* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15: Psychological Disorders
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Memory disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Psychological trauma wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Social construction of schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
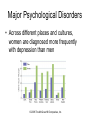
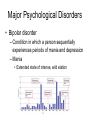
Chapter 15: Psychological Disorders © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Defining Abnormality • Abnormality – – – – – Deviation from the average Deviation from the ideal A sense of personal discomfort The inability to function effectively A legal concept • Abnormal behavior – Causes people to experience distress and prevents them from functioning in their daily lives © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Terrorist Suicide Bombers: Normal or Abnormal? • Suicide bombers are not psychologically disordered • Motivated by commitment to a particular group or cause – Political – Religious © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Perspectives on Abnormality • Medical perspective – Suggests symptoms of abnormal behavior are rooted in physiological causes • Psychoanalytic perspective – Views abnormal behavior as stemming from childhood conflicts over opposing wishes regarding sex and aggression © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Perspectives on Abnormality • Behavioral perspective – View abnormal behavior as a learned response • Humanistic perspective – Emphasize the responsibility that people have for their own behavior, even when such behavior is seen as abnormal • Sociocultural perspective – Makes the assumption that people’s behavior – both normal and abnormal – is shaped by the kind of family group, society, and culture • Cognitive perspective – Assumes that cognitions (people’s thoughts and beliefs) are central to a person’s abnormal behavior © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Perspectives on Abnormality © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Classifying Abnormal Behavior • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) – System devised by the American Psychiatric Association, used by most professionals to diagnose and classify abnormal behavior © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Anxiety Disorders – Phobic disorder • Intense, irrational fears of specific objects or situations – Panic disorder • Anxiety that is not triggered by any identifiable stimulus and last from a few seconds to several hours – Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) • Experience long term persistent anxiety – Anxiety disorder • Anxiety occurs without external justification and begins to affect a person’s daily functioning © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Phobic disorders © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Frequency of symptoms in GAD © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Obsessive-Compulsive disorder – Obsession • A persistent, unwanted thought or idea that keeps recurring – Compulsion • Urge to repeatedly carry out some act that seems strange and unreasonable, even to the individual who experiences them © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Somatoform Disorders – Psychological difficulties that take on a physical (somatic) form, but for which there is no medical cause • Hypochondriasis – Constant fear of illness and a preoccupation with their health • Conversion disorder – Involves an actual physical disturbance, such as the inability to see or hear, or to move an arm or leg whose cause is purely psychological © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Conversion disorders sometimes cause numbness in particular isolated areas of the body © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Dissociative disorders – Psychological dysfunctions characterized by the separation of critical personality facets that are normally integrated, allowing stress avoidance through escape • Dissociative identity disorder (multiple personality) – Individual displays characteristics of two or more distinct personalities • Amnesia – Disorder in which a significant selective memory loss occurs • Fugue – An amnesiac condition where people take sudden, impulsive trips, sometimes assuming a new identity © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Emotional disturbance that is strong enough to intrude on everyday living • Major depression – Severe form of depression that may last months or years in which the person experiences characteristic symptoms • • • • • Worthless feelings Loneliness Crying Sleep disturbance Suicide © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Across different places and cultures, women are diagnosed more frequently with depression than men © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Bipolar disorder – Condition in which a person sequentially experiences periods of mania and depression – Mania • Extended state of intense, wild elation © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Schizophrenia – Class of disorders in which severe distortion of reality occurs • • • • • • Decline from a previous level of functioning Disturbances of thought and language Delusions Hallucinations and perceptual disorders Emotional disturbances Withdrawal © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Schizophrenia – Process schizophrenia • Symptoms develop relatively early in life, slowly and subtly – Reactive schizophrenia • Onset of symptoms is sudden and conspicuous – Positive-symptom schizophrenia – Negative-symptom schizophrenia © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Schizophrenia – Type I schizophrenia • Positive symptoms are dominant – Type II schizophrenia • Negative symptoms are more prominent © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Causes of schizophrenia – Biological • • • • Heredity Dopamine hypothesis Glutamate hypothesis Schizophrenia occurs when there is excess activity in those areas of the brain that use dopamine as a neurotransmitter © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Psychological Disorders • Causes of schizophrenia – Environmental perspectives • Expressed emotion – Interaction style characterized by criticism, hostility, and emotional intrusiveness by family members – Cognitive perspective • Overattention • Underattention © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Major Types of Schizophrenia © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Personality Disorders • Disorders characterized by a set of inflexible, maladaptive behavior patterns that keep a person from functioning appropriately in society © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Personality Disorders • Narcissistic personality disorder – Exaggerated sense of self-importance • Antisocial personality disorder (sociopath) – Characterized by no regard for the moral and ethical rules of society or the rights of others • Borderline personality disorder – Characterized by their difficulty in developing a secure sense of who they are © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Childhood Disorders • Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) – Marked by inattention, impulsiveness, a low tolerance fro frustration, and generally a great deal of inappropriate activity © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Other Disorders • • • • Psychoactive substance-use disorder Eating disorders Sexual disorders Organic mental disorders © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Prevalence of Psychological Disorders © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.