* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Midterm Review - Earth Science
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Mercator projection wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
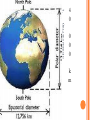
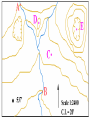
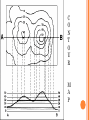
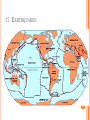
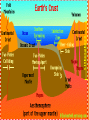
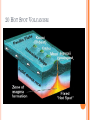
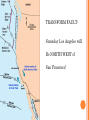
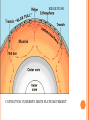
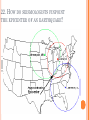
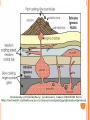
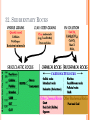
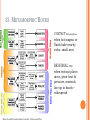
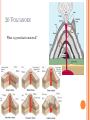
2013-2014 MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW 1-5 BRANCHES OF EARTH SCIENCE Oceanography Meteorology Ecology Geology Astronomy 2-SAFETY IN THE SCIENCE LAB- COMMON SENSE HYPOTHESIS- possible explanation for a problem THEORY- an explanation that is based on experimentation and supported by a large quantity of evidence LAW-widely accepted as a fact, based on repeated observations 3. HOW DID THE DINOSAURS BECOME EXTINCT? 3. EVIDENCE OF METEORITE IMPACT 1- high concentration of IRIDIUM in rocks that are 65 million yrs old 2- no dinosaur fossils after 65mya 3- layer of soot from worldwide wildfires 4- shocked quartz at impact sites 4. CALCULATE HOURS OF DAYLIGHT SUNRISE 7:07 a.m. SUNSET 5:13 p.m. _____________hours _______________ minutes 5. LABEL THE LAYERS OF THE EARTH ocean Continental crust Oceanic crust MOHO lithosphere Upper mantle- rigid Upper Mantle- fluid Lower Mantle STATISTICS OF THE EARTH Circumference= 40,000 km 25,000 miles Diameter = 12,800 km 8,000 miles LITHOSPHERE ASTHENOSPHERE MOHO MAGNETOSPHERE The source of the Earth’s magnetic field is the liquid IRON & NICKEL in the Outer Core TEXT Page 29 7. 4 0 OBLATE SPHEROID 0 0 0 k m 8. EARTH IS AN OPEN SYSTEM WITH REGARD TO ENERGY AND CLOSED WITH MASS 9 WHAT ARE THE 4 MAIN SOURCES OF ENERGY FOR THE EARTH SYSTEM? 9 WHAT ARE THE 4 MAIN SOURCES OF ENERGY FOR THE EARTH SYSTEM? 1- the SUN 2- mantle convection 3. Radioactive decay 4. Gravity 10. WHAT IS A RESERVOIR? 10. WHAT IS A RESERVOIR? A place where matter or energy is stored for a long period of time CARBON- Biosphere Nitrogen-Atmosphere Phosphorus- Geosphere Water- Hydrosphere 11. CREATE 2 FOOD CHAINS 12. FOOD CHAIN VS. FOOD WEB 12. FOOD CHAIN VS. FOOD WEB Food Chain- one possible path for matter/energy Food Web- shows every feeding relationship ECOSYSTEMS CONSUMERS PRODUCERS HERBIVORES CARNIVORES How do ecosystems respond to change? 13- LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE Latitude= degrees N or S of the Equator 69 miles (111 km) between each degree 90⁰ degrees = Poles Longitude = degrees E or W of Prime Meridian (Greenwich) Lines meet at poles, get closer as move N or S 13. DIVISION OF A DEGREE There are ___________ minutes in a degree, and ____________ degrees in a circle Latitude measures ____ and ____ of the _______ Longitude measure ___ and ____ of the ______ ____________ which runs through ____________ Latitude measures up to ___________ which represents the _______ Longitude measures as high as __________ The coordinates of the North Pole are _________ and the South Pole ______________ 13. DIVISION OF A DEGREE There are ___60_____ minutes in a degree, and _____360_____ degrees in a circle Latitude measures _N__ and __S_ of the equator__ Longitude measure _E and _W_ of the _Prime_ __Meridian__ which runs through _Greenwich, England___ Latitude measures up to ______90⁰___ which represents the Poles__ Longitude measures as high as ___180⁰___ The coordinates of the North Pole are___90⁰N_ and the South Pole ______90⁰S____ INTERNATIONAL DATE LINE What day is it here? If it is Monday here…. CONTOUR MAPS SHOW ELEVATION CONTOUR INTERVAL- distance between lines INDEX CONTOUR- every 5th line, drawn in bold print, makes it easier to read the map CARTOGRAPHY- map making RELIEF- difference between highest and lowest elevation GEOMAGNETIC NORTH- magnetic north pole, where a compass points C O N T O U R M A P MAP LEGEND Explains symbols used on map and the Scale. SCALE – the relationship between Distance on a map and distance on Earth. FRACTIONAL 1: 25 000 GRAPHIC- a bar VERBAL - one inch equals one mile COMPASS ROSE Geographic North Magnetic North Pole 16. WHY DO WE HAVE SEASONS? TILT 23.5 degrees Revolution-3651/4 day Leap Year Parallelism 17. EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT PLATE TECTONICS 17. EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT PLATE TECTONICS 1- matching shapes of continents 2- fossil evidence 3- similar rock type 4- mountain ranges continue across oceans 5- climate change 6- earthquake and volcanic activity 7- sea floor spreading 8Paleomagnetism 17. EARTHQUAKES SEA FLOOR SPREADING : See p 243 As magma rises through rifts in the ocean floor, it captures the magnetic orientation of the age. Rocks closer to the rift are younger. Rocks further from the Rift are older. Harry Hess Confirmed Wegener’s hypothesis 17. PLATE TECTONICS Alfred Wegener Similar fossils on widely separated continents Similar rock types or mountain ranges Shape of coastlines Sea floor spreading Paleo- magnetism 17. PLATE TECTONICS PANGAEA PANTHALASSA 19. THE SUPERCONTINENT CYCLE The supercontinent cycle is a geologic cycle where the Earth's continents alternatively merge into a single supercontinent, split into numerous continents, then merge again. The cycle is estimated to be 300 - 500 million years long. 20. PLATE BOUNDARIES DIVERGENT BOUNDARYmagma rises through rift between plates Ex: Mid-Atlantic Ridge CONVERGENT BOUNDARY- plates Collide, form trenches, mtn ranges Ex: Pacific Ring of Fire TRANSFORM BOUNDARY- two plates Slide past each other laterally Ex: San Andreas Fault 20 HOT SPOT VOLCANISM TRANSFORM FAULTSomeday Los Angeles will Be NORTH WEST of San Francisco! RIDGE PUSH CONVECTION CURRENTS DRIVE PLATE MOVEMENT 21. EARTHWEEK 22. SEISMIC WAVES 22. HOW DO SEISMOLOGISTS PINPOINT THE EPICENTER OF AN EARTHQUAKE? 23, 24, 25,26. GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE *Dinosaurs extinctMeteorite impact 4% * Pangea formed 6% PRECAMBRIAN-88% 4600 27, 28. FOSSILS FORM AND EXAMPLES Mummification Cast/mold Freezing Coprolite Petrification Tar Seeps Amber Gastrolith Hard part Petrified remains 29 & 30MINERAL FAMILIES SILICATE- 96% Solid Naturally occurring Definite chemical composition Inorganic Crystal system NON-SILICATE- 4% Luster Cleavage/Fracture Density Hardness (Moh’s Scale p 111) Crystal System Streak Fluorescence Radioactivity Double Refraction Magnetism WAYS TO IDENTIFY AN UNKNOWN MINERAL Tests or Properties that identify Minerals COLOR is NOT a good way to identify a mineral. 1. Many minerals have the same color. 2. Some minerals come in a variety of colors. 3. Weatherin g can change color of a mineral 31. IGNEOUS ROCKS- “FROM FIRE” From LAVA = EXTRUSIVE Fine grained From MAGMA = INTRUSIVE Coarse grained 32. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS 33. METAMORPHIC ROCKS CONTACT Metamorphism- when hot magma or fluids bake nearby rocks- small area REGIONAL m.when tectonic plates move, great heat & pressure, minerals line up in bands – widespread 34. ROCK CYCLE- ANY ROCK CAN TURN INTO ANY OTHER KIND OF ROCK ELASTIC REBOUND THEORY P 295 20 VOLCANOES What is pyroclastic material? 20 ICELANDIC VOLCANOES-MID-OCEAN RIDGE