* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antimatter
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Antiproton Decelerator wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
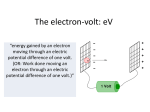
Dirac and Antimatter In 1927 Paul Dirac was working on the problem of combining the theory of the very small (quantum mechanics) with Einstein’s special theory of relativity. He came up with this equation describing the electron: i eA ( x ) m x ( x) 0 You DON’T need to learn this equation!! Solutions to the Dirac equation The equation explains very neatly the magnetic properties of the electron. Electrons he visualised as spinning like tiny gyroscopes but surprisingly they always have the same amount of “angular momentum” Which we now call spin. There is one very odd property of this equation: It has two solutions. As a comparison the much simpler equation below has two solutions y 4 y2 y 2 Solutions to the Dirac equation Dirac predicted that there must be a particle like the electron but with opposite properties (except mass). He called the new particle he predicted THE POSITRON Particle Symbol electron e positron e There are properties other than charge, of the positron which are exactly opposite the properties of the electron some of which you will discover later in the course. Just like the electron can be written ethe positron is sometimes written e+ The confirmation of the positron • The positron was the first particle of antimatter predicted. • Anderson discovered the positron in cosmic rays in 1932. Antimatter. • Every subatomic particle has its counterpart with exactly opposite properties. p p n n e e Some examples of particles and their antiparticles Proton and antiproton Neutron and antineutron Neutrino and antineutrino When a matter particle meets its counterpart antiparticle. They are both destroyed and produce gamma ray radiation. Measuring Mass-the Electron Volt ------------------------------------------------------------ ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ An electron has a negative charge so it is repelled by a negatively charged plate (electrode) and it is attracted to a positively charged eletrode It is accelerated and gains kinetic energy. The amount of energy it gains if it is accelerated by a p.d. of 1volt is called 1electronvolt 1eV This is an exceedingly small amount of energy A potential difference of 1volt between the plates The MeV • Because mass is just “compressed energy”, It is possible to use the electron volt units instead of kilograms to quantify mass. • But the electron volt is too small so we use the MeV which is equivalent to a million electron volts Particle electron Mass in MeV 0.511 positron 0.511 proton 938.27 antiproton 938.27 neutron 938.27 antineutron 938.27