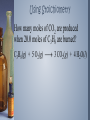* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Limiting reactant - Dr. Gregory Chemistry
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Depletion force wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Aerosol mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Measuring Matter Moles and Avogadro’s Number The Mole › A mole (mol) a measure of the amount of a substance. › The value of a mole is 6.02 x 1023 particles. This is also called Avogadro’s number. › Particles can be atoms, molecules, ions, formula units. › Equality: 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles Conversion Factors ›Each equality can be written as 2 conversion factors. ›Equality: 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles ›Conversion factors: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 6.02 𝑥 1023 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒𝑠 and 6.02 𝑥 1023 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒𝑠 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 Converting Between Particles and Moles ›A sample contains 8.3 x 1024 atoms of silver. How many moles is this? The Mass of a Mole › Molar mass is the mass (in grams) of one mole of substance. This is the mass on the periodic table. › Example. 1 mole of carbon atoms: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐶 𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑠 = 12.01 𝑔 𝐶 Conversion factors: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐶 𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑠 12.01 𝑔 𝐶 and 12.01 𝑔 𝐶 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝐶 𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑠 The Mass of a Mole › If the substance is a molecule or ionic compound, the molar mass of the compound must be calculated. Example: What mass of CH4 (methane) is contained in 8.12 moles of methane? Converting Between Grams and Moles ›A chunk of aluminum has a mass of 274 grams. How many moles of aluminum are in the sample? Converting Between Grams and Moles ›What mass of methane (CH4) is contained in 7.51 x 1025 molecules of methane? Converting Between Grams and Moles ›How many molecules of oxygen are contained in a 214 grams sample of water? Calculating Empirical Formula given % composition ›Steps 1. Change % to grams 2. Convert grams to moles 3. Divide all moles by the smallest mole 4. Write empirical formula Calculating Empirical Formula given % composition ›Practice Calculating Molecular Formula given Molecular Mass ›Steps Constant = 𝑀𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐸𝑚𝑝𝑖𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 (Empirical formula)constant = molecular formula Calculating Molecular Formula given Molecular Mass ›Practice Stoichiometry Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships between the amounts of reactants used and amounts of products formed in a chemical reaction. It is based on the law of conservation of mass. Stoichiometry Stoichiometric ratios can be used to determine how much product will form or how much reactant will be used in a chemical reaction. Using Stoichiometry Stoichiometric ratios can be formed for chemical reactions as shown below. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 Fe2O3(s) 4 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐹𝑒 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑂2 or 4 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐹𝑒 2 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐹𝑒2𝑂3 or 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑂2 2 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐹𝑒2𝑂3 Using Stoichiometry How many moles of CO2 are produced when 20.0 moles of C3H8 are burned? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) Using Stoichiometry How many moles of O2 are needed to completely react with 10.0 moles of C3H8? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) Using Stoichiometry How many moles of H2O are produced when 95.0 g of C3H8 are burned? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) Using Stoichiometry How many grams of CO2 are produced when 73.0 g of C3H8 are burned? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) Limiting Reactant Limiting reactant is the reactant that “runs out” in a chemical reaction; it also determines the amount of product formed. Reactant left over at the end of a chemical reaction is called the excess reactant. The amount of product formed when the limiting reactant is used up is called theoretical yield. Determining Limiting Reactant If 200.0 g sulfur reacts with 100.0 g chlorine, what is the limiting reactant? S8(l) + 4 Cl2(g) 4 S2Cl2(l)