* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
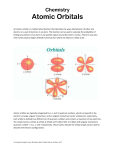
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Light can act as a ______________…. λ = wavelength (lambda) ν = frequency # waves/sec (nu), measured in Hertz, Hz = 1/s c=λν • c = speed of light (3.0 x 108 m/s) • What is the frequency of a beam of red light whose wavelength = 659 nm? What is the frequency of a beam of red light whose wavelength = 659 nm? • • • • c=λν ___________ m/s =___________ _____________ = _____________ ν = ____________1/s =___________ _________ _____________ is the only electromagnetic (EM) radiation we can see • electromagnetic radiation (EM): form of energy that travels through space as a __________ Light can also act as a ____________ • Supported by 2 experiments: –Photoelectric effect –Hydrogen atom spectrum Particle description of light • Max Planck, 1900 – studied ___________ of light by hot objects • Proposed that energy is not ____________ continuously but in small little ___________ called _____________ – This is a particle property • “quantum”: min am’t of energy than can be lost or gained by an atom • Energy _______________ Planck proposed the following relationship between a quantum of energy and its frequency of radiation: • Energy frequency • E= ( frequency ) • where h = Planck’s constant 6.626 x 10-34 J • s (or J/Hz) Duality of light explained photoelectric effect! Metal must be struck by a photon possessing a min. am’t of E – below this am’t, the electron won’t leave the metal! More light of the same E (same ν) just released more electrons…not more energetic • Ground state: atoms whose electrons are in their ___________ energy level • Excited state: an atom,having __________ E, jumps its electron(s) to a higher E level. The electron must jump completely from one level to another. • De-excitation: after a short time the electron ____________________________ and _____ a photon (packet of E) equivalent to the energy difference between the 2 steps. The photon will produce a spectral line with a discrete wavelength (color) associated with it. • Continuous spectrum:all wavelengths are present (i.e.sunlight) • Emission (bright line) spectrum: limited # of specific bright lines that are produced by pass the light emitted by an excited atom through a prism • Absorption (dark line) spectrum: light emitted by an excited atom passes through a substance that filters out certain wavelengths and thus produces a spectrum with missing (dark) lines. • Bright lines of an emission spectrum are _____________________ as the dark lines of an absorption spectrum for a given element. Bohr Model of the Atom, 1913 • Studied the absorption of light by ___________ • Absorption of light at definite wavelengths corresponds to the definite changes in the E of the _______________ • Electrons can circle the nucleus at ___________ _____________ distances…only in allowed paths, or orbits (Satellite model) • Energy of an electron is ____________ when it is in orbits farther away from the nucleus • His calculated energy values agreed with the observed spectral lines for hydrogen • Model did NOT work when applied to multielectron elements Duality of light • Proposed by Einstein after studying the works of Planck and Bohr • Light has been traditionally thought of as a __________ (it has freq. & wavelength) • But now.. light can also be thought of as a __________ ___ ______ of particles called photons • photons: particle of EM radiation having _______ mass and carrying a ______________ of energy • Explained photoelectric effect: EM radiation is absorbed only in whole numbers of photons 4-2 The Quantum Model of the Atom De Broglie, 1924 • If light could behave as both a wave and a particle, then could an electron (a particle) also behave as both a particle and a wave ????????????? • He said “_________” because…. – Since electrons could only exist at specific energies, and E can be equated to frequency (E = hν), they have wave properties – And electrons can be “focused” like light (electron microscopes) – particle nature of electrons had already been confirmed (cathode rays, oil drop exper, etc.) • Electrons have a dual wave-particle nature Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle • It is impossible to determine simultaneously both the __________ and __________ of an electron or any other particle Schrodinger Wave Equation, 1926 • If electrons have wave properties, then wave equations can be applied to electrons (and other small particles) • Laid foundation for __________ ___________: describes ______________________ the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles • Gives the ______________________ of finding an electron at a given place in time around the nucleus Quantum Theory (con’t) • Electrons do NOT travel around the nucleus like planets around the sun • Electrons exist in certain regions called ______________: a 3-D region around the nucleus that indicates the _________ location of an electron Quantum Numbers • Specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals • There are __________ quantum numbers….the first three of which come from solutions to Schrodinger’s wave equation Principal Quantum Number, n • Indicates the _________ __________ _________ (or shell) occupied by the electron • n = 1, 2, 3 etc. • The ↑n value, the ___________ the electron is from nucleus∴ principal quant # also gives ________ ________________ • Total # electrons on a level = __________ • Total # orbitals on a level = n2 since an orbital can hold two electrons (2n2/2= n2) Angular Momentum Quantum Number, l • Also known as “second quantum number” • Also known as “azimuthal quantum number” • Most energy levels (all but n=1) have orbitals of different __________, called ____________ • Describes the ______________ of the orbital • # orbital shapes possible is equal to the ______ _____________ – If n=3, then there can be 3 orbital shapes • The values of l = 0, 1, 2,……. (n-1) – If n=3, then l can be ___, ___, or ___. Angular Momentum Quantum Number, l (con’t) • An orbital LETTER is used to designate each shape: L value Letter designation 0 s (spherical) 1 p (dumbbell) 2 d (complex - p.102) 3 f (too complex for here) Energy level, n # sublevels 2nd quant # Letter denotation Magnetic Quantum Number, ml • also known as the 3rd quantum number • indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus • = (2 l + 1) Magnetic Quantum Number, m (con’t) • Sum of all orbitals in a sublevel (or E level) is a spherical cloud! Orbital shape # orientations s 1 p 3 d 5 f 7 Spin quantum number, s • Describes the spin of the electron • Could be either clockwise ( + ½) or counterclockwise (- ½ ) • Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, a pair, spinning in opposite directions 4-3 ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS Hund’s Rule • Orbitals of equal energy are ________ occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and… • All electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same _____ Aufbau Principle • An electron occupies the ________________ orbital that can receive it Noble Gas Notation • What is the noble gas electron notation for calcium? • 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 • What is the noble gas config for S? • 1s22s22p63s23p4 PREDICTED