* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Middle Ages AD 500- 1000
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Patrimonium Sancti Petri wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
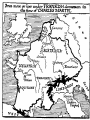
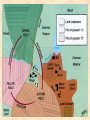
Early Middle Ages AD 500- 1000 Early Middle Ages A. Learning and Civilization Declined, but it was a great time for Germanic Kings and Warriors B. New society had three roots: 1. Classical heritage from Rome 2. Beliefs of the Roman Catholic Church 3. Customs of Germanic tribes Early M. A. • C. By 600, Priests were almost the only literate Europeans • D. Changes in citizenship: • 1. German tribes took over Roman lands • 2. Family ties and personal loyalty bound society together (beginnings of Feudalism) – a contract between serfs (produce food), nobility (protection) • 3. People belonged to a family and followed one leader (like a TRIBE or CLAN) • 4. They felt no obligation to obey a king who was a stranger Early M. A. • • • • • • E. Christianity won new followers 1. Roman Catholic Church was the strongest civilizing force in W. Europe 2. In the 300s and 400s Christian missionaries spread beliefs to German & Celtic groups 3. Clovis, leader of N. Gaul, converted to Christianity – won more German tribes over 4. AD 511 Kingdom of Clovis was divided among his heirs F. Benedictine rule 1. Monasteries – communities of Christian men or women Early M.A. 2. Lived according to rules of: poverty, chastity, obedience • 3. Benedict was a monk who wrote a book of rules for monastic life (Benedictine rule) • 4. Monasteries operated schools, maintained libraries, and copied books (manuscripts); these were the leading scholarly centers of the day Monk copying a book Early M.A. • G. Pope Gregory the Great • 1. Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power • 2. Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages • H. Charles Martel – “The Hammer” • 1. Led the Franks and defeated a Muslim army in Spain at Battle of Tours in 732 ; this checked the spread of Islam in Europe • 2. Son, Pepin the Short, takes control in 741: forced the Lombards out of Rome area, giving control to the Pope (Papal States) Early Middle Ages AD 500- 1000, Day 2 Charlemagne and the Vikings: • I. Charlemagne • 1. King of the Franks (768-814) • 2. Forced people to become Christian • 3. Conquered with his armies: by 800, had lands in Italy, France, Germany, and N. Spain (larger than Byzantine Empire) • 4. First to unite W. Europe since the Romans • 5. His court became a center of learning – the Carolingian revival • 6. Crowned emperor by Pope LeoIII – Holy Roman Empire II. The Vikings: • • • • • 1. From Scandinavia; still pagans, worshiped warlike gods (Thor, etc.) and had names like “Eric Bloodaxe” 2. Raided European settlements from Ireland to Russia, AD 800-1000 3. Were traders, farmers, and explorers 4. Settled Iceland; explored Greenland (Eric the Red) and Newfoundland in N. America (Leif Ericson) 5. Had kingdoms in Ireland and much of England – stopped there by Alfred the Great in 886 Vikings (Cont.) • 6. Last great raiders of W. Europe • 7. Settled down in many areas; such as French Normandy (Northmen or Norsemen = Normans) • 8. Adopted Christianity, decline after AD 1000 Feudalism: • A. A highly decentralized form of govt. that stressed mutual protection b/w monarchs & nobles. • B. Land for loyalty & military aid. • C. Most of Europe was using this system Feudal Relationships: • A. Fief-estates w/peasants, became manors • B. Manors were self sufficient • C. Lords took oath of loyalty in exchange for power over Manor • D. Knights provided protection for Manor & King Knights: • Code of Chivalry: – – – – – 1. be brave in battle 2. fight fairly 3. keep promises 4. defend the church 5. treat women of noble birth in a courteous manner