* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
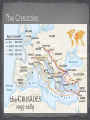
As Roman Civilization declined, Europe became an isolated land of disunity, conflict and poverty. People no longer had the Roman Empire to protect them and unite them Between 400 and 700, Germanic tribes carved Western Europe into small kingdoms. This signaled the beginning of the Medieval period Before After In Medieval Times, people lived difficult lives It took a lot of work to simply survive A political system called Feudalism was created to solve these issues Think back to our unit on Japan- how would you define feudalism? Feudalism is: A system where people pledge loyalty to a lord or powerful land holder and in return receive land and protection You travel in time to a Medieval Kingdom. You have never been here before and you are excited to meet as many different people as you can. Try to find a person who fits each of the following descriptions: The feudal system made sure each person played a distinct role for society to function. Without any one person in the system, the society would fail King: The ruler of the land and the one who was in charge of making decisions Lord and Ladies- The noble men, or wealthy land owners who were given manors from the King. Ladies were their wives and daughters Knights- the sworn protectors of the King and Lords Peasants- worked the land Serfs- Peasants who were not free to leave the land Life in feudal society was structured around the manor The manor was the house and grounds that everyone lived on Manors had everything one needed in order to survive Life was hard in Medieval Times and not very glamorous Even for wealthy families, castles were dim cold places Houses did not have in-door plumbing or hot water so people rarely bathed People would discard trash and bones of food onto the floor which led to insects, rats, and odor All these issues led to frequent disease Around 800, Western Europe was united when an emperor built a vast empire The Emperor is known in history as Charlemagne, or Charles the Great. He loved battle and spent most of his 46 years fighting. His conquest of various places reunited much of the old Roman Empire. Charlemagne did many things to exercise control over his many lands and create a United Christian Europe. He worked very closely with the church; he helped spread Christianity to conquered peoples. He appointed powerful nobles to rule local regions. Education had declined so much that even the clergy (members of the church) were sadly ignorant and uneducated. Charlemagne himself could read, but not write. He felt nobles and clergy needed to keep accurate records and write clear reports. He founded a school and created a curriculum or formal course of study. After Charlemagne died in 814, his empire soon fell apart. Finally in 843, Charlemagne’s grandsons drew up the Treaty of Verdun, which split the empire into the three regions Charlemagne’s legacy is that he spread Christianity to various parts of Europe What were 3 big accomplishments of Charlemagne? How do you think Europe would have been different without his rule? The church was the center of medieval life Every town and manor had a church or cathedral The church was a daily presence in people’s lives People even measured how long to cook an egg based on how many prayers they said Just like feudal society, the church had a very strict structure The church had incredible power The only common language in Europe was Latin- The language of the church Only church officials could read and write The church could excommunicate people which meant throwing them out of the church The church taught that the only way to salvation was through the sacraments Can you see any problems with the church having so much power? The crusades were a series of wars between Christians and Muslims over the holy land and Jerusalem. Both religions wanted to gain control of this important place. The Crusades began in 1095 when Pope Urban II made a urgent call to all Christians to stop the Muslims from taking control of the Christian cities Constantinople and Jerusalem. The crusades had a great impact on European society. Reasons people went on Crusades To seek wealth To guarantee their salvation Deep religious beliefs The crusades were extremely violent and seen as one of the most powerful examples of religious intolerance throughout history Why do you think these religious groups hated each other so much? What do you predict will be some lasting effects of the Crusades The impact of the Crusades was huge Kings grew more powerful as knights and nobles left to fight which helped to eventually end feudalism Thousands of people were killed and injured The increase in travel brought new economic systems to Europe Crusaders were exposed to many new styles of clothing and foods on their trips which encouraged trade routes to develop “All who die on their way, whether by land or by sea, or in battle against the Muslims, shall have immediate forgiveness of sins. This I grant them through the power of God with which I am given.” “Let those who go not put off the journey, but rent their lands and collect money; and as soon as winter is over and spring comes, let hem eagerly set out on the way with God as their guide.” “Let those who have been serving as knights for small pay now obtain the eternal reward.” http://www.wadsworth.com/history_d/templates/stud ent_resources/0534646026_spielvogel/interactive_ma ps/Map10_7.html http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072957549/student_view0/chapter20/i nteractive_map_quiz.html