* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 4 - protein synthesis
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
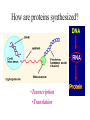
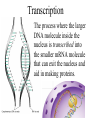
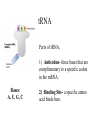
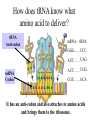
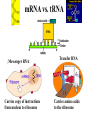
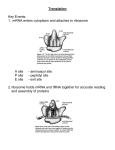
Aim: How are proteins synthesized? What are the main jobs of DNA? Replication & Protein Synthesis Why does DNA replicate? So new cells can get a copy of the instructions on how to make proteins How are proteins synthesized? •Transcription •Translation Transcription The process where the larger DNA molecule inside the nucleus is transcribed into the smaller mRNA molecule that can exit the nucleus and aid in making proteins. Why does mRNA have to leave the nucleus? mRNA Because the cytoplasm contains the sites of protein synthesis (ribosomes) and the free amino acids which make up the proteins. Ribosomes are in the cytoplasm Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis What transports the amino acids to the ribosomes? tRNA tRNA Parts of tRNA; 1) Anticodon- three bases that are complimentary to a specific codon in the mRNA. Bases: A, U, G, C 2) Binding Site- a specific amino acid binds here. How does tRNA know what amino acid to deliver? tRNA Anti-codon mRNA - tRNA GGG…… CCC AUC…… UAG mRNA Codon ACC…… UGG CGU…… GCA It has an anti-codon and also attaches to amino acids and brings them to the ribosome. mRNA - tRNA – amino acid GGG……CCC AUC……UAG ACC……UGG CGU……GCA mRNA vs. tRNA Messenger RNA Carries copy of instructions from nucleus to ribosome Transfer RNA Carries amino acids to the ribosome Steps of Protein Synthesis: 1. mRNA enters the cytoplasm. 2. tRNA picks up amino acids and carries them to the ribosome and the mRNA. Start Codon: AUG (met) 3. The anti-codon on the tRNA matches up with the mRNA codon. 4. Peptide bonds are formed between adjacent amino acids. Steps of Protein Synthesis: 5. A releasing factor binds to one of the 3 “stop codons” and this signals the release of the polypeptide chain. Stop Codons: UGA, UAA, UAG MOVIE Polypeptide synthesis