely related patterns of embryo development • Similarities in development show evidence of a common ancestor • Gill slits • Tail • 2-chambered heart Other evidence found in living species of a common ancestor • Comparative Anatomy • A. homologous structures-similar structures but different functions • Similarities: same number of bones and arranged in a similar way, embyrologically developed the same • Differences: • Human hand=grasping function • Whale flipper=swimming function • Bat or Bird wing-flying function Evidence for Evolution – Comparative Anatomy • A. Homologous structures: similar structures but different functions Evidence for Evolution – Comparative Anatomy B. Analogous structures: Similar functions, but different internal structures Example: Similarities: Birds and insects wings both are used for flying Differences: internal structures and embryo development are very different Evidence for Evolution – Comparative Anatomy • C. Vestigial structures – remnants of structures that were once functional in an ancestor • now-reduced in size and serve little or no function Vestigial structures in Pythons • Have hind leg bones and non-functional legs Examples: • • • • Tail bone: (coccyx) remnant of a reptilian tail Wisdom teeth Muscles that move nose and ears Whales and snakes have hind leg bones imbedded in their bodies from four legged ancestors • Molecular similarities-genetic DNA code and proteins Modern Theory of Evolution • Evolution happens to populations, not individuals. • Evolution is a change in the allele frequency within a population over time. • When the frequency of certain genes in the gene pool change, then the population changes or evolves.