* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cDNA Libraries
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
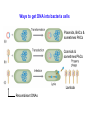
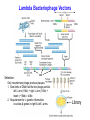
Cosmids: Plasmids that contain l cos sites. This allows them to be packaged into l particles. But don’t have l genes, therefore can clone larger insert fragments; 35-45 kb. PACs: Based on P1 bacteriophage. Replicate as low copy number plasmids inside E. coli. Can clone inserts in 80-100 kb range. BACs: “Bacteria Artificial Chromosomes” Based on 7 kb F1 plasmid (Ch. 7). Can clone inserts in 150-300 kb range. Ways to get DNA into bacteria cells Plasmids, BACs & sometimes PACs Cosmids & sometimes PACs Lambda Recombinant DNAs Recombinant DNA Libraries Collection of many clones derived from a single DNA source. Genomic Libraries: Many clones, each of which contains a fragment of chromosomal DNA from a particular species. Complete genomic library: Entire genome is represented in at least one clone. Making a Genomic Library 1. Digest chromosomal DNA & vector DNA with restriction enzyme(s). 2. Isolate desired size range of chromosomal DNA fragments. (Gel Electrophoresis) 3. Ligate chromosomal restriction fragments with vector DNA. 4. Either package clones (l and cosmids) or use DNA to transform E. coli (PACs and BACs). Lambda Bacteriophage Vectors cos Selection: cos cos Only recombinant phage produce plaques. 1. Size limits of DNA that fits into phage particle. left l arm (15kb) + right l arm (10kb) + insert (~15kb) = 40kb 2. Requirement for l genetic information: cos sites & genes in right & left l arms. Library Complete Genomic Library Entire genome is represented Mininum number of clones (genome equivalent) needed depends on size of genome & vector used. Example: Human genome = 3 x 106 kb Average sizes of inserts l: ~15 kb Cosmids: ~35 kb Human genome equivalents ~2 x 105 l clones ~8.6 x 104 cosmid clones 104 BAC clones (~300 kb/clone) Recombinant DNA Libraries Collection of many clones derived from a single DNA source. Genomic Libraries: Many clones, each of which contains a fragment of chromosomal DNA from a particular species. Complete genomic library: Entire genome is represented in at least one clone. cDNA Libraries: cDNAs = DNA copies of RNA molecules. cDNA libraries: Each clone contains DNA copy of an individual mRNA. Very useful for studying just the part of a gene that is present in mRNA. Making a cDNA Library 1. Prepare poly(A)+ RNA from desired source. 2. Synthesize cDNAs: 3’ Anneal oligo(dT) primers to mRNAs. Synthesize 1st cDNA strand using Reverse Transcriptase. 1st cDNA strand Degrade RNA with NaOH. Synthesize 2nd cDNA strand using DNA polymerase I. Nick hairpin loop using S1 nuclease. 3. Ligate with vector. (plasmid or l) 2nd cDNA strand