* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Themes of Geography
Diver navigation wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
Enhanced 9-1-1 wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Arctic exploration wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
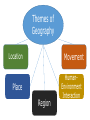
5 Themes of Geography How does geographic questioning help you make sense of a subject as large as Earth and its people? Equator 6.4B Identify and explain the geographic factors responsible for patterns of population in places and regions. 6.3B Pose and answer questions about geographic distributions and patterns for various world regions and countries shown on maps, graphs, charts, models, and databases. Themes of Geography Movement Location Place Region HumanEnvironment Interaction Location where something is found on Earth. Relative Location: describes where a place is compared to another place. This approach uses the cardinal directions on a compass rose – north, south, east, and west. Relative location can also tell us about the characteristics of a place. For example, knowing that Galveston is on the natural harbor of a bay along the Gulf of Mexico helps us understand why the city became an important trading post. Absolute Location The exact location of something. Geographers identify the absolute location of places using a system of imaginary lines called latitude and longitude. Those lines form a grid for locating a place precisely. Latitude North Pole Tropic of Cancer Run east to west, but they measure distance on Earth in a north-south direction. Equator Tropic of Capricorn Note: the equator, north pole and south pole, tropic of cancer, tropic of Capricorn, and is measured in degrees. South Pole Prime Meridian Longitude Run from north to south, but they measure distance on Earth in an east to west direction. Note: The national dateline is called the Prime Meridian. Absolute Location Is shown in latitude and longitude. Latitude is shown first. Longitude is shown second. For example: Washington, DC 38 degrees N, 77 degrees S Place The features that help define a place can be physical or human. Houston “Space City” because of Mission Control. El Paso “Sun City” because we get 302 sunny days a year. Region Places that are close to one another and share some characteristics belong to the same region. Southern California Los Angeles San Diego Both by the ocean. Both have temperate climates. West Texas El Paso Midland Odessa All in the western part of Texas. Climate dry, arid, and windy. Islamic Region North Africa Similar cultural and religious beliefs. Bible Belt Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Georgia Bible Belt – strong Christian belief system. Regions Geographers study regions so they can identify broad patterns of larger areas. They can compare and contrast the features in one region with those in another. They also examine the special features that make each place in a region from the others. Human-Environment Interaction People affect the environment • Blast tunnels through mountains to build roadways. • Drain swamps to make farmland can helpful to humans and bad for the environments. • Exhaust from roadways can pollute the air. • Turning swamps into farms destroy natural ecosystems and reduces biodiversity. Examples of Human Interaction • Flat, rich, well-watered soil is good for farming. • Mountains full of coal can be mined • Hazards include floods, droughts, earthquakes, tornadoes, volcanic eruptions, swamps, hurricanes. Landforms The shape and nature of the land. • • • • Hills Mountains Valleys Presence or Absence of water • Rivers • Lakes • Oceans Weather and Climate Climate – the average weather in a place over a long period of time. • Alaska – long, cold, wet winters, short, mild, summers • Hawaii – warm year round Resources Materials that can be used to produce crops or other products. Forests – trees can be used to build homes and furniture. Oil – a source of energy. Movement Geographers also look at how people, products, ideas, and information move from one place to another. Reasons for moving: • New job • War • Famine • Religious or racial prejudice Movement of Large Groups The sudden movement of large groups of people can have important effects. • Lack of housing • Lack of jobs • Shortages of food or water Transportation Services Transportation services help move items around the world leading to a global economy. • Washington Apples – Texas • Thailand Clothes – American Malls • Saudi Arabian Oil – American Gasoline Railroads, ships, airplanes, and trucks are used to move things. Ideas Move Even Faster Ideas move even faster than people, goods, or services. • Telephone • Radio • Internet • Television Examples, people on the Islands of Borneo watch American TV. Question: (Exit Ticket) Answer this question in a complete sentence in your ISN. How do the geographic themes of location and place relate to each other?