* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Force - Scarsdale Schools
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
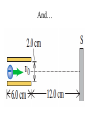
Superposition of Forces • Two point charges are located on the x axis of a coordinate system: q1 = -1 nC and is at = -2.0 cm; q2 = -3 nC and is at = 4.0 cm. What is the total electric force exerted by q1 and q2 on q3 = 5.0 nC at the origin? Fields • A point charge q = -8.0 nC is located at the origin. Find the electrical field at the field point x = 1.2 m and y = -1.6 m Different But the Same • A positron (the electron’s antiparticle) has mass 9.1 x 10^-31 kg and charge q = 1.6 x 10^-19 C. Suppose a positron moves in the vicinity of an (alpha) particle, which has charge 3.2 x 10^-19 C. The alpha particle’s mass is more than 7000 times that of the positron, so we assume that the particle remains at rest. Continued • When the positron is 1 x 10^-11 m from the particle, it is moving directly away from the particle at 3 x 10^6 m/s. (a) What is the positron’s speed when the particles are 2 x 10^-10 m apart? (b) What is the positron’s speed when it is very far from the particle? Realize Your Potential (a) An electron is to be accelerated from 3 x 106 m/s to 6 x 106 m/s. Through what potential difference must the electron pass to accomplish this? (b) Through what potential difference must the electron pass if it is to be slowed from to a halt? Tube TVs… • An electron with an initial speed of 6.5 x 106 m/s is projected along the axis midway between the deflection plates of a cathode-ray tube. The potential difference between the two plates is 22 V and the top plate possesses positive charge. (a) What is the force on the electron when it is between the plates? And… How They Work • (b) What is the acceleration of the electron when acted on by the force in part (a)? • (c) How far above the axis has the electron moved when it reaches the end of the plates • (d) At what angle with the axis is it moving as it leaves the plates? • (e) How far above the axis will the electron strike the fluorescent screen S? What Ya Think? • If you double the amount of charge on a parallel pate capacitor, what happens to its capacitance? (i) It increases; (ii) it decreases; (iii) it remains the same; (iv) the answer depends on the size or shape of the conductors Plates • The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor in vacuum are 5.00 mm apart and 2.00 m2 in area. A 10.0-kV potential difference is applied across the capacitor. Compute (a) the capacitance; (b) the charge on each plate; and (c) the magnitude of the electric field between the plates