* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Read the Case Study from “Introduction to Medical Terminology
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
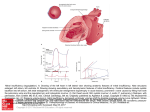
Read the Case Study from “Introduction to Medical Terminology” from Chapter 9 and answer the questions that follow. Case Study 9-1: PTCA and Echocardiogram A.L., a 68-year-old woman, was admitted to the CCU with chest pain, dyspnea, diaphoresis, syncope, and nausea. She had taken three sublingual doses of nitroglycerine tablets within a 10-minute time span without relief before dialing 911. A previous stress test and thallium uptake scan suggested car- diac disease. Her family history was significant for cardiovascular disease. Her father died at the age of 62 of an acute myocardial infarction. Her mother had bilateral carotid endarterectomies and a femoral-popliteal bypass procedure and died at the age of 72 of congestive heart failure. A.L.’s older sister died from a ruptured aortic aneurysm at the age of 65. Her ECG on admission presented tachycardia with a rate of 126 bpm with inverted T waves. A murmur was heard at S1. Her skin color was dusky to cyanotic on her lips and fingertips. Her admitting diagnosis was possible coronary artery disease, acute myocardial infarction, and valvular disease. Cardiac catheterization with balloon angioplasty (PTCA) was performed the next day. Significant stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery was shown and was treated with angioplasty and stent placement. Left ventricular function was normal. Echocardiogram, 2 days later, showed normal-sized left and enlarged right ventricular cavities. The mitral valve had normal amplitude of motion. The anterior and posterior leaflets moved in op- posite directions during diastole. There was a late systolic prolapse of the mitral leaflet at rest. The left atrium was enlarged. The impression of the study was mitral prolapse with regurgitation. Surgery was recommended. Case Study 9-2: Mitral Valve Replacement Operative Report A.L. was transferred to the operating room, placed in a supine position, and given general endotracheal anesthesia. Her pericardium was entered longitudinally through a median sternotomy. The surgeon found that her heart was enlarged with a dilated right ventricle. The left atrium was dilated. Preopera- tive transesophageal echocardiogram revealed severe mitral regurgitation with severe posterior and anterior prolapse. Extracorporeal circulation was established. The aorta was cross-clamped, and cardio- plegic solution (to stop the heartbeat) was given into the aortic root intermittently for myocardial protection. The left atrium was entered via the interatrial groove on the right, exposing the mitral valve. The middle scallop of the posterior leaflet was resected. The remaining leaflets were removed to the areas of the commissures and preserved for the sliding plasty. The elongated chordae were shortened. The surgeon slid the posterior leaflet across the midline and sutured it in place. A no. 30 annuloplasty ring was sutured in place with interrupted no. 2-0 Dacron suture. The valve was tested by inflating the ven- tricle with NSS and proved to be competent. The left atrium was closed with continuous no. 4-0 Pro- lene suture. Air was removed from the heart. The cross-clamp was removed. Cardiac action resumed with normal sinus rhythm. After a period of cardiac recovery and attainment of normothermia, cardio- pulmonary bypass was discontinued. Protamine was given to counteract the heparin. Pacer wires were placed in the right atrium and ven- tricle. Silicone catheters were placed in the pleural and substernal spaces. The sternum and soft tissue wound was closed. A.L. recovered from her surgery and was discharged 6 days later.CHAPTER 9 • CIRCULATION: THE CARDIOVASCULAR AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEMS 207 Case Studies, continued CASE STUDY QUESTIONS Write the word or phrase from the case study that has the same meaning as each of the following words or phrases: 1. The state of profuse perspiration 2. Under the tongue 3. Test of cardiac function during physical exertion 4. Disease that includes both heart and blood vessel pathology 5. Excision of the inner lining along with atherosclerotic plaque from an artery (plural) 6. An abnormal heart sound 7. Bluish discoloration of the skin; sign of anoxia 8. The noun form of stenotic 9. Between the atria 10. Below the sternum Multiple choice: Select the best answer and write the letter of your choice to the left of each number. _____ 11. The word transluminal means: a. acrossawall b. between branches c. throughanouterlayer d. through a central opening e. acrossavalve _____ 12.The term that means backflow, as of blood, is: a. infarction b. regurgitation c. amplitude d. prolapse e. tourniquet _____ 13. The term for a narrowing of the bicuspid valve is: a. atrialprolapse b. pulmonic stenosis c. mitralstenosis d. mitral prolapse e. atrialstenosis _____ 14. Blowout of a dilated segment of the main artery is: a. leftanteriordiastole b. peritoneal infarction c. coarctation of the aorta d. cardiac tamponade e. ruptured aortic aneurysmStudies, continue _____ 15. Sternotomy is: a. incisionintothesternum b. removal of the sternum c. narrowingofthesternum d. plastic repair of the sternum e. surgicalfixationofthesternum _____ 16. Extracorporeal circulation occurs: a. withinthebrain b. within the pericardium c. withinthebody d. in the legs e. outsidethebody _____ 17. Protamine was given to counteract the action of the heparin. This drug action is described as: a. antagonistic b. synergy c. potentiating d. similation e. addiction Abbreviations. Define the following abbreviations: 18. CCU __________________________________ 19. AMI __________________________________ 20. CAD __________________________________ 21. LAD __________________________________ 22. CHF __________________________________ 23. TEE __________________________________ 24. MVR __________________________________