* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download One Leaflet or Two?
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
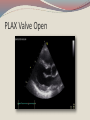
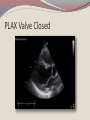
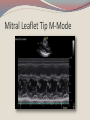
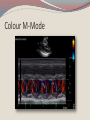
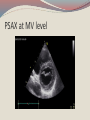
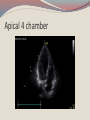
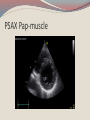
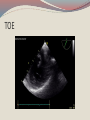
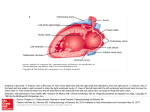
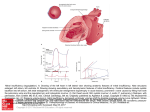
Seán Hendley Cardiac Technician Mater Private Hospital Initial Presentation 63 year old female smoker (20/day) presented to G.P. with respiratory tract infection. Medical history included osteopoenia diagnosed in 2007, old tuberculosis and more recently, influenza. No surgical history noted. Family history: Mother – osteoporosis Brother – Lung cancer S.O.A.P. Subjective symptoms included general lack of energy, dyspnoea on exertion, cough. Objective findings as follows: BP 132/89 Chest clear Loud bruit over right renal angle Plan of action: for specialist cardiology review Regional General hospital Patient attended her regional general hospital where upon examination, a possible diagnosis of mitral regurgitation and left ventricular hypertrophy were queried. Trans-thoracic echocardiogram and chest X-ray ordered. ECG ECG Abnormal Sinus rhythm Borderline left ventricular hypertrophy criteria Poor R-wave progression Chest X-Ray PA & lateral views obtained Bilateral apical pleural thickening and apical fibrosis due to old TB. Lungs are hyper-inflated with changes of COPD & emphysema. Lung markings generally increased on both sides. No focal lung lesion to suggest pneumonic consolidation noted. No pneumothorax detected Heart size within normal limits Lateral view shows hyperinflation of lungs with increased AP diameter of the chest Conclusion: COPD & emphysema. No pneumonia. Consultant Physician’s thoughts ? Radiation of murmur to upper abdomen Murmur described as Loud++ , 4/6. ? Serious cardiac lesion Further echo, TOE, Cardiac catheterisation under care of invasive cardiologist TTE PLAX PLAX Valve Open PLAX Valve Closed Mitral Leaflet Tip M-Mode Colour M-Mode PSAX at MV level PSAX at MV level Apical 4 chamber Mitral valve CW PSAX Pap-muscle TOE Official Echo Report Left ventricle normal in size with normal systolic function. Both atria appear normal in size. There appears to be only a single mitral valve leaflet, represented by a thickened anterior mitral leaflet. No posterior mitral leaflet is visualised. Despite this anatomic variant, the mitral valve is competent with only trivial regurgitation seen. Tri-leaflet aortic valve, with trivial, central aortic regurgitation. Dilation of coronary sinuses with an AP diameter of 4cm. Plus 1 TR with estimated right ventricular systolic pressure of 3035mmHg. Future Plan Sinus rhythm; no further action warranted. Should she have any extra systoles, aspirin recommended. Plan a re-echo in 1 year’s time. Patient feels her dyspnoea was related to urti and is much improved. To wrap up…. Congenital anomalies of the mitral valve apparatus are rare. Of such cases, congenital mitral stenosis, atresia, accessory valvular tissue, and cleft mitral valve are more common. Descriptions of functionally uni-leaflet mitral valves, either partial or complete leaflet agenesis/hypoplasia are extremely rare and largely limited to a few case reports. In the most severe form (complete leaflet absence,) cases are usually considered to be incompatible with life beyond the neonatal period. Asymptomatic patients, however, do exist. The prognosis in these asymptomatic patients is uncertain. The potential for worsening mitral regurgitation and hence potential morbidity and mortality primarily as a consequence of annular dilation, has also been put forward. Therefore, long-term monitoring with serial echocardiography seems most appropriate.