Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... This law states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only change from one form to another. - According to this Law: during any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants or starting materials must equal the mass of the products. - According to this Law :because atoms are ...
... This law states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only change from one form to another. - According to this Law: during any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants or starting materials must equal the mass of the products. - According to this Law :because atoms are ...
LECTURE_pptnotes Fipps Stochiometry
... C5H10O2 (5x12) + (10x1) + (2x16) = 102 g/mol Empirical mass = molecular mass, so molecular formula is the same C5H10O2 ...
... C5H10O2 (5x12) + (10x1) + (2x16) = 102 g/mol Empirical mass = molecular mass, so molecular formula is the same C5H10O2 ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure
... Application of the state symbols (s), (l), (g), and (aq) in equations. *Understandings 1-3, Application 3 were covered in Unit 1 ...
... Application of the state symbols (s), (l), (g), and (aq) in equations. *Understandings 1-3, Application 3 were covered in Unit 1 ...
sample problem - KFUPM Resources
... More practical aspect of Gibb’s free energy • The standard free energy (ΔGrxn) of a system is the change in free energy when reactants in their standard states are converted to products in their standard states. • Standard states are: ...
... More practical aspect of Gibb’s free energy • The standard free energy (ΔGrxn) of a system is the change in free energy when reactants in their standard states are converted to products in their standard states. • Standard states are: ...
diffuse-interface field approach to modeling self
... (a) Schematic of a capillary bridge between two solid spheres. (b) The Laplace pressure (negative) inside a capillary bridge is a monotonically increasing function of capillary bridge volume V cb . (c) Analogy between Laplace pressure stabilizing meniscus size through inter-liquid diffusion (bottom) ...
... (a) Schematic of a capillary bridge between two solid spheres. (b) The Laplace pressure (negative) inside a capillary bridge is a monotonically increasing function of capillary bridge volume V cb . (c) Analogy between Laplace pressure stabilizing meniscus size through inter-liquid diffusion (bottom) ...
topic: chemical formula, chemical equations and stoichiometry
... The relative atomic mass of an element = Mass of 1 atom of the element 1/12 x mass of 1 atom of carbon-12 The relative molecular mass, RMM, of a compound is defined as, The number of times the mass of one molecule of a compound is heavier than 1/12 times the mass of one carbon-12 atom. The relative ...
... The relative atomic mass of an element = Mass of 1 atom of the element 1/12 x mass of 1 atom of carbon-12 The relative molecular mass, RMM, of a compound is defined as, The number of times the mass of one molecule of a compound is heavier than 1/12 times the mass of one carbon-12 atom. The relative ...
Measurements
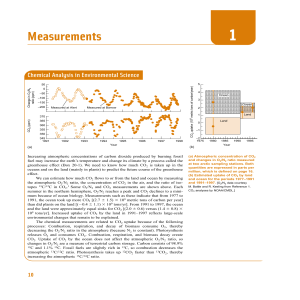
... large or small quantities. As an example, consider the pressure of ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere (Figure 1-1). Ozone is important because it absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun that damages many organisms and causes skin cancer. Each spring, a great deal of ozone disappears from the Anta ...
... large or small quantities. As an example, consider the pressure of ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere (Figure 1-1). Ozone is important because it absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun that damages many organisms and causes skin cancer. Each spring, a great deal of ozone disappears from the Anta ...
Structure and Properties of Polymers
... macromolecule, it can become a trifunctional branch point because three chains can emanate from it. Similarly, a monomer molecule containing two double bonds or four functional groups capable of condensation can give rise to a tetrafunctional branch point in a forming macromolecule because four chai ...
... macromolecule, it can become a trifunctional branch point because three chains can emanate from it. Similarly, a monomer molecule containing two double bonds or four functional groups capable of condensation can give rise to a tetrafunctional branch point in a forming macromolecule because four chai ...
AP Chemistry
... calculate moles of each reactant available calculate moles of one product based on moles of each reactant smallest = theoretical yield ...
... calculate moles of each reactant available calculate moles of one product based on moles of each reactant smallest = theoretical yield ...
UNIFORM PARTICLES WITH A LARGE SURFACE AREA FORMED
... Sh and “low sulfate” Sh, respectively). The low-sulfate schwertmannite was usually obtained at higher temperatures and at final pH ⬃ 5. According to Barham [7], Fe/S ratios as high as 25 to 50 could be reached by anionic exchange at pH ⬃ 7. As follows from the composition of sample A6, after heating ...
... Sh and “low sulfate” Sh, respectively). The low-sulfate schwertmannite was usually obtained at higher temperatures and at final pH ⬃ 5. According to Barham [7], Fe/S ratios as high as 25 to 50 could be reached by anionic exchange at pH ⬃ 7. As follows from the composition of sample A6, after heating ...
some basic concepts of chemistry
... (b) Chemical classification : Many of the substances present around you are mixtures. For example, sugar solution in water, air, tea etc., are all mixtures. A mixture contains two or more substances present in it (in any ratio) which are called its components. A mixture may be homogeneous or heterog ...
... (b) Chemical classification : Many of the substances present around you are mixtures. For example, sugar solution in water, air, tea etc., are all mixtures. A mixture contains two or more substances present in it (in any ratio) which are called its components. A mixture may be homogeneous or heterog ...
Estimate the strength of given sodium carbonate solution
... dilution to give a defined volume of solution. A primary standard solution must follow these conditions: Compound should be free from impurity. Compound should be completely soluble in dissolving solvent. Compound should not be hygroscopic. Solution formed should be stable and should not dec ...
... dilution to give a defined volume of solution. A primary standard solution must follow these conditions: Compound should be free from impurity. Compound should be completely soluble in dissolving solvent. Compound should not be hygroscopic. Solution formed should be stable and should not dec ...
Thiolated macromolecules and methods of making and using thereof
... [0001] This application claims the bene?t of US. Provi sional Application No. 60/806,965 ?led Jul. 11, 2006. ...
... [0001] This application claims the bene?t of US. Provi sional Application No. 60/806,965 ?led Jul. 11, 2006. ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry
... As particles are extremely small chemists measure amounts of substance using a quantity called the MOLE which stands for 6.02 x 1023 a number which is know as Avogadro’s constant. So 1 mole of a substance = 6.02 x 1023 units of that substance; these units can be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons or ...
... As particles are extremely small chemists measure amounts of substance using a quantity called the MOLE which stands for 6.02 x 1023 a number which is know as Avogadro’s constant. So 1 mole of a substance = 6.02 x 1023 units of that substance; these units can be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons or ...
Mole calculations File
... • Weigh 5 1 cm strips of magnesium ribbon • Place 5 pieces of magnesium ribbon in the ignition tube • EITHER: Fill a 100 cm3 measuring cylinder with water and place upside down in a plastic bowl 2/3rds full of water. Arrange an upward delivery tube to collect the hydrogen gas • OR: Attach a gas syri ...
... • Weigh 5 1 cm strips of magnesium ribbon • Place 5 pieces of magnesium ribbon in the ignition tube • EITHER: Fill a 100 cm3 measuring cylinder with water and place upside down in a plastic bowl 2/3rds full of water. Arrange an upward delivery tube to collect the hydrogen gas • OR: Attach a gas syri ...
SOLLIQSOL questions
... The formula and the molecular weight of an unknown hydrocarbon compound are to be determined by elemental analysis and the freezing-point depression method. (a) The hydrocarbon is found to contain 93.46 percent carbon and 6.54 percent hydrogen. Calculate the empirical formula of the unknown hydrocar ...
... The formula and the molecular weight of an unknown hydrocarbon compound are to be determined by elemental analysis and the freezing-point depression method. (a) The hydrocarbon is found to contain 93.46 percent carbon and 6.54 percent hydrogen. Calculate the empirical formula of the unknown hydrocar ...
mole concept type 1 - teko classes bhopal
... Q.13 A sample of calcium carbonate contains impurities which do not react with a mineral acid. When 2 grams of the sample were reacted with the mineral acid, 375 ml of carbon dioxide were obtained at 27°C and 760 mm pressure. Calculate the % purity of the sample of CaCO3? Q.14 One gram of an alloy o ...
... Q.13 A sample of calcium carbonate contains impurities which do not react with a mineral acid. When 2 grams of the sample were reacted with the mineral acid, 375 ml of carbon dioxide were obtained at 27°C and 760 mm pressure. Calculate the % purity of the sample of CaCO3? Q.14 One gram of an alloy o ...
الشريحة 1
... Processes that occur spontaneously involve two distinct factors. The most obvious factor is energy, which we have used to analyze the dissolving of NaCl in water. The other factor is the distribution of each component into a larger volume – the tendency in nature for substances to mix and spread out ...
... Processes that occur spontaneously involve two distinct factors. The most obvious factor is energy, which we have used to analyze the dissolving of NaCl in water. The other factor is the distribution of each component into a larger volume – the tendency in nature for substances to mix and spread out ...
stoichiometric relationships - Assets
... Ideal gases An ideal gas is used to model the behaviour of real gases.Two assumptions made when defining an ideal gas are that the molecules themselves have no volume and that no forces exist between them (except when they collide). Gases deviate most from ideal behaviour at high pressure and low te ...
... Ideal gases An ideal gas is used to model the behaviour of real gases.Two assumptions made when defining an ideal gas are that the molecules themselves have no volume and that no forces exist between them (except when they collide). Gases deviate most from ideal behaviour at high pressure and low te ...
Analytical Chemistry
... Calculate the molar concentration of Ag+ in a solution having a pAg of 6.372 . pAg = - log[Ag+] = 6.372 log[Ag+] = -6.372 = - 7.oo + 0.628 [Ag+] = antilog ( -7 ) * antilog ( 0.628) = 10-7*4.246 ...
... Calculate the molar concentration of Ag+ in a solution having a pAg of 6.372 . pAg = - log[Ag+] = 6.372 log[Ag+] = -6.372 = - 7.oo + 0.628 [Ag+] = antilog ( -7 ) * antilog ( 0.628) = 10-7*4.246 ...
Chapter 3 Lecture notes
... Specialized cells in the stomach release HCl to aid digestion. If they release too much, the excess can be neutralized with antacids. A common antacid contains magnesium hydroxide, which reacts with the acid to form water and magnesium chloride solution. As a government chemist testing commercial an ...
... Specialized cells in the stomach release HCl to aid digestion. If they release too much, the excess can be neutralized with antacids. A common antacid contains magnesium hydroxide, which reacts with the acid to form water and magnesium chloride solution. As a government chemist testing commercial an ...
FM 10-67-2 Chapter 7
... Indicators are dyes that change color or shade of color when the pH (degree of acidity or alkalinity) of a solution changes. Therefore, they can be used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions of acids and bases. They are also used in volumetric analysis to mark the end point of ...
... Indicators are dyes that change color or shade of color when the pH (degree of acidity or alkalinity) of a solution changes. Therefore, they can be used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions of acids and bases. They are also used in volumetric analysis to mark the end point of ...
Exam No. 1
... **(a) Bonds broken are stronger than bonds formed. (b) Bonds broken are weaker than bonds formed. (c) Bonds broken are of equal strength to bonds formed (d) ∆Hreaction value has nothing to do with bond energies. 66- What equation must be used to represent the formation of nitric acid, HNO3(ℓ), when ...
... **(a) Bonds broken are stronger than bonds formed. (b) Bonds broken are weaker than bonds formed. (c) Bonds broken are of equal strength to bonds formed (d) ∆Hreaction value has nothing to do with bond energies. 66- What equation must be used to represent the formation of nitric acid, HNO3(ℓ), when ...
Ch 12 Solutions
... One example would be a protein is dispersed in water, where both components have H-bonding. The colloid is stable because the protein molecules have greater attractive forces towards each other than they do towards the water molecules. - Hydrophobic is a lack of attraction between phases. One exampl ...
... One example would be a protein is dispersed in water, where both components have H-bonding. The colloid is stable because the protein molecules have greater attractive forces towards each other than they do towards the water molecules. - Hydrophobic is a lack of attraction between phases. One exampl ...
1 Quantitative chemistry - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... 1.2.5 Determine the empirical formula from the percentage composition or from other experimental data. 1.2.6 Determine the molecular formula when given both the empirical formula and experimental data. ...
... 1.2.5 Determine the empirical formula from the percentage composition or from other experimental data. 1.2.6 Determine the molecular formula when given both the empirical formula and experimental data. ...