* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patofyziologie základních hematologických chorob
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
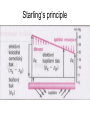
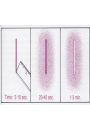
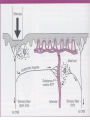
Microcirculation and inflammation M. Jurajda Anatomy of capillary bed Starling‘s principle Four signs of inflammation • Rubor et tumor cum calore et (dolore) – caused by hyperaemia of inflammed tissue • Cohenheim 1867 watched and described this events in the mesentery of the living frog • What happens when arterioles dilate? – Systemic pressure is not affected because limited area is involved – Flow acceleration and capillary pressure rise. – Venules become distended, but capillary dilatation is minimal The triple response of the skin • Sir Thomas Lewis (1920) • Histamine mediated three step reaction – 1. red line – 2. red flare – 3. wheal develops – local oedema of the skin • The initial trauma to the skin releases the histamine. Histamine causes the vasodilatation and vascular leakage. The flare is caused by axon reflex. Increased perfusion of inflammed tissue • • • • Dilution of noxious materials. Increased temperature. Thermotaxis? Diapedesis Exudation – antibodies escapes blood vessels Inflammatory swelling • Vascular leakage • Filtration pressure increase • Reabsorption decrease due to protein escape into extracellular spaces The structure of the capillary wall • Endotelium, BM, pericytes Mechanisms of vascular leakage • Impairment of endothelial layer causes lost of permeability barrier and plasma leaks out, basement membrane (BM) holds the vessel together • Destruction of BM causes hemorrhage. Methods for demonstrating vascular leakage • Soluble dyes • Colloidal suspensions of pigment • Bacteria in circulation tend to localize in inflammed tissue • Presence of fibrin in extracellular space is the histological sign of vascular leak Types of vascular leakage • Direct injury of vessels – destroys endothelia in arterioles, capillaries and venules • Histamine mediated leakage – leakage is restricted only to the venules, endothelia of venules are equipped with histamine receptors and reacts by contracting itself • Late capillary leakage develops after 12 – 18 • Probably effect of IL-1, TNF a INF-gamma • Cytoskeletal changes • • • • • • Direct injury Histamine Cytokines Neutrophils Prostaglandins - vasodilatation Regenerating vessels – leaky sprouts