* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG Event Represented Duration (Sec)
Survey
Document related concepts
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
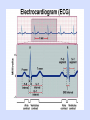
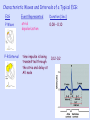
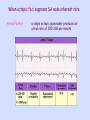
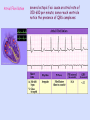
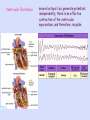
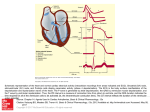
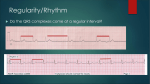
Objective 12 Electrocardiograms Electrocardiogram: a graphical recording of the potential changes that occur in the heart during a cardiac cycle Electrocardiograph: a device used to measure these changes Lead: a combination of electrodes that are used to detect electrical changes; there are 12 standard leads (3 bipolar, 9 unipolar) William Einthoven Characteristic Waves and Intervals of a Typical ECG: ECG Event Represented Duration (Sec) P Wave atrial depolarization 0.08 – 0.10 P-R Interval time impulse is being transmitted through the atria and delay at AV node 0.12-0.2 Name QRS Complex Event Represented Duration (Sec) ventricular depolarization 0.06 – 0.10 ST Segment time between the end of 0.08-0.12 ventricular depolarization and ventricular repolarization T Wave ventricular repolarization 0.16-0.24 Objective 13 Common Arrhythmias Analysis of ECG tracings include an evaluation of these characteristics: 1. Overall rate and rate of individual wave formations 2. Rhythm 3. Shape, height, and duration of wave formations 4. Deviation from the baseline Common deviations include: Sinus bradycardia: impulses arise at the SA node at a slow rate < 60 bpm Note: in well conditioned athletes this may not be an abnormality Sinus Tachycardia impulses arise at the SA node at an accelerated rate > 100 bpm Causes may include: •Exercise •Excessive sympathetic stimulation •Ischemia •Increased temperature When ectopic foci suppress SA node inherent rate: Atrial Flutter a single ectopic pacemaker produces an atrial rate of 200-300 per minute Reentry causes many arrhythmias Usually an ectopic pacemaker or a reentry Atrial Fibrillation several ectopic foci cause an atrial rate of 350-600 per minute; some reach ventricle notice the presence of QRS complexes Ventricular Fibrillation several ectopic foci generate potentials independently; there is no effective contraction of the ventricular myocardium, and therefore, no pulse Atrioventricular block First degree AV block: all impulses are conducted from the atria into the ventricles, but with a greater than normal delay; P-R interval > 0.20 seconds Second degree: some, but not all impulses are conducted from the atria into the ventricles; further defined as 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, etc; there is a consistent P-R interval Third degree: called complete AV block; no impulses are conducted from the atria into the ventricles; the P-R interval varies because the atria and the ventricles are contracting independently Bundle Branch Block: conduction by one of the bundle branches is impaired; ECG shows a widening of the QRS complex RBBB LBBB