* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
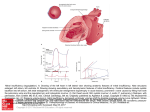
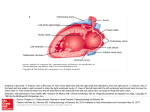
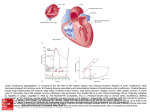
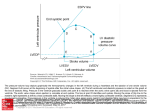
Mitral insufficiency (regurgitation). A: Drawing of the left heart in left lateral view showing anatomic features of mitral insufficiency. Note structures enlarged: left atrium, left ventricle. B: Drawing showing auscultatory and hemodynamic features of mitral insufficiency. Cardinal features include systolic backflow into left atrium, left atrial enlargement, left ventricular enlargement (hypertrophy in acute lesions), prominent v wave caused by filling from both the pulmonary veins and the regurgitant jet, and holosystolic murmur. (3, third heart sound; SM, systolic murmur; A, aortic; P, pulmonary.) (Redrawn, with permission, from Cheitlin MD et al, eds. Clinical Cardiology, 6th ed. Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright © 1993 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.) C: Pressure-volume loop in mitral insufficiency. Increased ventricular volumes shift the diastolic pressure-volume curve rightward. Stroke Source: Cardiovascular Disorders: Heart Disease, Pathophysiology of Disease: An Introduction to Clinical Medicine, 7e volume is increased because the ventricle can now eject blood into the low-pressure left atrium. With chronic volume loads, the isovolemic pressureHammer GD, volume curveCitation: eventually shifts to theMcPhee right. SJ. Pathophysiology of Disease: An Introduction to Clinical Medicine, 7e; 2013 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 12, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved