* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
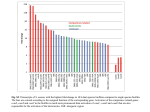
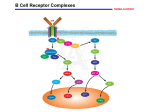
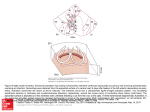
B cell subsets Mature B cells Fetal liver stem cells …….B-1 B cell Bone marrow stem cells…..B-2 B cells….marginal zone B cells and follicular B cells with Both IgM & IgD B-1 B cells (CD5+) found in peritoneum and mucosal sites Limited diversity Secrete IgM Marginal zone B cells Located in the spleen Express IgM and CD21 Respond to blood-borne microbes B cell surface markers B cell receptor(Ag recognition) CD19 (B cell activation) CD21or CR2 (B cell activation and EBV receptor) CD25 (binds IL- 2) CD27 (memory B cells ) CD40 (B cell activation) CD80 or B7(costimulator for T cell activation) CD81 (B cell activation) CD19 is one of the most reliable surface biomarker for B cells It is expressed from pre-B cells until the terminal differentiation to plasma cells. CD19 expression in mature B cells are 3-fold higher than that found in immature B cells, with slightly higher expression in B1 cells than in B2 cells CD19 acts as a critical co-receptor for BCR signal transduction The CD19 gene encodes a cell surface molecule that assembles with the antigen receptor of B lymphocytes in order to decrease the threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation It primarily acts as a B cell co-receptor in conjunction with CD21 and CD81 B regulatory cells The hallmark of an effective immune response is inflammation. After infection, the inflammatory response is critical for clearing pathogens and initiating wound healing If unresolved, this inflammatory response causes injury to host tissues, which can lead to the development of a wide variety of immune-mediated pathologies in cascades that control wound healing Directly, cognate interactions between Breg cells and T cells are thought to control Treg cell induction, given that B cells deficient in major histocompatibility complex class II and B7 do not exhibit regulatory function). Indirectly,Breg cells suppress the differentiation of T helper 1 plasmablasts can also suppress inflammatory responses supports the proposal that any B cell has the potential to differentiate into a Breg cell it has now been demonstrated that immature B cells, mature B cells, and plasmablasts all have the capacity to differentiate into IL-10-producing Breg cells in both mice and humans. This supports the concept that the primary requisite for Breg cell differentiation is not the expression of a Breg-cell-specific lineage factor but rather the environment in which a B cell finds itself. Toll-like receptor (TLR) and/or CD40 activation is the most well-characterized signal known to induce their differentiation pro-inflammatory cytokines can also drive the induction of IL-