* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2: The Cell - Mrs. Hale`s Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
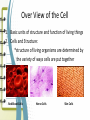
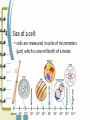
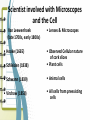
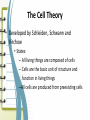
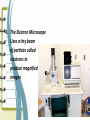
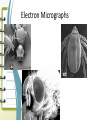
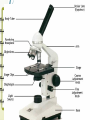
Unit 2: The Cell Microscope Section 1 Over View of the Cell 1. Basic units of structure and function of living things 2. Cells and Structure: *structure of living organisms are determined by the variety of ways cells are put together Red Blood Cells Nerve Cells Skin Cells 3. Cells and Function: • function of an organisms includes obtaining oxygen, getting rid of waste, obtaining food and growing 4. Size of a cell: • cells are measured in units of micrometers (µm) which is one millionth of a meter. Scientist involved with Microscopes and the Cell • Van Leewenhoek (late 1700s, early 1800s) • Lenses & Microscopes • Hooke (1665) • Schleiden (1838) • Observed Cellular nature of cork slices • Plant cells • Schwann (1839) • Animal cells • Virchow (1858) • All cells from preexisting cells The Cell Theory • Developed by Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow • States: – All living things are composed of cells – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things –All cells are produced from preexisting cells Early Scientists Robert Hooke Early Microscope Cork Cells Microsopes • One or more lenses that makes an enlarged image of an object. Types of Microscopes 1. Simple Microscope: • Similar to a magnifying glass and has only one lens. 2. Compound Microscope • Lets light pass through an object and then through two or more lenses. 3. Binocular (Stereoscopic) Microscopes • Gives a three dimensional view of an object. (Examples: insects and leaves) 4. The Electron Microscope • Uses a tiny beam of particles called electrons to produce magnified images Electron Micrographs Parts of the Microscope Parts of the Microscope Answers