* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
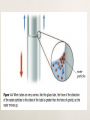
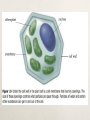
Learner Outcomes: Investigate plant uses; and identify links among needs, technologies, products and impacts Describe the parts of a seed plant Describe the life processes and structure of plants; explain the processes that a plant uses to stay alive Describe the life cycle of seed plants What do plants need to live? The same, but different? Although they look very different, the structures that make up these plants are the same. What are the structures? The Body of Seed Plants We are going to study only the plants that make seeds, which are called seed plants. Some Examples: Daisies, Evergreen Trees, Maple Trees, Wheat and Orchids. Seed plants come in all shapes and sizes… Just like seeds! Seed plants are the largest group of plants in the world. Each Plant Structure Has A Function And, all seed plants have the same kinds of structures which do the same job in all plants. Check and Reflect Page 101 1-4 Plant Processes This tall tree has to move water up from its roots and food down from its leaves. How do plants transport these substances? Process for moving water up from the roots? Water moves up a plant from the roots to the leaves by a combination of processes. Transpiration: Main process that draws water up from a plant’s roots. Is the evaporation of water from the surface of the plant (mainly the leaves). As water particles evaporate from the surface of the leaves, more water particles move up with the plant to take their place. This process continues down through the plant with particles continually moving up from the roots. Capillary Action In this process, water travels from the roots to the leaves through tiny tubes in the roots and stems. Water particles are attracted to one another, and “stick” to one another, and they’re also attracted to the sides of the tiny tubes. These attractions helps move the water up inside the plant. Osmosis Water from the soil enters root cells by osmosis. When the concentration of water in the soil is greater than the concentration of water in the roots of the plant, water moves into the root cells. A Process to Make Food Plants make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis produces a type of sugar. Photosynthesis takes place in structures inside the leaves called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts capture the sun’s energy and uses it to join carbon dioxide and water together to make sugar. The process also produces oxygen. A Process to Use Food When plants use the sugar produced by photosynthesis for food, they get energy and produce carbon dioxide and water as waste. This process is called cellular respiration. Word Equation for Cellular Respiration Processes to Move Substances In & Out of Plants After a plant has made sugar in its leaves by photosynthesis, it must transport food throughout its body. It also has to move the water out of the stem into the rest of its cells. Pores Tiny openings in the membrane of a cell. Allow some substances to move in and out of a cell. Diffusion: When there is a difference between the concentration of a substance inside and outside of a cell. Requires no energy use. Active Transport: Does not require a difference in substance concentration. Uses energy to move substances in and out of a plant. A Process to Exchange Gases Gas exchange is the process of gases (carbon dioxide and oxygen) entering and leaving the plant. Check & Reflect Page 107 #s 1-4 Reproduction of Seed Plants A life cycle is the stages that a living thing passes through to go from one generation to the next. For seed plants, the life cycle starts when a seed begins to grow into a plant and ends when that plant produces seeds of its own. The Seed Stage 3 Main Parts The embryo Stored food Seed coat The embryo uses the stored food to survive until it begins to photosynthesize and produce its own food. The Seedling Stage The Seedling Stage Plants grow very fast at this time and produce new leaves, roots, and stems. Seedling plants produce their own food through photosynthesis, but they also need nutrients from the soil to build their new parts. The Adult Stage The Adult Stage A plant is an adult when it produces reproductive structures. For seed plants, these structures are either a flower or a cone. Flowers usually have both male and female parts. Plants produce flowers & cones… Only so they can make seeds. To do this, they must undergo the process of pollination. A plant produces millions of pollen grains-male- (sperm) Pollination occurs when after a pollen grain lands on the stigma of the flower, above the ovary- the female part of the flower is the ovule (egg) The pollen grain produces a pollen tube, and grows down the stigma to the ovule. Pollinators Plants need a way to get the pollen to the ovules. Some plants release pollen to the air, where it is carried by the wind (conifer trees and grain crops). Many plants rely on pollinators, which are organisms that carry pollen from one flower to another. Examples of pollinators? Reproduction Without Seeds? Vegetative Reproduction: Involves one parent and produces organisms that are genetically identical. Happens during less than “ideal” conditions. Technology to Reproduce Plants Growers also produce plants using vegetative reproduction. Cuttings: Small pieces of a plant can produce new roots from a cut stem under the right conditions. Grafting: Attaching a part of one plant on to another plant. Usually a small branch is grafted. The two sections eventually grow together. Check & Reflect Page 115 #s 2, 3, and 5 Plant Structures are Adapted to their Environment When you are outside building a snowman, if you get hungry, can you pick an orange off of a tree in your yard? List some trees that are able to grow in a cold climate! Turn to pages 118 & 119 Read together! Then complete Check & Reflect Page 120 #s 2-4 Plant Needs & Growing Conditions All plants need light, but some need lots of light and others need shade. Which is which? Plant Needs & Growing Conditions Plants need different amounts of water. Plants that are adapted to grow in very dry conditions are easily damaged or killed by too much water. Others need lots of water all of the time. Plants Need Different Nutrients Nutrients: are substances that provide the energy and materials that plants need to grow. The main nutrients plants need are: Nitrogen Phosphorous Potassium Calcium Magnesium What happens if plants don’t get enough of these nutrients? Plants Need Different Amounts of Space Growing Plants Requires Knowing the BEST growing conditions! Knowing about the needs of different plants is an important tool for growing plants. I kill everything If you know exactly what a plant needs at each stage of its life, you might be able to make sure it grows exactly under those conditions. Check & Reflect Page 124 #s 1-4