* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Earth - ReedEarthScience
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
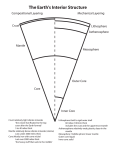
Inside the Earth Mr. Reed Earth Science Madras Middle School What is Inside Earth? • We are not sure? Why? – Extreme conditions inside Earth • Temperature rises – Why? Heat left over from formation of planet and radioactive substances inside Earth’s interior releasing energy • Pressure increases – Because of the weight of the rock above How do we study the inside of the Earth • Rock Samples – Geologists can drill into the Earth and bring up rock samples • Theses samples allow scientists to infer about conditions inside Earth – Seismic Waves (Earthquake waves) • Geologists study how the seismic waves travel through Earth (speed and path) • This data has help geologists realize that the Earth is made up of several different layers Composition (What it is made of) • Crust • Mantle • Core The Crust • • • • Outer layer Solid Rock 5-70 km thick 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very thin, made of basalt) – Continental (thicker, made of granite) The Mantle • • • • • • • • Middle layer Very thick layer 3000 km thick Very hot , but solid rock Made up of three sublayers: 1. lithosphere 2.asthenosphere 3.lower mantle The Mantle • Lithosphere – Uppermost part of the mantle – 100 km thick • Lower Mantle – Solid material that extends to the core • Asthenosphere – Bottom part of the mantle – Less rigid, soft rock – Can bend like plastic The Core • Made mostly of metal irons and nickel • Very hot • 3,486 km thick • Made up of 2 parts: – Outer core and the inner core The Core • Outer Core – Molten metal – LIQUID LAYER • Inner Core – Solid Metal Earth’s Magnetic Field • Movement in Earth’s outer core create Earth’s magnetic field Earth’s Layers • How are the earth’s layers similar to an egg? • Shell=crust • Egg white=mantle • Yolk=core