* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unlocking The Key To Arrhythmias
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
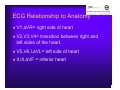
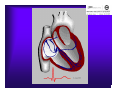
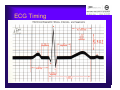
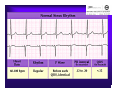
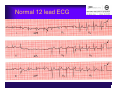
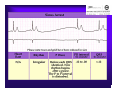
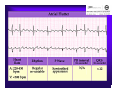
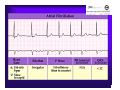
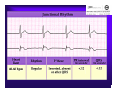
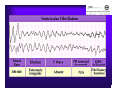
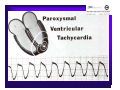
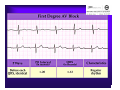
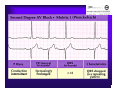
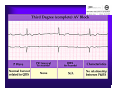
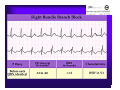
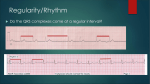
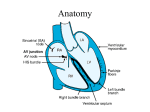
Unlocking The Key To Arrhythmias Kristen Hallisey RN,BSN,CVN Stress Lab Nurse Goals ♦ Understand the normal electrical conduction of the heart ♦ Setting up for ECG with lead placement ♦ Distinguish between atrial and ventricular arrhythmias ♦ Identify lethal arrhythmias ♦ Understand basic treatments for arrhythmias Electrocardiography ♦ The recording of voltage variations of the heart plotted against time. ♦ ECG paper is graph paper with 1mm lines horizontally and 1mm lines vertically. ♦ 1 millivolt change produces a 10mm stylus deflection.(Each vertical line = .1 millivolt) ♦ The recorder moves at 25mm/sec(each horizontal line = .04 seconds) ECG ♦ 10 electrodes produce 12 leads ♦ Limb leads:I,II,III(bipolar) ♦ Augmented leads: aVR, aVL, aVF(unipolar) ♦ Precordial leads:V1,V2,V3,V4,V5,V6(unipolar) ECG Relationship to Anatomy ♦ V1,aVR= right side of heart ♦ V2,V3,V4= transition between right and left sides of the heart. ♦ V5,V6,I,aVL= left side of heart ♦ II,III,aVF = inferior heart NORMAL ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION ♦ SA node (Sinus Atrial) ♦ AV node (Atrio-Ventricular) ♦ Bundle of His ♦ Left and Right bundle ♦ Perkinje fibers NORMAL MEASUREMENTS ♦ Measurements are in seconds ♦ PRI </= .20 seconds ♦ QRS </= .12 seconds ♦ Tracing paper has 1mm lines both vertically and horizontally small box measures 0.04 seconds, large box measures .20 seconds Normal Intervals Interval Large block Small block P PR QRS Normal (sec) 0.2 0.04 0.11 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.10 Small Boxes 5 1 <3 3 to 5 < 2.5 ECG Timing Irregular Heart Rate Determination Normal Sinus Rhythm ♦ Regular Rhythm ♦ Rate 60-100 BPM ♦ One P wave per QRS complex ♦ PRI = < .20 ♦ QRS= < .12 ♦ No contradiction for stress test Normal 12 lead ECG SINUS ARREST ♦ One P to QRS ♦ Rhythm is irregular PRI .12sec - .20 sec, QRS < .12 sec ♦ Common causes: vagal stimulation, acute MI, electrolyte imbalance. ♦ Treat patient if symptomatic. ATRIAL ARRYHTHMIAS ♦ Initiated from the Atrium ♦ Atrial Tachycardia ♦ Atrial Fibrillation ♦ Atrial Flutter ♦ A-V Block ATRIAL FLUTTER ♦ Atrial Rate > 150 BPM ♦ Regular Rhythm ♦ Saw Tooth in Appearance ♦ QRS Measurement </= .12 ♦ Common causes: COPD, metabolic changes, CHF ♦ Treat underlying cause ♦ May be contraindication for stress test physician decision ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ♦ Atrial rate > 400 BPM ♦ No PRI ♦ Rhythm is irregular ♦ Common causes: Digoxin toxicity, hypoxia, intoxication, smoking, COPD, acute MI ♦ Most common treatment is Antiarrhythmics and Anticoagulation to Cardioversion. ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA ♦ Rate > 100 BPM ♦ Irregular Rhythm ♦ One P wave to QRS complex ♦ Common Causes: Sepsis, COPD,CHF, electrolyte imbalance ♦ Treat the cause ♦ Stress test would mostly likely not be ordered until patient was stable Junctional Rhythm ♦ Regular R-R Rhythm ♦ Rate 40-60 BPM ♦ P wave is either inverted, or absent ♦ Can also be accelerated with rates 60-100 BPM ♦ Common causes: drug administration, rheumatic heart disease, acute MI ♦ Only treat if patient is symptomatic ♦ Physician decision to proceed with stress test VENTRICULAR ARRYTHMIAS ♦ Initiated from the Ventricle ♦ Ventricular Tachycardia ♦ Ventricular Fibrillation ♦ A-V Block VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION ♦ No measurable contraction ♦ CPR required ♦ Most lethal arrhythmia VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA ♦ Rate > 100 BPM (usually 140-200 bpm) ♦ Regular Rhythm ♦ QRS > .12 ♦ Common causes: Acute MI, hypoxia, hypokalemia ♦ Treatment is based on patient’s stability ♦ Stress test would be stopped A-V Blocks ♦ Conduction delay between Atria and Ventricles ♦ Three types ♦ 1st, 2nd, 3rd degree First Degree A-V Block ♦ One P wave per QRS complex ♦ PRI interval > .20 ♦ Commonly caused by digitalis administration ♦ Treatment observe patient possibly hold digitalis ♦ Not a contradiction for stress test Second Degree (Type 1) ♦ Also known as Mobitz I (Wenckebach) ♦ PR interval gradually lengthens until a QRS complex is completely dropped ♦ Commonly caused by certain drug administration, Vagal stimulation, Acute inferior MI ♦ Treatment observe patient ♦ Physician decision to continue with stress test Second Degree (Type 2) ♦ Known as Mobitz II ♦ More P waves than QRS complex ♦ Common causes: Acute MI, hypoxia, chronic ischemia ♦ Treatment: Monitor patient and treat with Atropine 0.5mg if symptomatic ♦ Physician may decide to hold stress if patient is symptomatic THIRD DEGREE A-V BLOCK ♦ Also called complete block. Atria and Ventricles contracting independently ♦ Atrial rate 60-100 BPM with a regular rhythm ♦ Ventricular rate 40-60 BPM, QRS > .12 with a regular rhythm ♦ Common causes: Large MI, hypoxia, cardiac trauma, hypokalemia ♦ Treatment is pacemaker insertion BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK ♦ The bundle of His breaks off into the right and left bundle. The left bundle further divides in to anterior and posterior branches ♦ Common causes: Ventricular hypertrophy, cardiomyopathy, ischemia, acute MI(inferior RBBB, anterior LBBB), acute pulmonary embolism ♦ Treatment is based on type of block and patient condition ♦ Physician may choose not to stress with RBBB because this could signify PE or IMI CONCLUSION ♦ Physicians ultimately make the final decision, however recognizing arrhythmias can assist you in understanding their decision. Recognizing arrhythmias also enables all of us to provide safe stress testing.