4º ESO. Física y Química. Apuntes bilingües
... Plus sign (+) is for MRUA and minus sign (-) is for MRUR. In the previous formulas, the acceleration must be always positive, even in the case of a MRUR, which has a negative acceleration. You cannot have two consecutive minus signs: - - . Example: an object is moving from 50 km/h to 70 km/h in 5 s ...
... Plus sign (+) is for MRUA and minus sign (-) is for MRUR. In the previous formulas, the acceleration must be always positive, even in the case of a MRUR, which has a negative acceleration. You cannot have two consecutive minus signs: - - . Example: an object is moving from 50 km/h to 70 km/h in 5 s ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... ____ 89. After the correct formula for a reactant in an equation has been written, the a. subscripts are adjusted to balance the equation. b. formula should not be changed. c. same formula must appear as the product. d. symbols in the formula must not appear on the product side of the equation. ___ ...
... ____ 89. After the correct formula for a reactant in an equation has been written, the a. subscripts are adjusted to balance the equation. b. formula should not be changed. c. same formula must appear as the product. d. symbols in the formula must not appear on the product side of the equation. ___ ...
preview as pdf
... products and excess fluid from the body. They also reabsorb electrolytes such as potassium and produce hormones that regulate blood pressure and calcium blood levels. Diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure can cause a decrease in kidney function. Symptoms of kidney malfunction include pro ...
... products and excess fluid from the body. They also reabsorb electrolytes such as potassium and produce hormones that regulate blood pressure and calcium blood levels. Diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure can cause a decrease in kidney function. Symptoms of kidney malfunction include pro ...
MEDICAL CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE
... lab because they interfere with your ability to hear what is going on in the Lab. 5 Fire: In case of fire or an accident, inform your instructor at once. Note the location of fire extinguishers and, if available, safety showers and safety blankets as soon as you enter the laboratory so that you may ...
... lab because they interfere with your ability to hear what is going on in the Lab. 5 Fire: In case of fire or an accident, inform your instructor at once. Note the location of fire extinguishers and, if available, safety showers and safety blankets as soon as you enter the laboratory so that you may ...
Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... Students often have difficulty grasping the meaning of incomplete reactions. This discussion shows the practical economic, as well as scientific ramifications of reactions that have low yields. ...
... Students often have difficulty grasping the meaning of incomplete reactions. This discussion shows the practical economic, as well as scientific ramifications of reactions that have low yields. ...
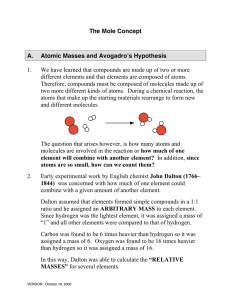
The Mole Concept A. Atomic Masses and Avogadro`s Hypothesis 1
... The CONCENTRATION of a substance in solution provides a way to find how much of the substance exists in a given volume of the solution. Chemists use the “mole” to describe the amount of substance in a solution. MOLAR CONCENTRATION or MOLARITY of a substance is the number of moles of the substance co ...
... The CONCENTRATION of a substance in solution provides a way to find how much of the substance exists in a given volume of the solution. Chemists use the “mole” to describe the amount of substance in a solution. MOLAR CONCENTRATION or MOLARITY of a substance is the number of moles of the substance co ...
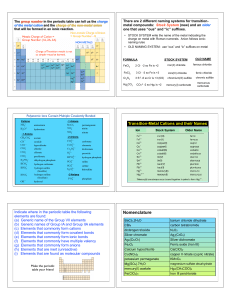
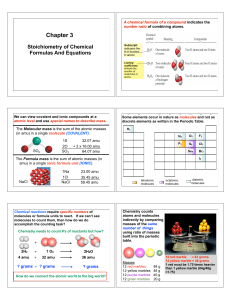
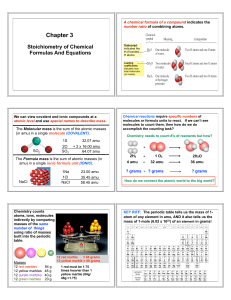
Chapter 3 2013
... What’s In A Chemical Formula? Urea, (NH2)2CO, is a nitrogen containing compound used as a fertilizer around the globe? Calculate the following for 25.6 g of urea: a) the molar mass of urea? b) the number of moles of urea in 25.6 g urea? b) # of molecules of urea in 25.6 g of urea? c) # hydrogen ato ...
... What’s In A Chemical Formula? Urea, (NH2)2CO, is a nitrogen containing compound used as a fertilizer around the globe? Calculate the following for 25.6 g of urea: a) the molar mass of urea? b) the number of moles of urea in 25.6 g urea? b) # of molecules of urea in 25.6 g of urea? c) # hydrogen ato ...
Experimental Chemistry I
... 1. pipet 100mL of Standardized Acid into a 1000mL volumetric flask; 2. add deionized water until the 1000mL mark is reached; 3. store the diluted reference acid in a tightly locked 1L plastic container; 4. label container with concentration (c ≈ 0.1mol/L or 0.1M), date, group, etc.; 5. repeated proc ...
... 1. pipet 100mL of Standardized Acid into a 1000mL volumetric flask; 2. add deionized water until the 1000mL mark is reached; 3. store the diluted reference acid in a tightly locked 1L plastic container; 4. label container with concentration (c ≈ 0.1mol/L or 0.1M), date, group, etc.; 5. repeated proc ...
IIT-JEE - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Q.16 The density of KBr is 2.75 g cm–3 . The length of the edge of the unit cell is 654 pm. Show that KBr has face centered cubic structure. (N = 6.023 ×1023 mol–1 , At. mass : K = 39, Br = 80) Q.17 An element crystallizes in a structure having FCC unit cell of an edge 200 pm. Calculate the density, ...
... Q.16 The density of KBr is 2.75 g cm–3 . The length of the edge of the unit cell is 654 pm. Show that KBr has face centered cubic structure. (N = 6.023 ×1023 mol–1 , At. mass : K = 39, Br = 80) Q.17 An element crystallizes in a structure having FCC unit cell of an edge 200 pm. Calculate the density, ...
Chapter 3 Sem 2 2013-14
... Think of the mole as a counting unit for a collection of: 6.02 x 1023 things---unlike all other counting numbers it is also linked to masses given in the ...
... Think of the mole as a counting unit for a collection of: 6.02 x 1023 things---unlike all other counting numbers it is also linked to masses given in the ...
Solutions for Chapter 8 End-of-Chapter Problems
... Solutions for Chapter 8 End-of-Chapter Problems Problem 8.1. (a) Ice cream melting will decrease the organization of the system. Rather than being in identifiable scoops of ice cream perched securely on a cone, there now will be liquid ice cream dripping on the outside of the cone, onto your hands, ...
... Solutions for Chapter 8 End-of-Chapter Problems Problem 8.1. (a) Ice cream melting will decrease the organization of the system. Rather than being in identifiable scoops of ice cream perched securely on a cone, there now will be liquid ice cream dripping on the outside of the cone, onto your hands, ...
The Mole - Bakersfield College
... 23.72% sulfur, and 47.35% oxygen. The experimental molar mass of 270.0 g/mol. What are the empirical and molecular formulas of potassium persulfate? To find the molecular formula: Calculate the MM of KSO4 = (1 mol K x 39.10 g/mol K) + (1 mol S x 32.07 g/mol S) + (4 mol O x 16.00 g/mol O) = 135.17 g/ ...
... 23.72% sulfur, and 47.35% oxygen. The experimental molar mass of 270.0 g/mol. What are the empirical and molecular formulas of potassium persulfate? To find the molecular formula: Calculate the MM of KSO4 = (1 mol K x 39.10 g/mol K) + (1 mol S x 32.07 g/mol S) + (4 mol O x 16.00 g/mol O) = 135.17 g/ ...
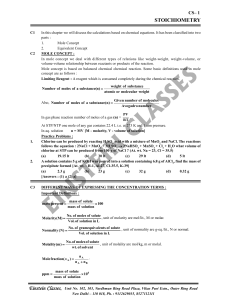
stoichiometry - einstein classes
... EQUIVALENT CONCEPT It is based on law of equivalence which is explained as follows : Law of chemical equivalents : In a chemical reaction the equivalents of all the species (reactants or products) are equal to each other provided none of these compounds is in excess. N1V1 = N2V2 (when normalities an ...
... EQUIVALENT CONCEPT It is based on law of equivalence which is explained as follows : Law of chemical equivalents : In a chemical reaction the equivalents of all the species (reactants or products) are equal to each other provided none of these compounds is in excess. N1V1 = N2V2 (when normalities an ...
Chemistry_Stoichiome..
... 82. How many millilitres of 0.1 M H2SO4 must be added to 50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH to give a solution that has a concentration of 0.05 M in H2SO4? a) 400 mL b) 200 mL c) 100 mL d) None of these 83. 1 M HCl and 2 M HCl are mixed in volume ratio of 4 : 1. What is the final molarity of HCl solution? a) 1.5 b ...
... 82. How many millilitres of 0.1 M H2SO4 must be added to 50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH to give a solution that has a concentration of 0.05 M in H2SO4? a) 400 mL b) 200 mL c) 100 mL d) None of these 83. 1 M HCl and 2 M HCl are mixed in volume ratio of 4 : 1. What is the final molarity of HCl solution? a) 1.5 b ...
File
... substance you have, you can find its total mass using the molar mass of that substance. Ex: What is the mass of 2.42 mol of H2O? ...
... substance you have, you can find its total mass using the molar mass of that substance. Ex: What is the mass of 2.42 mol of H2O? ...
Module 2
... these particles. The disorder in a system depends only on the conditions that determine the state of the system, such as composition, temperature, and pressure. The change in entropy therefore depends only on the initial and final states of the system. Entropy, like enthalpy is a state function. Def ...
... these particles. The disorder in a system depends only on the conditions that determine the state of the system, such as composition, temperature, and pressure. The change in entropy therefore depends only on the initial and final states of the system. Entropy, like enthalpy is a state function. Def ...
Supplemental information
... Figure: 9 S1 Characterization of the modified HFO nanoparticles Figure s1 demonstrates the physical stability and settleability of HFO nanoparticles prepared at a particle concentration of 100 mg·L-1 as Fe but with various concentration of CMC ranging from 0 to 0.161 wt %. Based on the results, this ...
... Figure: 9 S1 Characterization of the modified HFO nanoparticles Figure s1 demonstrates the physical stability and settleability of HFO nanoparticles prepared at a particle concentration of 100 mg·L-1 as Fe but with various concentration of CMC ranging from 0 to 0.161 wt %. Based on the results, this ...
solliqsol - chemmybear.com
... (a) greater: Zn(OH)2(s) + 2 H+ Zn2+ + 2 H2O (b) lower: increased [Zn2+] decreases [OH-] and decreases the amount of Zn(OH)2 in solution. Ksp =[Zn2+][OH-]2 (c) greater: Zn(OH)2(s) + 2 OH- Zn(OH)42- (Can also site common ion effect) (d) greater: Zn(OH)2(s) + 4 NH3 Zn(NH3)42+ + OH1977 D The state ...
... (a) greater: Zn(OH)2(s) + 2 H+ Zn2+ + 2 H2O (b) lower: increased [Zn2+] decreases [OH-] and decreases the amount of Zn(OH)2 in solution. Ksp =[Zn2+][OH-]2 (c) greater: Zn(OH)2(s) + 2 OH- Zn(OH)42- (Can also site common ion effect) (d) greater: Zn(OH)2(s) + 4 NH3 Zn(NH3)42+ + OH1977 D The state ...
Structural determination of organic compounds
... To separate an insoluble solid from a liquid (fast) To separate a solid from other solids based on their different solubilities in suitable solvent(s) To separate a component from a mixture with a suitable solvent ...
... To separate an insoluble solid from a liquid (fast) To separate a solid from other solids based on their different solubilities in suitable solvent(s) To separate a component from a mixture with a suitable solvent ...
Calculation of the mass of material in a given number of moles of at
... 8 Fe 20.14%; S 11.51%; O 63.31%; H 5.04% 9 When 14.97 g of hydrated copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4.xH2O, is heated it produces 9.60 g of anhydrous copper(II) sulfate. What is the formula of the ...
... 8 Fe 20.14%; S 11.51%; O 63.31%; H 5.04% 9 When 14.97 g of hydrated copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4.xH2O, is heated it produces 9.60 g of anhydrous copper(II) sulfate. What is the formula of the ...
File
... 2. How many moles of H2SO4 are in 20 mL of a10M solution? 3. How many liters of HCl are there if you have a 2M solution and .15 moles of solute? ...
... 2. How many moles of H2SO4 are in 20 mL of a10M solution? 3. How many liters of HCl are there if you have a 2M solution and .15 moles of solute? ...
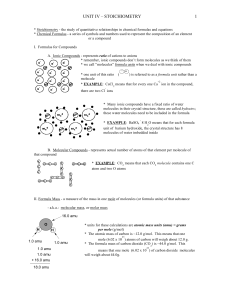
unit iv – stoichiometry 1
... XIII. Redox Titrations – the equivalence point is determined when the oxidizing agent is completely reduced * MnO4- is good for this because it is deep purple, and when reduced to Mn+2, it shows colorless to light pink T. 1) A 16.42 mL volume of 0.1327 M KMnO4 solution is needed to oxidize 20.00 mL ...
... XIII. Redox Titrations – the equivalence point is determined when the oxidizing agent is completely reduced * MnO4- is good for this because it is deep purple, and when reduced to Mn+2, it shows colorless to light pink T. 1) A 16.42 mL volume of 0.1327 M KMnO4 solution is needed to oxidize 20.00 mL ...
Answer
... • In the spaces provided, explain the meanings of the following terms. You may use an equation or diagram where appropriate. (a) hydrogen bonding An unusually strong dipole-dipole interaction that forms when a hydrogen atom is bonded to one of the very electronegative atoms F, O or N. ...
... • In the spaces provided, explain the meanings of the following terms. You may use an equation or diagram where appropriate. (a) hydrogen bonding An unusually strong dipole-dipole interaction that forms when a hydrogen atom is bonded to one of the very electronegative atoms F, O or N. ...
Chemistry
... 1. If 495g of NaOH is dissolved to a final total volume of 20.0 L, what is the molarity of the solution? 2. How many moles of the indicated solute does each of the following solutions contain? a) 2.50 L of 13.1 M HCl b) 15.6 mL of 0.155 M NaOH 3. What mass of the indicated solute does each of the fo ...
... 1. If 495g of NaOH is dissolved to a final total volume of 20.0 L, what is the molarity of the solution? 2. How many moles of the indicated solute does each of the following solutions contain? a) 2.50 L of 13.1 M HCl b) 15.6 mL of 0.155 M NaOH 3. What mass of the indicated solute does each of the fo ...