* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medieval Europe Power Point - Wappingers Central School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
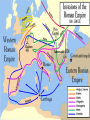
Medieval Europe (500 – 1500) The Middle Ages or Medieval Europe is the 1,000 year period after the fall of Rome and before the Renaissance. I. Geography: A. Europe is on the western end of Eurasia. B. Natural Resources: • Dense forests • Fertile soil • Rich minerals • Seas Tribal Warfare Fall of Rome No central gov’t Money is not used Literacy declined Greek & Roman learning forgotten Dark Ages in W. Europe A. Farmers and herders 1. No written laws 2. Created small kingdoms Not these Franks! B. The Franks- most powerful in Gaul (France) 1. Clovis • 1st King of the Franks • Allied (supported) with the Roman Catholic Church 2. The Battle of Tours - In 732 CE, the Franks defeated the Muslims in Spain. DON’T WRITE THIS This could have changed European history! Christians did not want Islam to spread into Europe, even though they learned science and math from Arab Muslims. C. Charlemagne (Charles the Great) 1. 800 CE- king of the Franks 2. Pope Leo III named him Roman Emperor 3. Legacy • Blended and spread Christian, Roman and German culture • Efficient gov’t (bureaucracy) • Set up schools Don’t write this! Curriculums, or formal courses of study, included reading, grammar, math, music, and astronomy. Don’t write this! When Charlemagne died in 814, his empire fell apart as his heirs fought over it. Peace Out, Charlemagne! 4. The Treaty of Verdun divided the empire. 5. This became the Holy Roman Empire. Feudal Hierarchy Draw this in your notes! (the best you can) Feudalism- A political system that exchanges land for military service. DON’T WRITE THIS! –Lords gradually became more powerful than kings as they acquired more land. I. Feudalism (Political) King or lord Vassal Was required to give a Was required to give fief (land) loyalty & military service II. Social • Kings and Lords were at the top of the social hierarchy. • Knights- mounted warriors – Chivalry- code of conduct for knights – be brave, loyal, polite • By the 1100’s, fighting declined so lords held tournaments (fake battles) to entertain people. • Serfs- peasants who worked the lord’s land – They couldn’t leave without permission – They paid for the lord’s protection in food and labor (no $$). DON’T WRITE THIS! • Role of Women – Noblewomen managed the household and were in change when men were away. – Rights: • Received a limited inheritance • Arranged marriages, expected to have many kids • Few knew how to read and write • Chivalry raised women to a new status. They were protected and cherished. III. Economic Manorialisman economy where land, not money, is the basis of wealth Manor- the lord’s estate including the town, peasant houses, church, and fields - It was selfsufficient, which slowed trade • Three-field system- two fields planted, one left fallow (empty) to regain fertility Europe was isolated BUT, there were advanced civilizations in the Middle East, South Asia, and China!