* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development of Feudalism
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Aachen Cathedral wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Patrimonium Sancti Petri wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
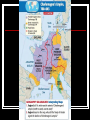
Warm Up Create a 3 column T chart with the following categories: People, Places, Things. Place at least 3 vocabulary terms in each category People Places Things Agenda Warm Up Intro: “What problems did people face after the “Fall of Rome?” Taking Cornell Notes Read Chapter 13, Section 1 Create Cornell Notes Homework: Read Chapter 13, Sec 2 Introduction to the Middle Ages A. Decline of the Roman Empire 1. 2. Led to the Middle Ages or medieval period (Sometimes called the Dark Ages) Spanned ~ 500-1500 a. Roots i. ii. iii. Classical heritage of Rome Beliefs of the Roman Catholic Church Customs of various Germanic tribes B. Invasions of Western Europe 1. 2. Germanic invaders overran western Roman Empire ~ 5th Century Repeated invasions/constant warfare caused changes a. Disruption of trade b. Downfall of cities c. Population shifts d. Decline of learning e. Loss of a common language i. By 800s French, Spanish, and other languages had developed from Latin C. Germanic Kingdoms Emerge 1. Between 400 and 600 Germanic kingdoms replaced Roman provinces a. 2. Borders changed constantly with fortunes of war Concept of government changed a. b. Loyalty to public government and written law (Roman) changed to family ties and personal loyalty (German) Germanic Kingdoms Emerge German chiefs led a band of warriors iii. Warriors pledged loyalty to him iv. Lived in the chief’s hall A. chief gave them food, weapons, treasure v. Warriors fought to the death at their lord’s side A. Felt it was a disgrace to outlive their chief Germanic stress on personal ties made it impossible to establish orderly governments for large territories c. 3. Clovis Rules the Franks 1. 2. 3. 4. Roman province of Gaul (modern-day France & Switzerland) Leader of the Franks was Clovis Clovis (and his people) became Christian Alliance between Clovis’ Frankish kingdom and the Church marked the start of a partnership between two powerful forces. Illuminated manuscripts, such as the one to the right, were usually the work of monks. D. The Church Organizes 1. The Church built religious communities a. b. 2. Monasteries built for monks (men) Convents built for nuns (women) Rules for Christian communities a. b. Practical rules for monasteries written by Benedict Practical rules for convents adapted by Scholastica (Benedict’s twin sister) The Church Organizes 3. Papal authority expands under Pope Gregory I a. b. Pope also became a secular power (secular = worldly, not having to do with religion) E. An Empire Evolves 1. 2. 3. By ~700 the major domo (mayor of the palace) most important person in the Frankish kingdom. Charles Martel (Charles the Hammer) major domo 719 a. Extended the Franks’ reign to north, south, & east b. Defeated Muslims at the Battle of Tours/Stopped Muslim advance in Europe c. Passed power to his son, Peppin the Short Began the Carolinian Dynasty Charlemagne Becomes Emperor 1. Peppin’s son Charlemagne (Charles the Great) inherited the Frankish kingdom a. Built an empire greater than any since Ancient Rome i. ii. Conquered lands and spread Christianity In 800 went to Rome to help the Pope A. Pope Leo III crowned him Holy Roman Emperor Charlemagne’s Accomplishments 1. 2. 3. 4. Strengthened royal power by limiting nobles’ authority Made sure counts governed their counties justly Kept a close watch on his estates (regularly visited all parts of his kingdom). Encouraged learning (made Aachen a center of learning) H. Charlesmagne’s Heirs 1. 2. 3. Charlemagne’s grandsons fought one another for control of kingdom Treaty of Verdun and divided the empire into 3 kingdoms Lack of strong rulers led to a new system of governing and landholding – feudalism • When Charlemagne died in 814, he was buried in his own Cathedral at Aachen. • In 1165, Emperor Frederick Barbarossa opened the vault and placed the remains in a sculptured sarcophagus made of Parian marble, said to have been the one in which Augustus Caesar was buried. • The bones lay in this until 1215, when Frederick II had them put in a casket of gold and silver.