* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG - Derriford ED
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
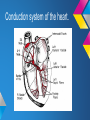
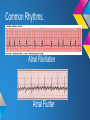
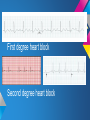
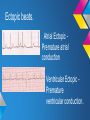
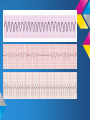
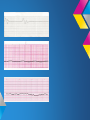
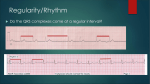
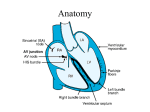
ECG Rhythm recognition. LEARNING OUTCOMES. • To recognise and understand the ‘Normal’ heart rhythm and what it represents. • To perform a step by step basic rhythm strip analysis. • To recognise common cardiac arrhythmias. Conduction system of the heart. Normal sinus rhythm 7 Questions to ask. 1. Is the rhythm fast or slow? 2. Are all the P waves alike? 3. Are all the QRS complexes alike? 4. Is there a P wave in front of every QRS? 5. Is the PR interval constant or does it vary? 6. Is the PR interval too short or too long? 7. Is the QRS complex widened? Common Rhythms? Tachycardia Bradycardia AF Heart Blocks 12 lead ECG may be required to confirm a diagnosis. Common Rhythms. Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter First degree heart block Second degree heart block Complete heart Block/Third degree heart block. Look back at the conduction picture and consider where these blocks are! Ectopic beats. Atrial Ectopic Premature atrial conduction Ventricular Ectopic Premature ventricular conduction. What symptoms may your patient present with if they experience a change is heart Rhythm? Discuss possible causes of a cardiac arrhythmia. POP QUIZ! 1. Which stage of Normal sinus rhythm represent ATRIAL DEPOLARISATION? 2. What does the T wave on ECG represent? 3. Describe how to measure HR on 12 Lead ECG. 4. Which Heart Block presents with a prolonged P-R interval? 5. How can you tell the difference between an atrial or a ventricular premature conduction? 6. What HR may be on the cardiac monitor if patient is in PEA? 7. What is the normal length of time for the P-R interval? 8. What does the term Paroxysmal mean? There is a prize for the winning team!! Further reading and references. • • • • J. R. Levick (2003) 4th ed. An introduction to cardiovascular Physiology. ECG Interpretation made incredibly easy.(2011) 5th ed - Available as PDF online. http://www.youtube.com/cardiacconduction http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/healthtopics/topics/arr