* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Structure - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
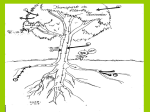
Plant Structure Higher Level Objectives At the end of this sub-section students should be able to: 1. Label a diagram of the external parts of a typical flowering plant shoot, root, stem, leaves, flower, fruit & seed 2 State the function of the root and shoot 3. Identify tap and fibrous root systems 4. Explain the term Meristem and give its location in the stem and root 5. Name and give the function of four zones in a longitudinal section of a root 6. State the function of Vascular Tissue 7 Give the location of three tissue types, Dermal, Ground and Vascular, in transverse sections of the of the root and stem and leaf 8. Give the location of three tissue types, Dermal, Ground and Vascular, in longitudinal sections of the root and stem. 9. Identify and draw the structure of Xylem and Phloem and state their function 10. Distinguish between Xylem Vessels and Xylem tracheids, and between Phloem Sieve Tube Cells and Companion Cells 11. Identify Monocots and Dicots under the headings Number of flower parts Vein pattern in leaf Arrangement of Vascular Bundles Number of Cotyledons in the seed Woody or Herbaceous Practical Activity 1)Prepare and examine a transverse section of a Dicot stem under the microscope Gas Exchange Higher Level Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 1. Explain diffusion 2. Explain how gases are exchanged by diffusion between cells and their environment 3. Understand that the efficiency of exchange is proportional to the surface area over which diffusion can take place. 4. Say why plant leaves are flattened 5. Draw the structure of the leaf in relation to gaseous exchange 6. Identify the stomata in a leaf in transverse section and lower surface 7. Identify lenticels on a stem 8. Give the role of lenticels as excretory organs of plants 9. Give the role of leaves as excretory organs of plants 10. Identify the transverse section of a leaf blade under the microscope 11. See the need for intercellular air spaces allowing free diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the leaf Practical Activity 1) Examine microscopically a T.S. of a leaf blade. Note the intercellular air spaces allowing free diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen. 2) Examine stomata distribution on a leaf blade. Page 1 of 2 Plant Structure & Gas Exchange: Where is your learning at? Green – I know it all 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Orange - I have some idea Red - I need to start studying this section Plant Structure Label a diagram of the external parts of a typical flowering plant Shoot, root, stem, leaves, flower, fruit & seed State the function of the root and shoot Identify tap and fibrous root systems Explain the term Meristem and give its location in the stem and root Name and give the function of four zones in a longitudinal section of a root State the function of Vascular Tissue Give the location of three tissue types, Dermal, Ground and Vascular, in transverse sections of the of the root and stem and leaf Give the location of three tissue types, Dermal, Ground and Vascular, in longitudinal sections of the root and stem. Identify and draw the structure of Xylem and Phloem and state their function Distinguish between Xylem Vessels and Xylem tracheids, and between Phloem Sieve Tube Cells and Companion Cells Identify Monocots and Dicots under the headings Number of flower parts Vein pattern in leaf Arrangement of Vascular Bundles Number of Cotyledons in the seed Woody or Herbaceous Explain how to prepare and examine a transverse section of a Dicot stem under the microscope Gas Exchange Explain diffusion Explain how gases are exchanged by diffusion between cells and their environment Understand that the efficiency of exchange is proportional to the surface area over which diffusion can take place. Say why plant leaves are flattened Draw the structure of the leaf in relation to gaseous exchange Identify the stomata in a leaf in transverse section and lower surface Identify lenticels on a stem Give the role of lenticels as excretory organs of plants Give the role of leaves as excretory organs of plants Identify the transverse section of a leaf blade under the microscope See the need for intercellular air spaces allowing free diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the leaf Examine microscopically a T.S. of a leaf blade. Page 2 of 2 Green Orange Red