* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Defining Marketing for the 21st Century
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
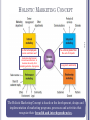
LECTURE 1 BASICS OF MARKETING MANAGEMENT MBA 649 : Marketing Management M Wahidul Islam Fall 2014 KEY QUESTIONS What is Marketing? What is Marketing Management? Marketing Management Tasks What is Marketed? What are the core concepts of marketing management? Key Customer Markets Company Orientations How and why marketing scenario have changed 1-2 WHAT IS MARKETING? Marketing is meeting needs profitably 1-3 Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders. WHAT IS MARKETING MANAGEMENT? 1-4 Marketing management is the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value. MARKETING MANAGEMENT TASKS Develop market strategies and plans Capture marketing insights Connect with customers Build strong brands Shape market offerings Deliver value Communicate value Create long-term growth 1-5 Goods Ideas Services What is Marketed? Experiences Organizations Persons Properties Places 1-6 Events Information 1-7 1-8 1-9 1-10 CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS Needs, 1-11 wants, and demands Target markets, positioning, segmentation Offerings and brands Value and satisfaction Marketing channels Supply chain Competition Marketing environment CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS NEEDS, WANTS, AND DEMANDS Needs are basic human requirements Need becomes want when the requirement is directed toward an specific object Demand are wants for specific products Five Types of Needs Stated needs (the customer wants an inexpensive car) Real needs (customer wants a car with low operating cost) Unstated needs (expects good service from the dealer) Delight needs (would like to include a GPS) Secret needs (wants to be seen as a savvy customer) 1-12 Transport Car / Bike / Bicycle Toyota / BMW / Honda CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS NEEDS, WANTS, AND DEMANDS: DEMAND STATES Nonexistent Declining Full Latent Irregular Overfull Unwholesome 1-13 Negative KEY CUSTOMER MARKETS Business Markets Global Markets Nonprofit & Government Markets 1-14 Consumer Markets KEY CUSTOMER MARKETS CONSUMER MARKETS Companies selling Mass consumer goods and services 1-15 KEY CUSTOMER MARKETS BUSINESS MARKETS Company to Company B2B 1-16 KEY CUSTOMER MARKETS GLOBAL MARKETS Companies in global marketplaces must decide which countries to enter, how to enter, how to adapt product and service features to each counties, how to price product in different countries 1-17 KEY CUSTOMER MARKETS NONPROFIT & GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS Non-profit organizations: churches, universities, charitable organizations, Social organizations Government agencies Very price sensitive 1-18 COMPANY ORIENTATIONS • One of the oldest concept • Assumes that consumers prefer that are widely available and inexpensive • Example: Lenovo group The Product Concept • Proposes that consumers favor products offering the most quality, performance and innovative features • Example: Mousetrap 1-19 The Production Concept The Selling Concept • Assume that customers will not buy if not left alone. Practiced most aggressively for unsought products • Example: Insurance, cemetery plots etc. The Marketing Concept • A customer centered, sense and respond philosophy. • Find out right customers for your products • Example: Dell HOLISTIC MARKETING CONCEPT 1-20 So that all employees serve customers well Understanding financial & non-financial returns to business & society from marketing activities & programs. The whole is greater than the sum of its parts Long-term relationship The Holistic Marketing Concept is based on the development, design and implementation of marketing programs, processes and activities that recognize their breadth and interdependencies. THE TRADITIONAL FOUR P’S 1-21 THE MARKETPLACE ISN’T WHAT IT USED TO BE… Information technology Globalization Deregulation Privatization Competition Convergence Consumer resistance Retail transformation 1-22 NEW CONSUMER CAPABILITIES A substantial increase in buying power A greater variety of available goods and services A great amount of information about practically anything Greater ease in interacting and placing and receiving orders An ability to compare notes on products and services An amplified voice to influence public opinion 1-23 THE TRADITIONAL FOUR P’S 1-24 REFERENCES Chapter 1 – Defining Marketing for the 21st Century Kotler, Philip, Keller, Kevin L., Koshy, Abraham and Jha, Mithileshwar (2013-14) Marketing Management: A South Asian Perspective (14thEdition) Pearson Education Inc