File - Evergreen Tutor Zone
... If the gas is at STP then you can use molar gas volume of 22,4 dm3 to find the volume of the gas. If this problem had been at STP then: 1 mole of H2 at STP occupies 22,4 dm3 ...
... If the gas is at STP then you can use molar gas volume of 22,4 dm3 to find the volume of the gas. If this problem had been at STP then: 1 mole of H2 at STP occupies 22,4 dm3 ...
Powerpoint notes
... for counting accurately the number of atoms, molecules, or formula units in a sample of a substance. • As you know, atoms and molecules are extremely small. There are so many of them in even the smallest sample that it’s impossible to actually count them. • That’s why chemists created their own coun ...
... for counting accurately the number of atoms, molecules, or formula units in a sample of a substance. • As you know, atoms and molecules are extremely small. There are so many of them in even the smallest sample that it’s impossible to actually count them. • That’s why chemists created their own coun ...
MOS (metal-oxide- semiconductor)
... These charges can be created, for example, by X-ray radiation or high – energy electron bombardment the trap are distributed inside the oxide layer. Most of process-related oxidetrapped charge can be removed by ...
... These charges can be created, for example, by X-ray radiation or high – energy electron bombardment the trap are distributed inside the oxide layer. Most of process-related oxidetrapped charge can be removed by ...
Quantitative chemistry 1
... 1.2.1 Define the terms relative atomic mass (Ar) and relative molecular mass (Mr). 1.2.2 Calculate the mass of one mole of a species from its formula. 1.2.3 Solve problems involving the relationship between the amount of substance in moles, mass and molar mass. 1.2.4 Distinguish between the terms emp ...
... 1.2.1 Define the terms relative atomic mass (Ar) and relative molecular mass (Mr). 1.2.2 Calculate the mass of one mole of a species from its formula. 1.2.3 Solve problems involving the relationship between the amount of substance in moles, mass and molar mass. 1.2.4 Distinguish between the terms emp ...
Limiting reactant - Dr. Gregory Chemistry
... › A mole (mol) a measure of the amount of a substance. › The value of a mole is 6.02 x 1023 particles. This is also called Avogadro’s number. › Particles can be atoms, molecules, ions, formula units. › Equality: 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles ...
... › A mole (mol) a measure of the amount of a substance. › The value of a mole is 6.02 x 1023 particles. This is also called Avogadro’s number. › Particles can be atoms, molecules, ions, formula units. › Equality: 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles ...
Macroscopic electric field and osmotic pressure in ultracentrifugal
... non-aqueous dispersions, are rather uncommon. Therefore we describe experimental aspects of the method in detail, referring to Overbeek [14-15] and Lyklema [16] for extensive discussion of theoretical aspects. The aim is to measure the electrical potential difference between top and bottom fractions ...
... non-aqueous dispersions, are rather uncommon. Therefore we describe experimental aspects of the method in detail, referring to Overbeek [14-15] and Lyklema [16] for extensive discussion of theoretical aspects. The aim is to measure the electrical potential difference between top and bottom fractions ...
surface chemistry - einstein classes
... to a certain critical value or neutralised, the particles approach close enough to coalesce to form bigger particles of the suspension range. This phenomenon of change of colloidal state to suspension state is known as coagulation or flocculation of colloidal solution. It is generally brought about ...
... to a certain critical value or neutralised, the particles approach close enough to coalesce to form bigger particles of the suspension range. This phenomenon of change of colloidal state to suspension state is known as coagulation or flocculation of colloidal solution. It is generally brought about ...
The Mole
... • A representative particle is any kind of particle such as atoms, molecules, formula units, electrons, or ions. ...
... • A representative particle is any kind of particle such as atoms, molecules, formula units, electrons, or ions. ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... describe what chemical change can happen to the substance. * Chemical bond: force of attraction between two atoms that hold them together, H2O. Any change in a substance that involves a rearrangement of the way atoms are bonded is a chemical change. Material undergoing a chemical change is said to b ...
... describe what chemical change can happen to the substance. * Chemical bond: force of attraction between two atoms that hold them together, H2O. Any change in a substance that involves a rearrangement of the way atoms are bonded is a chemical change. Material undergoing a chemical change is said to b ...
Chapter 13: Properties of Solutions
... equilibrium has been established after the barrier has been removed, the two liquids together occupy a volume of 1000 mL. Formation of a homogenous solution has increased the degree of dispersal, or randomness (entropy), because the molecules of each substance are now mixed and distributed in a volu ...
... equilibrium has been established after the barrier has been removed, the two liquids together occupy a volume of 1000 mL. Formation of a homogenous solution has increased the degree of dispersal, or randomness (entropy), because the molecules of each substance are now mixed and distributed in a volu ...
30 - Edgemead High School
... magnitudes and directions of forces acting on a body/particle that has been isolated from its surroundings) Resolve a two-dimensional force (such as the weight of an object on an inclined plane) into its parallel (x) and perpendicular (y) components. Determine the resultant/net force of two or more ...
... magnitudes and directions of forces acting on a body/particle that has been isolated from its surroundings) Resolve a two-dimensional force (such as the weight of an object on an inclined plane) into its parallel (x) and perpendicular (y) components. Determine the resultant/net force of two or more ...
1 mole = 6.02 X 10 23 Particles
... element in a rep. particle of that cmpd. 2) Calculate the gram molecular mass (gmm) or gram formula mass (gfm) by adding together the atomic masses of the atoms making up a molecule or F.U. ...
... element in a rep. particle of that cmpd. 2) Calculate the gram molecular mass (gmm) or gram formula mass (gfm) by adding together the atomic masses of the atoms making up a molecule or F.U. ...
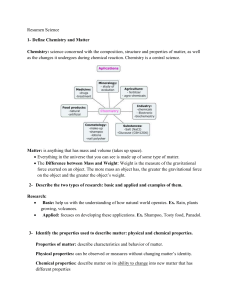
Resumen Science I Trimestre II Parcial Definitions: Element: pure
... condensation to occur. Removing energy slows the movement of gas particles which allows them to clump together. Condensation point: is the temperature at which the gas becomes a liquid. Sublimation: is the change of sate from solid to gas, For sublimation to occur, the attractions between the partic ...
... condensation to occur. Removing energy slows the movement of gas particles which allows them to clump together. Condensation point: is the temperature at which the gas becomes a liquid. Sublimation: is the change of sate from solid to gas, For sublimation to occur, the attractions between the partic ...
The Mole and Chemical Formulas
... formula (shown by the subscript) 2. find the sum of all the atomic masses --this is formula mass (unit is a.m.u.) 3. express formula mass in grams (unit is g/mol). This is the Molar Mass. ...
... formula (shown by the subscript) 2. find the sum of all the atomic masses --this is formula mass (unit is a.m.u.) 3. express formula mass in grams (unit is g/mol). This is the Molar Mass. ...
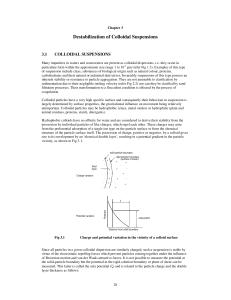
Destabilisation of colloidal suspensions
... animal residues, proteins, starch, detergents). Hydrophobic colloids have no affinity for water and are considered to derive their stability from the possession by individual particles of like charges, which repel each other. These charges may arise from the preferential adsorption of a single ion t ...
... animal residues, proteins, starch, detergents). Hydrophobic colloids have no affinity for water and are considered to derive their stability from the possession by individual particles of like charges, which repel each other. These charges may arise from the preferential adsorption of a single ion t ...
CP Chemistry Midterm Study Guide
... of explosives and fireworks. It is produced by treating nitric acid (HNO3) with ammonia gas (NH3). The balanced equation for this reaction is: HNO3 + NH3 NH4NO3 37. If 6 moles of ammonia gas are used with 4 moles of nitric acid for the reaction, what is the limiting reactant? 38. How many moles of ...
... of explosives and fireworks. It is produced by treating nitric acid (HNO3) with ammonia gas (NH3). The balanced equation for this reaction is: HNO3 + NH3 NH4NO3 37. If 6 moles of ammonia gas are used with 4 moles of nitric acid for the reaction, what is the limiting reactant? 38. How many moles of ...
Molar Mass - Science With Horne
... for measuring the amount of a substance. The definition of a mole comes from how many particles (atoms, in this case) there is in exactly 12 grams of Carbon-12. Through many years of experimentation, it has been confirmed that a mole of any substance has 6.022*1023 representative particles ...
... for measuring the amount of a substance. The definition of a mole comes from how many particles (atoms, in this case) there is in exactly 12 grams of Carbon-12. Through many years of experimentation, it has been confirmed that a mole of any substance has 6.022*1023 representative particles ...
TYPES OF SOLUTION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... i. HCl(aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl + H2O b. The net ionic equation will be : ii. H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O Exercise ?? – I made this up. Write a balanced molecular equation for the reaction between aqueous solutions of acetic acid (CH3COOH) and barium hydroxide (figure out the formula). ...
... i. HCl(aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl + H2O b. The net ionic equation will be : ii. H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O Exercise ?? – I made this up. Write a balanced molecular equation for the reaction between aqueous solutions of acetic acid (CH3COOH) and barium hydroxide (figure out the formula). ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... molecules to pass but large solute molecules cannot • Osmosis: flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane • π = MRT (M = molar conc., R = gas constant, T = absolute temperature) • Reverse osmosis: apply greater pressure to more co ...
... molecules to pass but large solute molecules cannot • Osmosis: flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane • π = MRT (M = molar conc., R = gas constant, T = absolute temperature) • Reverse osmosis: apply greater pressure to more co ...
Electrostatic analysis of the interactions between charged particles
... applications that cover many areas of chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering. Areas of interest include circumstances where charged particles might coalesce, for example, aerosol and water droplets in clouds,1 dust particles in space,2 toner particles in electrophotographic printers,3 and susp ...
... applications that cover many areas of chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering. Areas of interest include circumstances where charged particles might coalesce, for example, aerosol and water droplets in clouds,1 dust particles in space,2 toner particles in electrophotographic printers,3 and susp ...
POWERPOINT - Chapter 8
... ◦ The mole allows chemists to count the number of representative particles in a substance. ◦ The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is the mass of a mole of the element. ...
... ◦ The mole allows chemists to count the number of representative particles in a substance. ◦ The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is the mass of a mole of the element. ...