* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
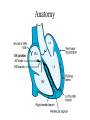
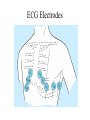
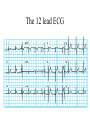
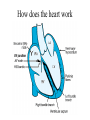
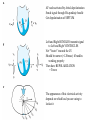
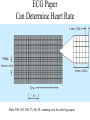
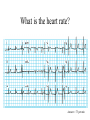
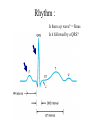
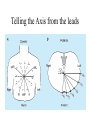
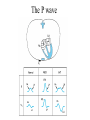
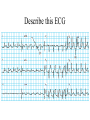
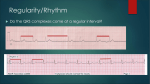
Anatomy ECG Electrodes ECG Waveform The 12 lead ECG How does the heart work AV node activated by Atrial depolarization Sends signal through His-purkinje bundle Get depolarization of SEPTUM Left and Right BUNDLES transmit signal to Left and Right VENTRICLES Net “Vector” towards the LV Should be narrow (<120msec) if bundles working properly Then have REPOLARIZATION = Twave The appearance of this electrical activity depends on which lead you are using to look at it Review of waveforms How to Look at an ECG • Rate: • Rhythm: • Axis: • • • • • Is the heart rate too fast or slow? Sinus rhythm or not? Where does the majority of electrical activity point? P wave: How big are the atria? PR interval: How healthy is the AV node? QRS wave: Is there abnormal conduction or a ventricular source? QT: Long is bad Ischemia and hypertrophy ECG Paper Can Determine Heart Rate Rule: 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 counting over for each big sqaure What is the heart rate? Answer = 75 per min Rhythm : Is there a p wave? = Sinus Is it followed by a QRS? Is the rhythm regular or irregular? Reasons to have an irregular rhythm • Irregular pacemaker – Multifocal atrial rhythm – Atrial fibrillation – Atrial fib/flutter • Ectopic beats – PVC – PAC – PJC • Irregular conduction – AV node block • 1st degree: – PR interval > 200 msec • 2nd degree: – Type 1: Wenkebach – Type 2: dropped beat • 3rd degree: – p waves marching independent to QRS Examples of Rhythms Multifocal Atrial Rhythm AFIB Atrial Flutter AFIB V TACH Example of a PVC Telling the Axis from the leads The axis wheel The P wave The QRS QRS < 120 msec QRS > 120 msec Rabbit ears in V1 & V2 Wide S wave in V5 & V6 R axis deviation QRS > 120 msec Deep slurred S wave in V1 Wide R wave in V6, I & avL L axis deviation Ishcemia vs Acute Infarct Example of Ischemia Examples of Infarctions Review • Rate: • Rhythm: • Axis: • • • • • Is the heart rate too fast or slow? Sinus rhythm or not? Where does the majority of electrical activity point? P wave: How big are the atria? PR interval: How healthy is the AV node? QRS wave: Is there abnormal conduction or a ventricular source? QT: Long is bad Ischemia and hypertrophy Describe this ECG Describe this Strip