* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems: Components, Energy Flow, and Matter - RHS-APES
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
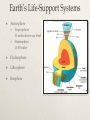
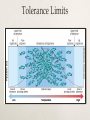
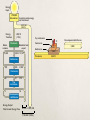
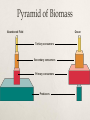
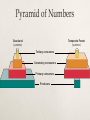
What is Ecology? How organisms interact with one another and with their nonliving environment Study of CONNECTIONS What are Organisms? Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Ecological Organization •Individual •Species are groups of organisms that resemble one another •Populations •Group of interacting individuals of the same species •Communities •Populations of different species occupying the same place •Ecosystems •Community environment interacting with one another and nonliving •Biomes •Regions made up of ecosystems •Biosphere •Zone of earth where life is found Fig. 4-2 p. 66 Earth’s Life-Support Systems Atmosphere Troposphere 11 miles above sea level Stratosphere 11-30 miles Hydrosphere Lithosphere Biosphere Sustaining Life on Earth THE Source of Energy Greenhouse Effect Not the same thing as global warming! Unreflected solar radiation degraded to infrared radiation Greenhouse gases reduce heat flow back to space What are some greenhouse gases? Abiotic Components Nonliving, physical and chemical factors that influence organisms in land ecosystems and aquatic life zones Terrestrial Ecosystem Aquatic Life Zone Law of Tolerance Presence of a species determined by abiotic factors falling within the range of tolerance Individuals in a population may have slightly different tolerance ranges because of genetic differences, health, age Tolerance Limits Limiting Factors Limiting Factor Principle: Too much OR too little of any abiotic factor can limit/prevent growth, even if all other factors are at or near optimum range Terrestrial Ecosystem Aquatic Life Zone Biotic Components Living organisms in land ecosystems and aquatic life zones, producers or consumers Producers (autotrophs) chemosynthesis photosynthesis Biotic Components Consumer Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Scavenger Examples Biotic Components Detritivores: feed on parts of dead organisms, cast-off fragments, and wastes of living organisms Using Energy Aerobic Respiration Use oxygen to convert organic nutrients back into carbon dioxide and water Anaerobic Respiration Break down glucose without oxygen End products vary Biodiversity Genetic Diversity Functional Diversity Species Diversity Biodiversity Ecological Diversity Ecotone Trophic Levels Human Blue whale Sperm whale Killer whale Crabeater seal Leopard seal Emperor penguin Adélie penguins Petrel Squid Fish Carnivorous plankton Herbivorous zooplankton Krill Phytoplankton Food Webs Elephant seal Biomass Each trophic level contains a certain amount of organic matter which is transferred from one trophic level to another First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Ecological Efficiency Energy Input: 1,700,000 kilocalories Incoming solar energy not harnessed 1,679,190 (98.8%) Energy Transfers 20,810 (1.2%) Top carnivores 21 Waste, remains Producers 4,245 Metabolic heat, export 3,368 13,197 Herbivores 720 383 2,265 Carnivores 90 21 Top carnivores 5 272 16 Decomposers, detritivores Energy Output Total Annual Energy Flow 20,810 + 1,679,190 1,700,000 (100%) Decomposers/detritivores Carnivores Herbivores 383 3,368 Producers 20,810 5,060 Pyramid of Biomass Abandoned Field Ocean Tertiary consumers Secondary consumers Primary consumers Producers Pyramid of Numbers Grassland (summer) Temperate Forest (summer) Tertiary consumers Secondary consumers Primary consumers Producers Primary Productivity Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) Primary Productivity Net Primary Productivity (NPP) 1. Explain why food chains are typically short 2. Make an argument for vegetarianism based on the second law of thermodynamics