* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HEART FUNCTION AND HEART SOUNDS
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
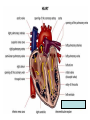
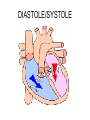
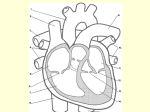
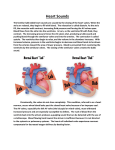
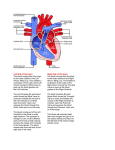
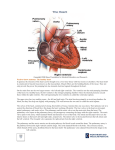
HEART FUNCTION AND HEART SOUNDS What is the Heart • The heart is a pear shaped muscular organ with chambers. It pumps blood received from the veins into the arteries. MUSCLE OF HEART • Apex (bottom) is the point of the heart which angles down and to the left – Rests on the diaphragm. • Base (top) is the broader part, which is just behind the sternum. • Pericardium is the membranous sac that encloses the heart. – Pericardial fluid lubricates the heart as it beats within the pericardium • Myocardium is the cardiac muscle. – Makes up the walls of the heart HEART FACTS • The location of the heart is in the mediastinum of the thoracic cavity • Heart is enclosed in double layered membrane the pericarduim • It has four chambers 2 ventricles –right and left and 2 atriums- right and left • There are 4 valves – tricuspid, pulmonic, mitral, aortic • Papillary muscles tether the tricuspid and mitral valves, when blood is pumped into the ventricles they relax ,when blood is pushed into pulmonic or aorta they contract. Heart facts ctnd… • Coronary arteries supply the myocarduim with oxygenated blood while coronary veins remove deoxygenated blood from the myocarduim. Blood Flow • As the vein is carrying the deoxygenated blood it enters the right atrium where it contracts and opens the tricuspid valve leading to the right ventricle, the right ventricle contracts which leads to the opening of pulmonic valve, blood goes thru the pulmonic valve and enters the pulmonary artery. The deoxygenated blood then enters the lung capillaries where gas exchange occurs O2 inhaled;CO2 exhaled. The blood is now oxygenated and enters the left atrium where there will be contraction and opens the mitral valve and blood flows into the left ventricle which contracts and opens the aortic valve. The oxygenated blood goes into the aorta, there the aorta leads the blood to the organs in the body and nourishes the body.. HEART SOUNDS • During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins to contract. Closure of the AV Valves produce the first sound LUBB. The Lubb sound can be heard best in the tricuspid and mitral valves. HEART SOUNDS CTND….. • The semilunar valves are located at the base of the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. Blood is bieng taken out of the ventricles, this prevents the backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles. The closure of these valves produces the second heart sound DUBB, its best heard over pulmonic and aortic valve/region. MORE SOUND FACTS • Systole is contraction, while diastole is when blood is dilated from an atrium or ventricular, its relaxing rather than contracting. • LUBB has longer duration of a loud sound, while DUBB is shorter with a sharp sound DIASTOLE/SYSTOLE Clinical • Diastolic Heart Failure – Trouble relaxing between beats is a growing cause of heart failure • Why the heart can’t relax? – Open space inside the ventricles can be restricted by heart muscle that “bulks up” due to overwork or other causes or that stiffens and loses it flexibility. – Symptoms: • Shortness of breath with mild activity, such as easy walking • Difficulty breathing, especially when lying down • Swollen legs and feet. Treatment • Fluid control – Limiting the amount of salt (sodium) in your diet – watching how much you drink can ease breathing, reduce swelling, and lighten heart’s workload. • Pressure control – The long-term damage wrought by high blood pressure can lead to diastolic heart failure. That’s why controlling blood pressure is one of the best things can be done to avoid or control this condition. • Exercise – The breathlessness and fatigue brought on by activity often people with diastolic heart failure to become less and less active. – It actually makes the problem worse. A tailored exercise program can strengthen the heart, slow your heart rate, and improve the condition of muscles in the heart and throughout the body. Drug Therapy • Diuretics (water pills) to get rid of excess fluid • Beta blockers to slow the heart rate. Fewer beats per minute means more time for the ventricles to fill with blood between beats • Calcium-channel blockers and long-acting nitrates to relax blood vessels, especially those that feed the heart muscle • ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers to reduce blood pressure and reverse some of the physical changes that lead to thickening of the heart muscle.