* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline the control of the heart beat in terms of myogenic muscle
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
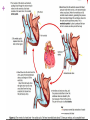
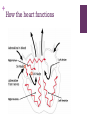
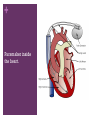
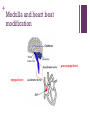
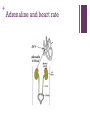
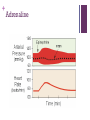
+ Outline the control of the heart beat in terms of myogenic muscle contraction, the role of the pacemaker, nerves, the medulla of the brain and adrenalin (epinephrine). + + The heart is is myogenic The cardiac muscle in the heart can contract and relax without stimulation from the nervous system + + + Three stages of cardiac cycle Atrial Systole (contraction) Ventricular Systole (contraction). The sinoatrial node (SAN) contracts and transmits electrical impulses throughout the atria, which both contract, pumping blood into the ventricles. The electrical impulse passes to the ventricles via the atrioventricular node (AVN) Diastole (relaxed) The atria and the ventricles relax, while the atria fill with blood. The semilunar valves in the arteries close as the arterial blood falls back against them. + How the heart functions + + Key terms Sinoatrial node (SAN) Atrio-ventricular node (AVN) Atrial systole Ventricular systole Diastole + Pacemaker A pacemaker replaces the sinus node when your heart beats to fast, having a heart failure or a heart block which is a delay in the electrical conduction. + Pacemaker inside the heart. + Almost all pacemakers are implanted to treat slow heart beating, which is called “bradycardia”, possible reason could be : sick sinus syndrom Possible reason for implanting a pacemaker a medical procedure to treat an arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation. heart medicines, such as beta blockers. the heart usually beats about 50 to 70 times each minute, and the heart rate may increase 2- to 3-fold during stress or exercise. If the heart beats too slowly, the brain and body do not get enough blood flow and a variety of symptoms may result. faint or have other symptoms of a slow heartbeat heart muscle problems that cause electrical signals to travel too slowly through your heart muscle. Sympathetic nerve secretes adrenaline (also known as “epinephrine”) The sympathetic nervous system belongs to autonomic nervous system along with parasympathetic nervous system. which carries messages from the brain to the pacemaker telling the pacemaker to speed up the beating of the heart. vagus nerve tells it to slow it down, and Adrenalin, carried to the pacemaker by the bloodstream tells it to speed up the beating of the heart. Nerves and Hormones Nerves and hormones can transmit messages to the pacemaker + Medulla and heart beat modification parasympathetic sympathetic + Adrenaline and heart rate + Adrenaline