* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rabies
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
2015–16 Zika virus epidemic wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
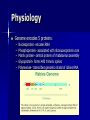
Infectious Disease Report: Rabies By: Anu Gandhi and Val Riguero What are Rabies? Rabies virus causes an acute encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) in all warm-blooded hosts. Rabies is not, in the natural sense, a disease of humans. The impact of rabies on public health includes an estimate of the animal population that is affected and the steps involved in preventing transmission of rabies from animals to humans. Raccoons, skunks, foxes, coyotes, and several species of insectivorous bats have been identified as reservoirs for the disease. Rabies in History Rabies cases have been reported since before 2300 BC. 1st century AD a Roman scholar named Aulus Cornelius Celsus gave the first accurate description of the disease 1st scientist to test rabies infection through inoculation of saliva was a German scientist named Zinke in 1804 Pasteur’s Contribution 1885 he published a method for protecting dogs against rabies A dog exposed to rabies was protected by inoculation with an emulsion prepared from the dried spinal cord of a diseased rabbit Pasteur had the chance to test this same method on humans when Joseph Meister, a nine-year-old boy who was bitten by a rabid dog was brought to him in July of 1885 Joseph was injected over several days with the emulsions prepared from animal spinal cord material After 2 weeks, Joseph was given an injection of virus that had maximal virulence when tested in a rabbit Joseph survived as did thousands of others treated by the same procedure. Epidemiology In 2001, 49 states, the District of Colombia, and Puerto Rico reported 7,437 cases of rabies in animals to the Center of Disease Prevention and Control and no cases in humans were reported. Pennsylvania reported the largest number of rabid domestic animals (46) for any state, followed by New York (43) The number of rabies-related human deaths in the U.S. has declined from 100 or more each year at the turn of the century to an average of 1-2 each year in the 1990’s Morphology Order- Mononegavirales Nonsegmented Negative stranded RNA genome “Bullet” shapedRhabdovirus 180nm x75nm 400 trimeric spikes on surface of virus 2 major structural components – Helical RNP core – Surrounding envelope Physiology Genome encodes 5 proteins: – – – – – Nucleoprotein- encases RNA Phosphoprotein- associated with ribonuceoprotein core Matrix protein- central protein of rhabdovirus assembly Glycoprotein- forms 400 trimeric spikes Polymerase- transcribes genomic strand of rabies RNA Virulence Depends on severity of bite If treatment is given and when Once the disease manifests in CNS: ultimate death Pathogenicity Defined by encephalitis and myelitis Perivascular infiltration throughout entire central nervous system Causes cytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusion bodies (Negri bodies) in neuronal cells Several factors may affect outcome of rabies exposure. – – – – – Rabies variant Dose Route Location of exposure Individual host factors Transmission Begins when infected saliva of host is passed to uninfected animal. Scratches Bites Discharge and Intermediate Hosts Infection of new host via saliva Death of host Wild rabid animals may infect domestic animals/people – Cattle, horses, pigs, dogs, cats – Humans Rabid domestic animals may infect humans Vehicles of Transmission Saliva Mucous membranes Aerosol transmission Corneal transplantations Symptoms of Rabies The first symptoms of rabies may be nonspecific flu- like signs, such as malaise, fever or headache which may last for days. There may be discomfort or paresthesia at the site of exposure (bite) progressing within days to symptoms of cerebral dysfunction, anxiety, confusion, and agitation which eventually progress to delirium, abnormal behavior, hallucinations, and insomnia. Rabies Diagnosis in animals The direct fluorescent antibody test (dFA) is the test most frequently used to diagnose rabies. This test requires brain tissue from animals suspected of being rabid. The dFA test is based on the fact that infected animals have rabies virus proteins (antigen) present in their tissues. Positive dFA Negative dFA Rabies Diagnosis in humans Saliva can be tested by virus isolation or reverse transcription by polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Serum and spinal fluid are tested for antibodies to rabies virus. Skin biopsy specimens are examined for rabies antigen in the cutaneous nerves at the base of hair follicles. Methods of Cure Rabies Vaccine: A killed virus vaccine (Human Diploid Cell Vaccine, HDCV) grown in human fibroblasts is available for safe use in humans. The unusually long incubation period of the virus permits the effective use of active immunization with vaccine post-exposure. If rabies has not been diagnosed and the victim is not treated with a vaccine and the clinical disease manifests, it is nearly always fatal, and treatment is typically supportive. Related Studies In the journal Antibiotics and Chemotherapy, an article was published which presented the results of an experimental study of the action of rifampicin on the process of rabies infection in albino mice contaminated with 1-10 LD50 of the fixed rabies virus. Exposure to rifampicin in doses of 250-500 mg/mouse resulted in survival of 66.783.4% of the animals respectively while the controls did not exceed 16.6-25%. The infection of target cells by rabies is effected through membrane receptors; it has been suggested that nicotonic receptors could be used by the virus. In a study published in Neuroscience Letters, mouse dorsal root ganglia cells were treated with various nicotonic antagonists (mecamailamine, dtubocurarin, hexametonium, etc.). After incubation the cultures were infected with the rabies virus, the cells were then processed for immunodetection of rabies virus. Treatment with mecamilamine or d-tubocurarine reduced the % of infected neurons. Control and Prevention Pre-exposure prophylaxis vaccination Post-exposure prophylaxis If you are exposed to a possible rabid animal: – Wash wound with soap and water – Seek medical attention immediately Control and Prevention Be a responsible pet owner – Keep vaccinations up to date – Keep pets under direct supervision – Spay and neuter pets Enjoy wild animals from far away Don’t adopt wild animals “Love your own, leave others alone” policy References National Center for Infectious Diseases Microbial Life, Perry Keen, Anthony Rabies.com Antibiotiki Khimioterapiia Zubovich,I K Volume 34, Issue 2, Feb 1989, 123-125 Partial inhibition of the in vitro infection of adult mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons by rabies virus using nicotinic antagonists Castellanos, J E, Neuroscience Letters, Volume 229, Issue 3, July 4, 1997