* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Biotechnology File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
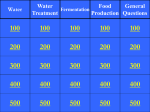
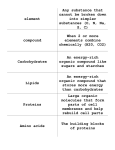
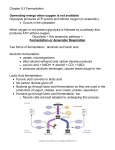
Classical Biotechnology •Application & refinement of fermentation techniques to industry. (use of cells or enzymes to produce large quantities of useful substances) •limited to chemicals/organisms produced in nature • Mass production of biotech products made possible by invention of fermenters (a.k.a. bioreactors), large growth chambers for cultivating cells. Classical Biotechnology Fermenters (Bioreactors) • In conjunction with aseptic technique and steam sterilization, can be used to produce huge variety of products. • Different products achieved by manipulating 1) species of microorganism 2) substrate fed to microbes 3) environmental conditions Alcohol • Breweries & distilleries • large scale alcohol production since early 1700’s. • 1886 – process for making Brewer’s yeast refined – still in use today. • Originally discovered by accident. • Wine allowed to sit in shallow barrels, oxidized by acetic acid bacteria via aerobic fermentation. • Requires exposure to air (O2). Vinegar Explosives & Organic • Glycerol (sweetener, Solvents WWI (Germany) – products for explosives moisturizer, made by manipulation of fermentation lubricant and process to yield products other than ethanol. preservative for rubber, and the organic portion of some widely used explosives and medications ) • Acetone • Butanol Organic Acids • • • • Citric acid lactic acid acetic acid produced for food processing. • Developed in 1940’s (WWII). • Antibioticproducing fungi & bacteria are cultured & fermented. • Antibiotic is purified from fermentation products. • Methods for increasing yields were developed. • Penicillin – 1st antibiotic commercially produced. Antibiotics • Microorganisms change chemical structure of a substrate (starting material) into a desired product. • In 1950’s, cholesterol cortisone or sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone). • Insulin made in bulk. Hormones, enzymes, amino acids, vitamins, pigments • Fermenters allow large quantities of microorganisms to be grown & dried as a source of protein for humans & animals. • First used in Germany during WWI. • Vegemite – yeast extract, popular in Australia, NZ • Brewer’s yeast & baker’s yeast mass-produced early 1900’s. Single-cell Protein Vaccines & Monoclonal Antibodies • fermentation techniques on the largest scale. Wastewater Treatment















![NUTRICELL START [en tête: NUTRIENTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007854045_2-c4164e6cb36cf3b1ce13f2bee9ca3ea2-150x150.png)